March 17, 2015
World:
¶ A new study says that if the UK invests in electric vehicle infrastructure and supports its electric vehicle market, oil imports could be cut by 40% by 2030. If the UK does provide such support, the average fossil fuel motorist that switches to an EV might also save about $1,500 in annual fuel costs. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Denmark and Poland are both preparing to have feed-in tariffs for small wind turbines. In Denmark, where benefits of small units have been studied, units of up to 10 kW would get €0.33 per kWh, and those up to 25 kW would get €0.20 per kWh. Polish tariff rates will be €0.17 for up to 3 kWh and €0.10 for 15 kWh. [Sun & Wind Energy]

Wind turbine on farm. photo by Hywel Williams. From Wikimedia Commons
¶ MWH Treatment has secured its second gasification EPC contract for an innovative £51.6 million waste wood gasification project in Northamptonshire. MWH Treatment’s aim in building the plant is to provide the equivalent of 17,000 homes with electricity from waste wood by March 2017. [Northampton Herald and Post]
¶ The $850 billion Norwegian Government Pension Fund has sold the majority of its shares in companies exposed to the Indian coal sector, citing financial and environmental risks inherent in their operations. The fund has also sold shares in US and European companies similarly exposed to the coal sector. [New Kerala]
¶ Scottish clean energy developer Banks Renewables has submitted plans for an 88.4-MW wind farm in East Ayrshire, and says the project could deliver around £15 million in community benefit payments over its 25-year lifespan. The wind farm could provide enough renewable power for 58,600 homes. [Business Green]
¶ Iceland is preparing to become one of the world’s largest producers of silicon metal and polysilicon as low electricity prices attract four companies vying for the nation’s renewable energy resources. Iceland is seeking to diversify its economy as it recovers from Europe’s biggest banking collapse this century. [Bloomberg]
¶ In Australia, the category three Cyclone Olwyn tore through the WA towns of Exmouth, Coral Bay and Carnarvon on Friday, leaving power blackouts and water shortages in its wake. On the nearby Thevenard Island, however, a relatively newly installed solar-hybrid mini grid continued running throughout. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Three aging nuclear reactors in Japan will be decommissioned due to the high cost of upgrading them in line with tougher safety standards set after the Fukushima disaster. Another two reactors were also likely to be scrapped, local media reports said, with announcements expected later in the week. [Reuters]
US:
¶ The US Energy Department plans to award $1.8 million to help develop larger wind turbine blades. The funding will support research and development to improve the manufacturing, transportation, and assembly of blades longer than 60 metres to be installed on towers taller than 120 metres. [reNews]

Wind turbine blades.
¶ New work from Carnegie’s Rebecca Hernandez (now at UC Berkley), Madison Hoffacker and Chris Field found that the amount of energy that could be generated from solar equipment constructed on and around existing infrastructure in California would exceed the state’s demand by up to five times. [Laboratory Equipment]
¶ Governor Earl Ray Tomblin of West Virginia signed legislation restricting owners of solar installations who want to sell clean energy back to the grid. The bill caps the solar power generated from net metering at no more than 3% of the total state’s peak demand—and only 0.5% from residential solar customers. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Clean energy companies are finding a home in Illinois. The Environmental Law and Policy Center says more than 20,000 Illinoisans work in wind power and solar energy markets and predicts continued investments in renewable energy development will mean more new business and increased economic activity. [Public News Service]
¶ A company that for years has been planning a wind turbine farm in an area of southeastern North Dakota where endangered birds nest and fly over is proposing changes that might help reduce potential harm. The company proposes a move to fewer and larger turbines in the latest design. [Greenfield Daily Reporter]
¶ Elected officials from four Kansas counties reacted Monday with alarm to a Senate bill imposing a property tax on renewable energy producers and retroactively undermining long-term financial agreements between wind power generators and county governments. Their concern is the rural economy. [The Garden City Telegram]
¶ US solar giant SolarCity today announced the launch of a microgrid product with built in energy storage capability. SolarCity is going after the commercial market, targeting municipalities, which is a segment the company views as underserved. One reason to have municipal microgrids is extreme weather. [Breaking Energy]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 16, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “New Renewable Energy Studies: ‘Garbage In, Garbage Out'” – Somebody must have been handing out free cigars last week, because not one but three new renewable energy studies popped up in the US, and all three seek to undercut the economic evidence in favor of renewable energy. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Decentralisation is the key to energy success and development, according to Søren Hermansen, director of the Samsø Energy Academy. Instead of focusing on Putin’s gas, the EU should create its own independent energy grid, including the national feed-in tariffs the Energy Union project opposes, he said. [EurActiv]
World:
¶ China’s National Energy Administration released its General Outline for the Solar Power Disadvantaged Support Implementation Plan (Trial) which envisages a raft of policy measures for expediting the deployment of solar power in disadvantaged communities, including subsidies of up to 70% for the poor. [CleanTechnica]

Rooftop solar in Hong Kong. Photo by Snowacinesy, from Wikimedia Commons.
¶ More than 60% of electricity demand in the Australian town of Alice Springs can be met via solar PVs without causing grid instability, according to a study partly funded by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. The remote central Australian town currently has a solar PV capacity of 4.1 MW, and a population of 29,000. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The government of Egypt inked two pacts for the construction of 5 GW of solar parks in the country. Canadian solar firm SkyPower and Gulf Development Companies will build a 3-GW of PV facility, Bahrain-based Terra Sola Group and Tera Nix involves the construction of a 2-GW solar complex. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ Tim Yeo, a former environment minister who has been de-selected by party members in his South Suffolk constituency and must stand down at the election, is a Conservative who supports wind farms. He used his farewell speech in the House of Commons to condemn the Tories’ policy on wind turbines. [Western Daily Press]

UK wind turbine. Photo by James Allan. From Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Punjab’s hard-working farmers can look forward to the end of some of their power-cut woes with the state government planning to launch soon a “farm-level solar power generation scheme”. The New and Renewable Energy Minister said farmers will be allowed to set up solar power plants of 1 MW to 2.5 MW. [SME Times]
¶ The UK system for subsidizing new nuclear reactors is “a bad example” for the European power market, according to a top Finnish energy official. He said studies in Finland estimate what it would cost the government to subsidize nuclear power and that those estimates are in the hundreds of millions of euros.
[Platts]
US:
¶ Wisconsin state regulators will decide in the coming weeks whether to approve new power lines that together are projected to cost up to $900 million. The cases involve projects by American Transmission Co and other utilities seeking to expand the transmission system to lower costs or for upgrade. [Milwaukee Journal Sentinel]
¶ Interior Assistant Secretary for Insular Areas Esther Kia’aina announced nearly $600,000 in grant assistance to the Guam Power Authority to complete the Guam Wind Turbine Pilot project. This grant supplements $1.5 million previously awarded and the project is expected to be completed this summer. [Saipan Tribune]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 15, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “Crony Biofuel Politics Wag the Dog” – Failure to back the Renewable Fuel Standards means sayonara to any White House hopes, candidates campaigning in Iowa were told. Appropriately chastened, many normally free market proponents dutifully took to the podium to endorse the mandates. [Eurasia Review]
Science and Technology:
¶ Traditionally, the electricity grid has relied upon dirty “peaker” power plants to balance the load during periods when electricity demand exceeds supply. Today, technology is available that can help fill the need for these peaker plants. This technology, also known as demand-side resources. [Energy Collective]

World:
¶ Siemens and the Egyptian government have reached firm agreements to build a 4.4-GW combined-cycle power plant and install wind power capacity of 2 GW. Siemens will build a factory in Egypt to make rotor blades for wind turbines, creating up to 1,000 jobs and nearly trebling Siemens’ footprint in the country. [Utilities-ME.com]
¶ The second day of Egypt’s Economic Development Conference saw the country sign agreements and memoranda of understanding with international companies worth $158 billion. Most of the deals signed on Saturday were concentrated in the field of energy, reaching over $30 billion worth of investment. [Egyptian Streets]
¶ India’s target of coal production for the next fiscal year is estimated to be 700 million tonnes. This production target could be considered India’s biggest annual output growth in Coal. Targets are not always met. The country’s the coal output in the current fiscal may be lower than the target of 630.25 million tonnes. [SteelGuru]
¶ Tens of thousands of people opposed to nuclear energy yesterday gathered in Taiwan in antinuclear parades and rallies, joining an alliance of civic groups to raise awareness about perceived problems with the nation’s nuclear policies. Protesters held banners bearing such messages as “Nuclear Energy RIP.” [Taipei Times]

A solar-powered vehicle from National Kaohsiung University of Applied Sciences leads an antinuclear energy protest in Kaohsiung. Photo: Ke Yu-hao, Taipei Times
US:
¶ Three years ago, the nation’s top utility executives gathered at a Colorado resort to hear warnings that solar panels posed a grave new threat to operators of America’s electric grid. Now, the industry and its fossil-fuel supporters are waging a determined campaign to stop a home-solar insurgency. [Buffalo News]
¶ The largest anaerobic digester in Maine, built three years ago, is among the largest in the United States. It produces enough electricity to power all the homes in a town the size of Boothbay Harbor. Its owners are planning to build a new bio-digester three times as big, to consume 50,000 tons of waste each year. [Press Herald]
¶ Marin Clean Energy, a California-based Community Choice Aggregation program, has signed a new $20 million contract with Calpine Corp that will further reduce the carbon emissions produced by the electricity it sells to its customers. Marin Clean Energy will optionally buy 10 MW to 15 MW. [Marin Independent Journal]
¶ Columbia, Missouri, has an electric system in need of more power. How to best pay for it is the question. Bond issue or drastic rate increase? If it passes, city utility customers would see a 6 percent rate increase over three years. If it fails, rates could rise 20% to 25% to pay for the projects the bond would have funded. [Columbia Missourian]

Columbia Water and Light operates 70 miles of transmission lines throughout the city, according to the department’s website. Photo by Jenny Justus
¶ North Carolina’s environmental regulators put business first and the environment second, state Representative Rick Glazier said in a speech. The Department of Environment and Natural Resources and Department of Commerce are supposed to work together to protect the environment as business grows. [Fayetteville Observer]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 14, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “US Transportation System Could Save $1 Trillion Annually, Reduce Carbon Emissions By 1 Gigaton” – In the United States each year, our cars alone cost us well over $1 trillion, to which the indirect societal cost adds another $2 trillion. Cars burn about 2 billion barrels of oil, producing a quarter of all US emissions. [CleanTechnica]
Science and Technology:
¶ The International Energy Agency announced Friday that energy-related CO2 emissions last year were unchanged from the year before, totaling 32.3 billion metric tons of CO2 in both 2013 and 2014. It shows that efforts to reduce emissions to combat climate change may be more effective than previously thought. [Climate Central]
World:
¶ According to the new report from BCC Research, the global wind energy market was worth $130 billion in 2013 and $165.5 billion in 2014. The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.2% between 2015 and 2020 resulting in $176.2 billion in 2015 and $250 billion in 2020. [Bihar Prabha]

Wind Energy has a strong potential in Asia-Pacific
¶ GE is to invest $200 million in a manufacturing, engineering, services and training center in Egypt that will focus on sectors including renewables. The Suez facility will serve Egypt and the region, and provide a shared center of excellence on process, capability and human capital aimed at driving economies of scale. [reNews]
¶ A renewable power company is getting ready to take delivery of the world’s biggest and most powerful tidal turbine – about the same size as a WWII submarine – for its sea-trials off Orkney this summer. The turbine is being built for Scotrenewables Tidal Power at the same shipyard that built the Titanic. [Green Building Press]

A smaller prototype version of the turbine
US:
¶ A new report published by the US DOE seeks to develop a new “Wind Vision,” which aims to document the contributions wind has made to date, and the continuing and growing contributions it can make to the country’s national energy portfolio. The report has projections for 2020, 2030, and 2050. [CleanTechnica]
¶ NRG is the biggest privately owned centralized generator in the US, with large nuclear, coal and gas assets in a 50-GW portfolio that nearly matches the size of Australia’s entire electricity grid. Its CEO foresees a “tsunami” of closing polluting coal plants and uncompetitive nuclear, replaced by renewables. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In the 10 years of Montana’s Renewable Portfolio Standard, 60% of its new capacity has been wind powered. The 688 MW of wind energy development has brought $1.4 billion in economic investment, over $2 million in annual lease payment to landowners, and hundreds of jobs, without raising rates. [The Bozeman Daily Chronicle]
¶ Michigan must set attainable energy goals and look towards renewable energy sources to keep energy prices down and avoid widespread outages, Governor Rick Snyder said in a special message on energy. The state’s new goal is to get 30% to 40% of its energy from renewable sources and reduced waste by 2025. [Daily Detroit]
¶ Plans for a hydroelectric pumped-storage facility east of Klamath Falls, Oregon, have been scaled back, but are still moving forward, according to project managers. As a result of an economic study, the Swan Lake North pumped-storage facility’s price tag has been cut from $1.2 billion to $600 million. [Herald and News]
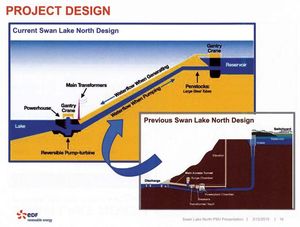
¶ Solar energy has taken a back seat to shale gas in Pennsylvania in recent years. But it’s getting renewed attention, thanks to a proposal from Governor Tom Wolf and new legislation aimed at funding the lapsed Pennsylvania Sunshine Solar, a rebate program for homeowners and small businesses. [StateImpact Pennsylvania]
¶ Dow Chemical Company has signed a long-term agreement with a wind farm under development in Texas. The farm will power Dow’s Freeport Texas Manufacturing plant. It will span 35,000 acres and produce enough electricity to power more than 55,000 homes. It is being developed by Bordas Wind Energy. [Chem.Info]
¶ Lawmakers from at least four states have introduced model legislation from the right-wing group Americans for Prosperity seeking to prohibit state funding for the EPA’s efforts to fight climate change. Nearly identical resolutions have been introduced in Missouri, Florida, Virginia, and South Carolina in 2015. [ThinkProgress]
¶ A report concludes that shaking from a powerful earthquake could exceed the design of California’s Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant, but the report claims the reactors are safe because components were built with more than enough strength to withstand the potential stress and no equipment would be at risk. [Manteca Bulletin]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 13, 2015
World:
¶ Navigant Research has published a new report analysing the small and medium wind turbine market, with forecasts through 2023. It finds that China, the UK, and Italy lead globally, while the US is lagging well behind. Small and medium wind turbines are defined as those of less than 500 kW capacity. [CleanTechnica]

Wind turbine being assembled in Chile. Photo by Green Energy, from Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Italy’s Enel Green Power SpA said Wednesday it has connected to the grid its 61-MW Talinay Poniente wind farm in Chiles Coquimbo region. The company installed 32 wind turbines to produce over 160 GWh a year, enough for nearly 60,000 homes in Chile. The plant operates under contracts awarded in 2013. [RenewablesBiz]
¶ The linked Quebec–California carbon market has shown advantages for cap-and-trade systems. The system’s second linked carbon dioxide auction sold 100% of available allowances, generating $1.02 billion for clean energy and emissions reduction projects, consumer bill relief, and government operations. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Kyocera Corporation, Energetik Solartechnologie-Vertriebs GmbH, and Solare Datensysteme GmbH have teamed up to offer an energy storage solution for residential use in Germany. The solution includes Kyocera’s battery storage system and Solare Datensysteme’s energy monitoring software and hardware. [solarserver.com]
¶ Uruguay’s wind power output jumped 432.9% to over 700 GWh last year, driven by the installation of new plants, the local power market administrator said in its annual report. Excluding hydroelectricity, renewable energy supplies more than doubled year-on-year to 1,364 GWh and covered 13.2% of demand. [SeeNews Renewables]
US:
 ¶ In a refresh to its 2008 Wind Vision report, the DOE said the wind industry had demonstrated an ability to scale up and drive down costs, avoid causing grid disruptions, and not be too big of a pain in the neck to critters or communities – making 35 percent by 2050 “an ambitious but feasible deployment scenario.” [Breaking Energy]
¶ In a refresh to its 2008 Wind Vision report, the DOE said the wind industry had demonstrated an ability to scale up and drive down costs, avoid causing grid disruptions, and not be too big of a pain in the neck to critters or communities – making 35 percent by 2050 “an ambitious but feasible deployment scenario.” [Breaking Energy]
¶ Local municipalities New York may soon receive more power to choose how their electricity is generated and distributed from available alternatives. A pilot program called “Community Choice Aggregation” was recently approved by the state Public Service Commission for New York State municipalities. [ithaca.com]
¶ Of 52 requests for proposals in North America, totaling 3.3 GW of capacity, 27 were for solar and 12 were for energy-smart technologies including storage, according to a report from Bloomberg New Energy Finance. These requests are typically a strong indicator of industry trends, BNEF’s head of analysis says. [Bloomberg]

Cedar Bay Generating Plant (dep.state.fl.us)
¶ Florida Power & Light filed with the Public Service Commission last week for approval to purchase the 250-MW coal-fired Cedar Bay Generating Plant near Jacksonville, Florida for $520.5 million. Though the plant is being run economically, FP&L is buying it to shut it down and eliminate its carbon emissions. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Entergy’s Louisiana utilities expect to need 8,000 MW of new generating capacity in the next two decades to replace about half of their aging power-plant fleet. They plan to rely almost exclusively on natural gas-fired generation to meet their capacity needs, according to papers filed with the state. [Argus Media]
¶ PJM, a regional authority that ensures reliable and low-cost power across the electric grid in 14 states, released economic analysis of the EPA’s Clean Power Plan. The report makes it clear that efficiency and renewables are the cheapest way forward. For Ohio, the report has particular significance. [Natural Resources Defense Council]
¶ Leelanau Township, Michigan, is finalizing its Renewable Energy Community Plan as it moves toward being 100% powered by wind and solar, with efficiency helping. It is one of a number of towns and cities that have done this or are in the process. The article links a web site tracking the progress of American communities. [SustainableBusiness.com]
¶ Xcel Energy is adding 140 MW of PV solar energy to its Texas-New Mexico generation mix with an agreement to purchase the output of two planned solar developments near Roswell, New Mexico. The company expects to add the solar energy capacity in 2016 before federal tax credits end for new projects. [Seminole Sentinel]
¶ The Selectboard of Milton, Vermont, will be asked at its March 16th meeting to authorize contract negotiations with preferred vendor Sun Edison to construct two solar arrays on leased Town property. Over 20 years these arrays are expected to yield the Town over $2 million from a variety of benefits. [vtdigger.org]
 ¶ Hawaii is on track to pass legislation this year requiring the state to go 100% renewable by 2040. Committees in the House and Senate both unanimously recommended bills that would raise the state’s Renewable Portfolio Standard from the current target of 70% by 2030 to the ultimate goal of 100% by 2040. [Solarenergy.net]
¶ Hawaii is on track to pass legislation this year requiring the state to go 100% renewable by 2040. Committees in the House and Senate both unanimously recommended bills that would raise the state’s Renewable Portfolio Standard from the current target of 70% by 2030 to the ultimate goal of 100% by 2040. [Solarenergy.net]
Posted in renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 12, 2015
Science and Technology:

Solar Impulse 2 during its landing
¶ Pilots of the world’s first circumnavigating solar plane, which landed in Ahmedabad on Tuesday, are now preparing for the most challenging legs of their journey crossing the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. Stopping in a number of places, they will fly the solar-powered aircraft across the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. [Mid-Day]
World:
¶ Figures from the China Electricity Council indicate that non-fossil fuel sources of energy accounted for more than a quarter of the country’s electricity generation in 2014. China’s total generation reached 5550 TWh in 2014; non-fossil fuel generation was 1420 TWh, rising by 19.6% year-on-year. [CleanTechnica]

Taro Kono in a 2011; Bloomberg News file photo.
¶ Japanese ruling-party lawmaker Taro Kono, a longtime critic of nuclear power, is using a document privately prepared for the Environment Ministry by Mitsubishi Research Institute to encourage the government to set a more ambitious target for renewable energy, a 30% goal by 2030. [Wall Street Journal]
¶ Renewable development and management company Enel Green Power announced that it had commenced construction of three solar PV plants in South Africa. The Aurora, Paleisheuwel and Tom Burke PV plants, located in different areas across the country, will have a combined generation capacity of 231 MW. [ESI Africa]
¶ A project in the Australian Outback that will more than double the country’s large-scale solar output should begin generating its initial power as early as this week, according to First Solar Inc. The Nyngan solar plant in New South Wales state will start at 25 MW before increasing to full capacity of 102 MW. [Bloomberg]

Solar panels in Nicaragua. Photo by Max L. Lacayo. Downloaded from Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Nicaragua produces no oil, but is a land of fierce winds, tropical sun and rumbling volcanoes. In other words, it’s a renewable energy paradise. Now it’s moving quickly to become a green energy powerhouse, and the vast majority of Nicaragua’s electricity will come from hydroelectric, geothermal, and wind. [NPR]
¶ The European Union continues to march toward its renewable energy goals for 2020, but some countries aren’t content to wait until then to meet their targets. Newly released data show that four countries, Sweden, Bulgaria, Estonia and Lithuania, have met their renewable energy target ahead of schedule. [Climate Central]
¶ Independent Electricity System Operator has launched a 565-MW renewable energy request for proposals, approved by Canadian Wind Energy Association. This will include the launch of 300 MW of wind energy. It is the first of three RFPs under IESO’s Large Renewable Procurement competitive process. [Greentech Lead]
¶ China is reviving growth of its nuclear power industry with approval of its first new project in two years. The Cabinet’s planning agency approved construction of two additional reactors at a power plant in the northeastern province of Liaoning, a unit of state-owned China General Nuclear Power Corp said. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ Concluding their US Solar Market Insight, 2014 Year-in-Review report, the authors from GTM Research and the Solar Energy Industries Association predict that installations will increase 31% in 2015, reaching 8.1 GW by the end of the year, with fastest growth coming from the residential sector. [CleanTechnica]
¶ As part of the US Solar Market Insight, 2014 Year-in-Review report, the authors provided national solar PV system pricing. Solar system costs fell by 9–12% over the course of 2014, depending on market segment. Total costs for utility-scale and large commercial-scale systems fell below $2.00/W DC. [CleanTechnica]
¶ If solar energy gained widespread use in Maine it would have a greater total value than conventional power generation, according to a state-sponsored study that analyzes the costs and benefits of generating power from the sun. The report also said that solar power would help lower costs at peak demand times. [Press Herald]
¶ Connecticut regulators Wednesday signaled they won’t shut down Vermont utilities’ sale of renewable energy credits to power companies in Connecticut, especially if Vermont passes changes to its renewable energy program now pending in the Legislature. House Bill 40 has passed and is before the Senate. [Rutland Herald]
¶ A bill moving through the New Mexico Legislature would remove higher renewable-energy requirements for utilities in the state in the future. House Bill 445 would roll back the requirement that 20% of retail sales for public utilities come from renewable-energy sources by 2020, to the current level, 15%. [Public News Service]
¶ What Michigan’s staunch conservatives want is a commitment to continue moving power production to green sources such as wind and solar at the rate of 1% to 1.5% a year; encouragement of micro-grids powered by solar panels and windmills, and a reduction in reliance on out-of-state fuel sources, namely coal. [The Detroit News]

Giant miscanthus, photo by Kreg8, downloaded from Wikimedia Commons
¶ Biomass industry leader, Repreve Renewables LLC, has been chosen to provide the agricultural and business development services for the University of Iowa’s Biomass Fuel Project. This project will reduce the use of coal, all part of the university’s sustainability goal of 40% renewable energy in 2020. [Biomass Magazine]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 11, 2015
Opinion:
 ¶ Today, the 11th of March 2015, marks the fourth year since beginning of one of the world’s worst nuclear disasters: the triple reactor core meltdowns and catastrophic containment building failures at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. It’s a nuclear crisis that, unfortunately, continues to unfold. [Greenpeace International]
¶ Today, the 11th of March 2015, marks the fourth year since beginning of one of the world’s worst nuclear disasters: the triple reactor core meltdowns and catastrophic containment building failures at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. It’s a nuclear crisis that, unfortunately, continues to unfold. [Greenpeace International]
Science and Technology:
¶ NuScale Power has successfully installed a full-length test version of its small modular nuclear reactor in Piacenza, Italy. NuScale plans to submit the project for approval in 2017 and begin operations in late 2023. In late 2013, the US Department of Energy selected NuScale for a commercialization project. [Next Big Future]

The Solar Impulse 2 takes off from Muscat airport in Oman.
¶ Solar Impulse 2 landed in India late on Tuesday, completing the first major sea leg of its epic bid to become the first solar-powered plane to fly around the world. The aircraft touched down in Gujarat at 11.25 pm to finish its second leg in a little less than 16 hours after taking off from the Omani capital Muscat. [Hindustan Times]
World:
¶ A group of experts is expected to finalize details this week of a road map to install 160 GW of battery storage worldwide by 2030. The International Renewable Energy Agency is developing the plan, which is due to be launched this summer following feedback next week from worldwide experts. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Germany’s E.ON suffered its biggest ever annual loss after booking billions of euros in charges on its ailing power plants, clearing the way for it to spin off these assets hit hard by ultra-low wholesale prices. Europe’s power companies are suffering from low oil prices and a surge in renewable energy capacity. [Reuters UK]
 ¶ A group of decision and policy makers and independent power developers, who met in Kenya’s capital Nairobi recently, said mini grids, utilizing solar PV and wind have capacity to generate up to 40% of sub Saharan Africa’s new power capacity with the region’s mini-grid market showing potential to grow to $4 billion per a year. [Solar Novus Today]
¶ A group of decision and policy makers and independent power developers, who met in Kenya’s capital Nairobi recently, said mini grids, utilizing solar PV and wind have capacity to generate up to 40% of sub Saharan Africa’s new power capacity with the region’s mini-grid market showing potential to grow to $4 billion per a year. [Solar Novus Today]
US:
¶ Renewables contributed 13.4% of all US electricity generation in 2014, when a CleanTechnica estimate for rooftop solar is added in (that is, solar PV projects under 1 MW in size… which are primarily rooftop solar power projects). The figure in 2013 was 13%, so the basic news is… we’re inching forward. [CleanTechnica]
 ¶ North Carolina has one of the fastest-growing solar industries in the country, and the evidence suggests the clean energy sector has helped boost the state’s economy. Now solar has taken another step forward with Principal Solar’s announcement that it will build a 73 MW solar farm in Fayetteville. [CleanTechnica]
¶ North Carolina has one of the fastest-growing solar industries in the country, and the evidence suggests the clean energy sector has helped boost the state’s economy. Now solar has taken another step forward with Principal Solar’s announcement that it will build a 73 MW solar farm in Fayetteville. [CleanTechnica]
¶ GTM Research and the Solar Energy Industries Association released the US Solar Insight 2014 Year in Review report, and it shows how far the industry has come in a short amount of time. The U.S. solar industry had another record year in 2014, with 6.2 GW of solar installed, 30% more than a year ago. [Motley Fool]
 ¶ Many US electric utilities are doubling down on natural gas to generate power as they retire old polluting coal plants. While this shift does provide some near-term benefits, dramatically expanding our use of natural gas is an ill-advised gamble that poses complex economic, public health, and climate risks. [Clean Energy News]
¶ Many US electric utilities are doubling down on natural gas to generate power as they retire old polluting coal plants. While this shift does provide some near-term benefits, dramatically expanding our use of natural gas is an ill-advised gamble that poses complex economic, public health, and climate risks. [Clean Energy News]
¶ The Vermont House passed H.40, a bill designed to reduce residents’ carbon footprint, despite complaints from Republicans who fear the new renewable energy targets will come at an unforeseen cost. The RESET program increases percentages for renewables from 50% of sales by 2017 to 75% by 2032. [vtdigger.org]

Source: US Energy Information Administration, Electric Power Monthly
¶ In 2015, electric generating companies expect to add more than 20 GW of capacity to the power grid. The additions are dominated by wind (9.8 GW), natural gas (6.3 GW), and solar (2.2 GW), which combine to make up 91% of total additions. Nearly 16 GW is expected to retire, including 12.9 GW of coal. [Business Spectator]
¶ New York State is poised for a much-needed breakthrough in the development of offshore wind power technologies to harness the vast renewable, carbon-free wind resources off its shores, according to a new report from prepared by the University of Delaware’s Special Initiative on Offshore Wind. [Natural Resources Defense Council]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 10, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “Rethinking the Addison pipeline” $154 million is a lot to spend on Vermont Gas Systems’ Addison County pipeline. That same amount of money could be much better spent weatherizing homes and businesses, installing more efficient heating systems and installing solar photovoltaic systems. [Barre Montpelier Times Argus]
World:
¶ At the RE-Invest 2015 summit in India last month, banks, financial institutions and the private sector offered commitments to shift the country’s power supply to clean, renewable resources. What didn’t come along with this was any explicit roadmap for how the grid would support such changes. [Energy Collective]
 ¶ RWE Innogy has started construction of the Sandbostel wind farm in the rural district of Rotenburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. The wind farm will consist of five wind turbines, each with a capacity of 2.35 MW and a total installed capacity of 12 MW. The wind farm is expected to be fully operational by the end of 2015. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
¶ RWE Innogy has started construction of the Sandbostel wind farm in the rural district of Rotenburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. The wind farm will consist of five wind turbines, each with a capacity of 2.35 MW and a total installed capacity of 12 MW. The wind farm is expected to be fully operational by the end of 2015. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
¶ Six community energy projects in northern New South Wales have been awarded grants by the NSW government, including a range of solar, bio-gas and mini-hydro projects, as the state pushes to assist community energy projects. One project is to take a whole village of 300 people off grid with renewables. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Germany continues efforts to expand its renewable energy capacity, with two German energy companies awarding separate contracts to Gamesa and Vestas for utility-scale wind power projects. Germany installed 4,750 MW of onshore wind generation capacity in 2014, a 58% increase in new capacity over 2013. [PennEnergy]
 ¶ Canada’s Halcyon Tidal Power has reaffirmed its commitment to construct an 1100-MW tidal range lagoon in the Bay of Fundy, although the company admits the timetable has slipped. Completion of the C$3.5 billion Scots Bay project in Nova Scotia was initially slated in 2020 but has been pushed back two years. [reNews]
¶ Canada’s Halcyon Tidal Power has reaffirmed its commitment to construct an 1100-MW tidal range lagoon in the Bay of Fundy, although the company admits the timetable has slipped. Completion of the C$3.5 billion Scots Bay project in Nova Scotia was initially slated in 2020 but has been pushed back two years. [reNews]
¶ A $10 million pilot biomass plant will be constructed in the Western Australian Capital of Perth, to use pyrolysis. This produces hydrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, methanol, turpentine, and a lot of tar, all of which are fuels. Also produce is biochar, which can improve the soil while sequestering carbon. [CleanTechnica]

Photo by Stever Herman. Public Domain, from Voice of America, downloaded from Wikimedia Commons.
¶ A Japanese report shows the number of deaths by radiation from the country’s Fukushima Disaster increased by 18% last year. The Japanese newspaper Tokyo Shimbun published figures, from authorities in Fukushima Prefecture, showing a total of 1,232 deaths in 2014 were linked to the nuclear disaster. [Press TV]
US:
¶ One Hickory, North Carolina, business has cut its energy bills by 90%. The Snyder Paper Corp cut its monthly energy bill from approximately $15,000 per month to about $1,500 by installing a new solar power system, new insulated and reflective roof, and LED lighting in its Hickory production plant. [Hickory Daily Record]
¶ According to New York System Operator, the state reached a power milestone when electricity generated by wind power hit a record. At 1 pm March 2, the 1,524 MW output provided 7% of the 20,894 MW of the state’s total system demand. One MW is about the amount of electricity required to supply 800 to 1,000 homes. [Auburn Citizen]
¶ A bill that would give large electric utilities an alternative way to comply with a state law requiring more energy from renewable sources passed the Washington Senate after a long fight over whether climate change is real and if humans contribute to it. It would give the utilities alternatives for cutting carbon emissions. [Fox Business]

“Just stick it in the sand, fellas, and everything bad goes away.”
Photo by Fwaaldijk, download from Wikimedia Commons.
¶ A report from the Florida Center for Investigative Reporting suggests state environmental officials were directed not to use the terms “climate change,” “global warming,” or “sustainability,” after Florida’s Republican governor, Rick Scott, took office in 2011. Scott denies that any directive of the sort was issued. [CNN]
¶ While local renewable energy and energy efficiency are both proving to be near-existential threats to electric utilities in the early 21st century, the trends aren’t the same. The rapid rise of renewable energy is big news, but energy efficiency may now be the more persistent threat to electric utilities. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Net electrical generation from non-hydro renewable energy sources increased by 10.9% in 2014 over the previous year, according to the US Energy Information Administration. The solar contribution to net generation increased by 102.8%, while wind grew by 8.3%, biomass by 5.7%, and geothermal by 5.4%. [Domestic Fuel]
¶ The DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory has used a simulation Tool to confirm that energy storage for demand-charge management can deliver attractive economic benefits. Absent incentives, small battery systems reducing peak demand by 2.5% offer the most attractive return on investment. [RealEstateRama]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 9, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ If the “true costs” of emissions — increased rates of premature death, illness, increased loads on the healthcare system, lowered crop yields, missed work days, etc — are factored in, a gallon of gasoline would cost you roughly $3.80 more at the pump than it currently does, according to Duke University research. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Superconducting magnetic energy storage (SMES) is a technology with almost negligible energy losses. A SMES system stores energy in a magnetic field, and can instantly release it. It is hence considered ideal for short duration energy storage, such as maintaining the quality of a power supply. [Virtual-Strategy Magazine]
World:
¶ Solar Impulse 2 took off from Abu Dhabi in the United Arab Emirates en route to the Omani capital Muscat at the start of a five-month journey of 35,000 km (22,000 miles) organised to focus the world’s attention on sustainable energy. The flight will be the first around the world in a solar-powered plane. [Reuters Africa]
¶ Construction of the first wind power farm in Viet Nam’s Central Highlands was kicked off in Dak Lak Province’s Ea H’leo District. The wind power farm is designed to generate 450 million kWh per year, according to HBRE Wind Power Solution Ltd, the investor of the $280 million wind power project. [VietNamNet Bridge]
¶ The Indian government formally confirmed the solar power capacity addition target for 2022 as 100 GW, bringing it to 25% of installed capacity. Currently, solar power capacity stands at around 3 GW, or about 10% of total renewable energy capacity, and just over 1% of the total power capacity of the country. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The UK’s largest biomass combined heat and power plant was officially opened. It promises to slash Scottish greenhouse gas emissions by up to 250,000 tonnes a year. RWE Innogy cut the ribbon on the Markinch Biomass CHP Plant in Glenrothes, Fife. It replaces a coal and gas-fired CHP power station. [Business Green]
¶ Byron Shire, in New South Wales, is aiming to become the first region in Australia to become “net zero emissions”, with a goal to reduce emissions from energy, transport, buildings, waste and land use to zero within 10 years. The town is following a plan created by the think tank Beyond Zero Emissions. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Nuclear power is risky and unprofitable, according to Mycle Schneider, an expert on nuclear energy. He expects bankruptcy in the nuclear industry and “substantial security risks,” because costs for nuclear energy continue to increase each year, as costs of other technologies, especially renewables, decline. [Deutsche Welle]
¶ Areva, France’s iconic nuclear power builder, reported a massive financial loss for 2014. The state-owned company revealed that it lost €4.9 billion ($5.6 billion) in 2014, an enormous decline from the €500 million loss it posted the previous year. The high cost of new nuclear reactors is one serious problem. [OilPrice.com]
US:
¶ With the purchase of electricity generated on giant wind farms in the Great Plains expected later this year, public officials in Aspen believe they will be able to claim consistent 100% electrical generation from renewable sources for the city’s electrical utility, one of just a handful of US cities that can do so. [Mountain Town News]
¶ Pennsylvania Governor Tom Wolf has proposed a $30 billion budget for the 2015-16 fiscal year. In part of it, Wolf would fund several energy initiatives by issuing $675 million in bonds. He would pay the interest on the bond money with $55 million from a proposed severance tax on oil and gas drillers. [Tribune-Review]
¶ Clean energy and transport projects across the US created 47,000 new jobs last year, according to a new study from business group Environmental Entrepreneurs. Analysis confirms that the US has created more than 233,000 clean energy and clean transportation jobs nationwide over the past three years. [Business Green]
¶ The owner of the shuttered Vermont Yankee nuclear plant wants an exemption to use money from the plant’s decommissioning fund to pay for guarding spent nuclear fuel. The state, saying this violates federal regulations and could delay decommissioning, sent a letter to the NRC calling for a hearing. [Valley News]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 8, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “U.S. falling behind on renewable energy” – Solar and wind facilities are growing exponentially in the US, but we are far behind China and European countries. China’s wind power is about one-third larger and increasing much faster than the US. China’s solar PV power is more than 20 times that of the US. [Roanoke Times]
¶ “Green is the best defense” – The US military has always been driven by innovation, developing technology often in tandem with the private sector to solve wartime military problems. Today, the same Armed Forces that invented the internet and GPS has turned its attention to energy technology. [Seacoastonline.com]
World:
¶ Residents from a UK village at the heart of the battle over fracking are in a new effort. The Repower Balcombe renewable energy co-operative would put solar PVs on two village schools but need to raise £49,000 through sales of shares to local people in less than a month, before Government incentives expire. [The Argus]
¶ The Union Minister of State for Power and Coal, Mr Piyush Goyal, said that the Power Grid Corporation of India will invest $4,816 million to improve transmission infrastructure from northern states to southern states. Other investments would provide $160 million in rural infrastructure and $58 million for nine towns. [SteelGuru]
¶ Launching Ireland’s largest ever wind farm this week, on isolated bogland at Mountlucas in Kildare, the head of Bord na Mona’s energy generation division said he expected returns “in the high teens”. He expects double-digit returns over the course of its lifetime, and it should pay for itself in 7 or 8 years. [Irish Independent]
¶ The Swiss-engineered airplane Solar Impulse 2 will begin its solar-powered flight around the world early on Monday morning, weather permitting. The plane was scheduled to launch earlier this month, but was delayed due to weather conditions. The flight should take around five months to complete. [The Verge]
¶ A wind-powered car might be science fantasy, but residents of Orkney have discovered the nearest thing. With their wealth of renewable energy, the islanders have become the keenest users of electric vehicles in Scotland outside the capital. The tiny community of just over 20,000 already has 50 EVs. [Scotsman]
¶ More than 5,000 protesters gathered outside Parliament in London calling on the Government to take tougher action on climate change. Crowds of environmental activists cheered as a host of speakers including Vivienne Westwood and Caroline Lucas attacked the Government and accused it of not taking action. [Belfast Telegraph]
¶ Key players from the Philippine government and the private sector are drawing up a blueprint to make Mindanao a greener region. During a recent meeting of the Mindanao Power Monitoring Committee, officials underscored the importance of advocating renewable energy as a source of electricity for the island-region. [Philippine Star]
¶ China’s wind farms have a combined capacity that exceeds the capacity of America’s nuclear plants, as the growing nation expands its power generation to fuel its new mega-cities. The capacity of the wind farms in China comes to 115,000 MW. America’s nuclear reactors have a total combined capacity of 98,400 MW. [Digital Journal]
US:
¶ Community solar gardens first took off in Colorado a few years ago, and the model, also known as community or shared solar, has spread to Minnesota, California, Massachusetts and several other states. Capacity is expected to grow sharply this year, with interest among both residential and corporate customers. [Fairfield Daily Republic]
¶ The prospective GOP presidential candidates at today’s Iowa Ag Summit were pressed to express their opinions on everything from federal policies that have boosted ethanol production to expanded trade with Cuba. Each candidate answered a series of questions from the event host, an Iowa agribusiness man. [Radio Iowa]
¶ This week saw announcements of significant cost savings for SolarCity, a major advanced energy investment from Citigroup, and a move into Mexico for Pattern Energy. So, costs are down, investment is up, and Advanced Energy Economy members are taking their influence worldwide. [Energy Collective]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 7, 2015
World:
¶ The UK has spearheaded a return to growth for the utility-scale solar sector in Europe, according to Wiki-Solar.org. The website, which tracks installation of solar projects over 5 MW solar worldwide, says there was a total of 35.9 GW of utility-scale solar capacity at the end of 2014, up 14.2 GW from 2013. [Solar Power Portal]
¶ Around the world there were 51,477 MW of wind capacity installed during the year, a 44% increase over the amount installed in 2013. This brings the total global wind capacity to 369,553 MW, a huge number! Also, growth figures indicate we could double wind capacity during the next 7 years. [Treehugger]
¶ Anyone in Malaysia could be an independent power producer. It doesn’t have to be only large favoured companies making money by selling power. Anyone could do it, once the country adopts net metering. That’s the plan Serdang MP Ong Kian Ming wants the government’s energy authorities to adopt. [Free Malaysia Today]
¶ India will achieve energy independence by 2050 if most households go for rooftop solar power generation under new policy, a leading expert says. The ministry of new and renewable energy is in the process of framing an ambitious policy to generate adequate electricity from non-conventional energy sources. [The Hans India]
¶ Environmental action group World Wide Fund for Nature-Philippines on Friday dismissed fears over the possible negative impact of wind power on the national grid. The group’s Climate Change Unit Head said adding 500 MW of wind power to the national grid will have no negative impact on grid operations. [The Manila Times]
¶ Water at the Takhini, Yukon, hot springs emerges warm enough for bathers to soak outdoors, even in the winter. Now, researchers will study Yukon’s fault lines and hot springs to examine their feasibility as sources of geothermal power. Takhini Hot Pools is one of the sites to be examined as part of the project. [CBC.ca]
US:
¶ Comparing 2014 to 2013 in terms of changes in power produced in the US, windpower increased most. In fact, windpower gained more than all traditional power sources put together. Solar was number two, with 2014’s output more than doubling 2013’s. Output from natural gas fell, despite increased capacity. [CleanTechnica]
¶ According to a new survey conducted by the Morgan Stanley Institute for Sustainable Investing, 71% of individual investors who trade actively on the financial markets were interested in sustainable investing, but 54% believe choosing between sustainable investments and making financial gains is a trade-off. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A California state utilities judge has said that a major new natural gas power plant at Carlsbad should be put on hold until clean energy options are more thoroughly explored. San Diego Gas & Electric is wrestling with how to replace power from the recently retired San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. [U-T San Diego]
¶ A study by GTM Research and the Energy Storage Association says Energy storage in the US will more than triple this year as regulators allow use of the technology by utilities and homeowners. Changes in regulatory policy, especially in California, and the growth of renewable energy are driving demand. [Buffalo News]
¶ Prominent leaders from agriculture’s diverse value chain issued an open letter to policymakers and presidential hopefuls attending the first ever Iowa Ag Summit, urging them to consider Iowa’s renewable energy record in wind, solar and biofuels as an example for clean energy policies for the nation. [KMAland]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 6, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ Raytheon Company and its partners, the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Primus Power, and Advanced Energy have successfully demonstrated an advanced microgrid system capable of islanded (off-grid) operation using stored and high penetration renewable energy. [Your Defence News]
World:
¶ The European Union and international NGO Adventist Development and Relief Agency announced a three-year program to expand renewable energy access in Somalia. The project will provide affordable and sustainable renewable power to 100,000 homes across Somaliland, Puntland and South Central Somalia. [ESI Africa]
¶ There are more indications that the world is reaching a tipping point, and it is firmly toward renewable energy and away from fossil fuels. A line from a report by the National Bank of Abu Dhabi is illustrative: “Going forward, almost all investments in the power sector will be in renewable energy.” [SustainableBusiness.com]
¶ China, the country that is building the most nuclear reactors, continued to get more electricity from the wind than from nuclear power plants in 2014. This came despite below-average wind speeds for the year. The electricity generated by China’s wind farms in 2014 was 16% more than the year before. [InvestorIdeas.com]
¶ “Lifting India out of poverty and pollution” India’s air is cutting 660 million lives short by about three years, while nearly all of the country’s 1.2 billion citizens are breathing in harmful pollution levels. Coal and nuclear have failed to provide 300 million Indians with electricity. Renewable power is an answer. [SBS]
US:
¶ Despite gas prices at the lowest point in years, new numbers show that using public transportation can be a money saver. The average annual savings for public transit riders in February is $9,238 ($770 per month), according to the American Public Transportation Association’s February Transit Savings Report. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In Texas, where consumers can buy electricity through competitive power plans, renewable energy plans are among the cheapest available. In a review of the state-run website PowertoChoose.org, three of the ten lowest-priced plans offered in Dallas this week were advertised as 100% renewable. [Dallas Morning News]
¶ Buoyed by tens of thousands of petitioners seeking to breathe new life into the Cape wind project, demonstrators took to Boston Common on February 28 to ask utility National Grid to rekindle its financial relationship with the project. Then about 96,000 more people signed online support petitions. [Barnstable Patriot]
¶ Raleigh-based Conservatives for Clean Energy commissioned a poll that shows overwhelming support for renewable and clean-energy sources, even among Republicans and self-described conservatives. Smaller numbers support oil and gas exploration, but a majority of those polled oppose fracking. [Charlotte Business Journal]
¶ Iowa generates 27% of its electricity from wind. It has 4,000 wind-related jobs. And wind companies pay farmers millions each year to host turbines. Now, for this Saturday’s caucus vote, Republican presidential candidates will have to answer for their position on the federal wind production tax credit. [U.S. News & World Report]
¶ New York is seeking to redefine the roles of electric utilities and change the regulatory framework to facilitate much larger use of distributed energy resources, such as energy efficiency, demand response, energy storage, and distributed generation, including on-site wind turbines and rooftop solar. [North American Windpower]
¶ Employment in the solar industry jumped 21.8% in 2014, adding 31,000 new jobs in that time for a total of 174,000 solar workers nationwide, and it is expected to jump by another 36,000 workers this year. Though not requiring special education, the jobs pay well. The average solar installer makes $24 an hour. [The Herald Journal]
¶ Cambridge, Massachusetts, currently purchases the electricity that powers its municipal buildings from TransCanada, Keystone XL’s parent company. But now its city council has passed a unanimous resolution advising the city manager not to do further business with the company and switch to renewable power. [EcoWatch]
¶ Jaffrey, New Hampshire, is pursuing a solar project. If it goes forward, town officials plan to have it built at the closed Jaffrey landfill. The town would use the energy generated to power the municipal wastewater treatment plant, leading to more than $1 million in savings over the course of 20 years. [The Keene Sentinel]
¶ A battle is brewing as Michigan Governor Rick Snyder prepares this month to lay out a new energy plan for the state and appoint Michigan’s first czar to oversee it. Michigan gets 62% of its electricity from coal and 31% from nuclear reactors. Its utility rates are above the Midwest and national averages. [The Detroit News]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 5, 2015
World:
¶ A recent, widely seen documentary on air pollution in China, “Under the Dome,” appears to have had a strangely pronounced effect on the Chinese government. Rather than stifle those involved, or brush the matter aside, some higher-ups have even praised the documentary. Does it indicate a sea change? [CleanTechnica]
¶ China will boost efforts this year to rid itself of its addiction to coal in a bid to reduce damaging pollution and cut the energy intensity of its economy, which is expected to grow at its lowest rate in 25 years. The National Development and Reform Commission says it will reduce coal consumption in polluted regions. [Reuters]
¶ The City of Oslo, Norway, has committed to divesting its $7 million worth of coal investments from its pension fund. The news comes only weeks after Global Divestment Day. This makes Oslo one of almost 40 cities around the world that have committed to divest from fossil fuels, and the first capital city to do so. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The EU took a step to reduce its energy dependence, especially on Russia, by improving transmission connections between Spain and Portugal, and the rest of Europe. The leaders of Spain, Portugal and France pushed moving spare renewable energy produced south of the Pyrenees to the rest of Europe. [The Local.es]
¶ Italian renewable energy firm Enel Green Power has completed a 102-MW wind farm in Mexico. Located in the state of Oaxaca, the wind farm features 34 3-MW turbines that will generate about 390 GWh of energy per year. Enel Green Power invested about $160 million in the project. [Clean Technology Business Review]
¶ EU State Aid approval for the Hinkley Point nuclear plant will be challenged in court by German green power supply company Greenpeace Energy, in the latest blow to the high-profile project, dubbed by its critics as ‘the world’s most expensive power plant’. Greenpeace Energy is a renewable energy cooperative. [Business Green]
¶ Area members of Renewable Power – the Intelligent Choice are joyfully greeting the news that a nuclear waste site won’t be built in northern Saskatchewan. The Nuclear Waste Management Organization announced on Wednesday that Creighton was no longer under consideration. [Prince Albert Daily Herald]
¶ Court battles are the sole remaining obstacle to nuclear restarts in Japan. The fight in the courts means power companies face the risk of further delays in firing up idled reactors if judges side with local residents worried about nuclear safety. Four reactors owned by two utilities cleared regulatory safety checks. [The Japan Times]
¶ A former UK opencast mine is to be home to a solar and wind energy site after property regeneration company Harworth Estates and RES, a leading renewable energy company, secured planning consent. The 7.5-MW scheme will cover 48 acres and generate enough energy to power 1,500 family homes. [Click Green]
¶ A surprise reduction in the cost of the UK’s offshore wind energy is one of the dominant themes in a new report to be published later today by the Offshore Wind Programme Board, a joint government and industry-backed group tasked with identifying and addressing barriers to the sector’s development. [Business Green]
¶ German Economy Minister Sigmar Gabriel has ruled out supporting EU subsidies for nuclear energy projects. His comments came ahead of a meeting of energy ministers. He was adamant on Thursday that atomic energy was the most expensive form of power generation that also bore “significant risks” to people and the environment. [Deutsche Welle]
US:
¶ The US Senate tried, but failed, to override President Barack Obama’s veto of legislation authorizing the Keystone XL pipeline on Wednesday. The measure drew 62 “yes” votes, with 9 Democrats joining Republicans in voting to override the veto. Separate consideration is ongoing, and the issue is not over. [Huffington Post]
¶ Solar (and wind) giant SunEdison announced it was acquiring the project development team, four existing projects, and roughly 100 MW of project pipeline of Solar Grid Storage. The Philadelphia-based startup specializes in packaging lithium-ion batteries and inverters with commercial solar PV projects. [Greentech Media]
¶ To the dismay of many climate activists, a major natural-gas pipeline expansion project that will impact southern New England, New York and New Jersey has been approved. The proposal has drawn grassroots opposition along the pipeline’s 1,127-mile path between New Jersey and Beverly, Massachusetts. [ecoRI news]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 4, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ A major new Deutsche Bank report has predicted that energy storage – the “missing link of solar adoption” – will be cheap enough – and technologically ready – to be deployed on a large-scale within the next five years. The report said economically competitive batteries were the “killer app” for solar power. [RenewEconomy]
World:
¶ India has moved forward to double the “clean energy cess” it levies on coal used in the country. While presenting the general budget, the Finance Minister announced a proposal to increase the Clean Energy Cess from ₹100($1.6) to ₹200($3.2) per metric tonne of coal, to finance clean environment initiatives.” [CleanTechnica]
¶ US-based SunEdison, now the largest renewable energy company in the world, says it sees a $4 trillion value opportunity in the global wind and solar markets by 2020. The company argues that the combined capacity for wind and solar will be more than 1,450 GW by 2020, about 2½ times larger than the end of 2014. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Over the last few years, Neste Oil has become the world’s largest producer of renewable fuels from waste and residues. In 2014, the company produced nearly 1.3 million tonnes of renewable fuel from such waste as animal and fish fats, used cooking oil and residues generated during vegetable oil refining. [Your Industry News]
¶ Australian firm Hydro Tasmania is planning a $10 million off-grid hybrid project on Flinders Island combining solar, wind, diesel, and storage and enabling technologies, including flywheels and batteries. This system will help displace 60% of the annual diesel fuel used on the island for power production. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ The UK government’s electricity capacity market could result in “higher than necessary energy costs and emissions” because its design has been “skewed” in favour of fossil fuel generation, according to the influential parliamentary Energy and Climate Change Committee, in a report released this morning. [reNews]
¶ Solar use in Japan has exploded over the last two years with ambitious national efforts to promote renewable energy. But the technology’s future is now in doubt. Utilities say their infrastructure cannot handle the numbers of solar entrepreneurs intent on selling their power. And government support is unclear. [New York Times]
¶ Around 71% of Fukushima Prefecture residents remain dissatisfied with the central government’s handling of the nuclear disaster four years after the triple meltdown forced hundreds of thousands to flee their homes, a survey showed. Only 14% of respondents were satisfied with the central government’s efforts. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ Given the extreme hype over shale oil and fracking, one would expect the enthusiasm to translate into above average share performance for shale operators. This has not been the case. Share performance has actually been at best quite mediocre and in most cases just downright poor. [Energy Collective]
¶ The town of Scituate, Massachusetts, has made more than a half-million dollars in less than three years through its agreement with Scituate Wind LLC, owner of a local wind turbine. The town has collected more than $500,000 since the 390-foot-tall wind turbine went online in April of 2012. [The Patriot Ledger]
¶ San Diego Gas & Electric is expanding an experimental micro-grid that is designed to run on renewable energy independently of the regional power grid. The micro-grid pilot is being expanded under a $5 million grant from the California Energy Commission, SDG&E announced in a statement. [U-T San Diego]
¶ A collection of companies recently partnered with a California city on a three-month pilot project that sought to determine the feasibility of effectively collecting plastic products that are difficult to recycle. The project converted plastic packaging products and dinnerware into synthetic crude oil. [Renewable Energy from Waste]
¶ What is likely to become the nation’s first offshore wind farm has closed on more than $290 million in financing, which will allow a five-turbine demo of the renewable energy system to be completed. The Block Island Wind Farm will be a 30-MW offshore facility located in waters about 15 miles off Rhode Island. [Computerworld]
¶ New York regulators published a major order effectively telling traditional utilities that they will not be permitted to own renewable generation sources except in rare cases. This is to enhance competition and create markets that will allow on-site wind and rooftop solar to flourish. [Environment & Energy Publishing]
¶ RES Americas has achieved commercial operation at the 110-MW Keechi wind farm in Texas. Construction on the scheme, which is owned by Enbridge, kicked off in December 2013. The facility features 55 Vestas V100 2-MW turbines. The wind farm has a 20-year power purchase agreement with Microsoft. [reNews]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 3, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “Renewable energy is conquering quirky nature of Britain’s climate” – Clever engineering is smoothing out the peaks and troughs of renewable power in Britain and having a positive effect on the power supply. It looks like this is making the nuclear industry redundant before a new station can be built. [The Guardian]
Science and Technology:
¶ Conversion of biogas into compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) is now frequently considered when penciling out project financials. The US EPA expanded cellulosic fuel pathways to include CNG and LNG from biogas created in landfills and a variety of kinds of bio-digesting systems. [Biomass Magazine]
World:
¶ The news from Kenya about its electricity situation has been quite positive. Electricity costs for both consumer and industrial customers have decreased by about 30%. One estimate says Kenya saves $24 million per month. This favorable shift results from a consistent investment in geothermal energy. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Spain’s Abengoa SA kicked off commercial operations at a 100-MW concentrated solar power plant in South Africa. The parabolic trough plant is expected to generate enough electricity for about 80,000 local households. It has enough molten-salt storage for up to 2.5 hours of power after sunset. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ Suzlon has announced the commissioning of the 65.1-MW Rouar SA’s wind energy farm at Artilleros in Uruguay. The wind park is 170 kilometers east of capital Montevideo and is the first joint wind venture between Brazil and Uruguay. The project has 31 turbines, each with a rated capacity of 2.1 MW. [Greentech Lead]
¶ A documentary examining the deadly effects of smog on China’s population gripped the country after its release online this weekend. The 104-minute film, Under the Dome, explores how China’s noxious smog problem is harming urban residents. It has already been viewed tens of millions of times online. [Mashable]
¶ Rame Energy Plc, a UK-based energy developer, is planning to build 130 MW of wind and solar projects in Chile over the next 18 months. The projects will require about $300 million in investment, some of which will come from Banco Santander SA. The developer is also pursuing other funding sources. [Bloomberg]
¶ Good news! Not only did China’s coal consumption fall by 2.9% in 2014, Glen Peters of the Global Carbon Project calculates that China’s CO2 emissions have also fallen, by 0.7%. So it’s clear that China’s efforts to cut its coal consumption and carbon emissions are not only real, but are already producing results. [Energy Collective]
¶ The European Union is edging closer to its ambitious target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 20% by 2020. The latest annual Eurostat study of the European Commission’s 2020 strategy, found the Member States had already collectively achieved an 18% reduction from 1990 baseline levels. [Click Green]
¶ Economist Jeremy Rifkin says a Digital Europe transition will revolutionize every commercial sector, disrupt workings of virtually every industry, bring unprecedented new economic opportunities, put millions back to work, and create a more sustainable post-carbon society, mitigating climate change. [Materials Handling World Magazine]
US:
¶ North Carolina is one of North America’s fastest growing markets for clean energy. The state’s cleantech sector grossed $4.8 billion in 2014 and, based on previous experience, most companies expect to grow between 30% and 35% this year. Close to ¾ of this money went to building efficiency and solar. [CleanTechnica]
¶ An effort to roll back Colorado’s renewable energy standard in the state Legislature died Monday in a House of Representatives committee. The bill, which passed the Republican-majority Senate last month, would have cut the standard for utilities from 30% back to 15% by 2020. [Denver Business Journal]
¶ Even though Oregon has an ambitious renewable portfolio standard and ranks second in the US for hydropower generation, it still receives a surprising 33% of its overall electricity from coal, mostly from out-of-state sources. A pair of bills in the state legislature would completely ban coal-fired electricity. [Energy Collective]
¶ A new 4.2-MW solar farm will provide up to 5% of the US Virgin Islands’ power needs during daylight hours. The Estate Donoe solar farm will generate clean electricity under a 25-year power purchase agreement with Main Street Power, which will also manage the operations and maintenance of the facility. [Energy Matters]
¶ Oakland Unified School District is celebrating completion of the new high efficiency solar PV at 16 schools at an event this morning. It reported today that SunPower solar power systems at the schools are expected to significantly reduce the district’s annual electricity costs over at least the next 25 years. [PennEnergy]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 2, 2015
World:
¶ Spain’s renewable energy plants produced 48% of the country’s power in February. Wind power generation produced 27.6% of the total Spanish electricity production for the month. Hydroelectric produced 15.7%. Solar PV and concentrated solar power accounted for 2.2% and 0.9%, respectively. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ National Bank of Abu Dhabi, one of the biggest banks in the oil-rich Gulf countries, says fossil fuels can no longer compete with solar technologies on price. The NBAD report says the most recent solar tender showed even at $10/barrel for oil, and $5/mmbtu for gas, solar is still a cheaper option. [RenewEconomy]
¶ According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, new funds invested into clean energy gained 16% in 2014 to reach $310 billion. The record is still $318 billion, set in 2011, but there was a significant upward trend last year. Overall, the world added about 100 gigawatts of solar- and wind-power capacity in 2014. [Investing.com]
¶ In Australia, talks between the government and Labor toward a compromise on the renewable energy target appear to have again broken down, with the Opposition rejecting a new offer on Monday. The rejected proposal would have set the target at 31,000 GWh of baseline power from renewables by 2020. [Sydney Morning Herald]
¶ Plans for a vast tidal lagoon power plant which could power every home in Wales have been launched. The lagoon, between Cardiff and Newport, would include 90 turbines set in a 14-mile breakwater and could provide enough electricity for 1.5 million homes, 8% of the UK’s electricity, for 120 years. [Sky News]
¶ French power producer Neoen plans to construct a 30-MW solar park in Mexico’s northeastern state of Nuevo Leon. The project calls for an investment of $60 million. The PV facility is to be installed on 227 acres in the town of Galeana and is slated to become the biggest of its kind in Nuevo Leon. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ A report from the African Development Bank shows that its support to Africa through the Climate Investment Funds increased exponentially in 2014 to include one regional and 25 national investment plans, with an additional nine poor countries being funded for renewable energy solutions. [solarserver.com]
¶ A draft law to reform the European Union’s Emissions Trading System, by cutting the surplus of carbon credits available for trading, has won approval from the European Parliment’s Environment Committee. Emissions Trading System is a cornerstone of EU policy to combat climate change. [Environment News Service]
¶ A sea of glass panels, to be located on Queensland’s Darling Downs, could be capable of cranking out two GW of power within eight years. That is equivalent to one fifth of the current total renewable energy target for the entire country in a single power station, and it is more than any coal station in the state. [The Guardian]
US:
¶ Policy squabbles and a fight over rebates may have clouded Missouri’s once blossoming solar industry, according to new data that shows the state lost 300 solar jobs last year. The latest analysis now ranks the state 16th in the nation for solar industry employment, down from 12th in 2013. [Public News Service]
¶ In Michigan, the Holland Board of Public Works, is replacing a coal-fired plant with a new fuel-efficient modern power plant. The CO2 emissions at the site will be reduced by approximately 50%. The plant’s surplus heat from in the circulating water system will go to expanding a downtown snowmelt system. [Renewable Energy Focus]
¶ New reports show Michigan’s 2008 renewable energy mandate has worked as intended, but lawmakers must now decide what to do next when the policy sunsets at the end of this year. One option is a new “clean-energy standard” that would credit sources like natural gas for lowering greenhouse gas emissions. [MiBiz]
Posted in renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 1, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ Water is eating away at the Antarctic ice, melting it where it hits the oceans. As the ice sheets slowly thaw, water pours into the sea — 130 billion tons of ice (118 billion metric tons) per year for the past decade, according to NASA satellite calculations. That’s the weight of more than 356,000 Empire State Buildings. [Huffington Post]
World:
¶ Algeria is the leading natural gas producer in Africa and is the second-largest supplier of gas to Europe, but that is not slowing down the North African country’s plan to ramp up solar power generation. The country’s energy minister has announced a plan to install 13.5 GW of solar PV capacity by 2030. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Presenting the General Budget 2015-16 in the Indian Parliament, the Finance Minister said, “Our de-facto ‘Carbon Tax’ on most petroleum products compares favourably with international norms.” He said with regard to coal, there was a need to find a balance between taxing pollution and the price of power. [Day & Night News]
… It was widely expected that Budget 2015-16 would include a lot of goodies for the renewable energy sector. But apart from a passing mention of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy’s well-publicised target of 175,000 MW of renewable energy capacity, the Budget had absolutely nothing for the sector. [Hindu Business Line]
¶ The UK’s Liberal Democrats set out plans to double the UK’s production of renewable electricity by the end of the next parliament and make Britain zero carbon by 2050. They say they have already created a low-carbon, pro-renewable, and more energy secure nation less reliant on unstable regimes for energy. [Liberal Democrats]
¶ South Korea’s nuclear commission decided to extend the operations of the country’s second-oldest nuclear reactor till 2022 despite growing concerns over safety. The 679-MW Wolsong-1 reactor completed its 30-year life span in 2012 and was turned off. The decision will extend its life for 10 more years. [EastDay.com]
US:
¶ Although the Eureka, California, City Council voted to participate in the clean-energy financing program known as Property Assessed Clean Energy, or PACE, in January, the council may take a second look after learning that the Federal Housing Financing Agency is actively opposing the measure. [Eureka Times Standard]
¶ A series of bills that would repeal New Hampshire’s Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative and Renewable Portfolio Standard are going before the New Hampshire House and Senate. The Governor Hassan indicated she will likely veto the RGGI bill but has not indicated any executive action on the RPS bills. [Seacoastonline.com]
¶ In an about-face from his first term, the governor of Wisconsin wants to eliminate funding for a University of Wisconsin-Madison renewable energy research center. He proposes cutting $8.1 million from a bioenergy program that was a key in landing one of the university’s biggest government grants ever. [Milwaukee Journal Sentinel]
¶ Colorado rural electric cooperatives want state lawmakers to rewrite parts of a new state law that essentially requires them to produce 20% of their power from renewable sources. The co-ops have drafted Senate Bill 46, which doesn’t attack the 20% requirement, but would change some of the ways co-ops can reach it. [Pueblo Chieftain]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 28, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “We Could Be Turning the Corner on Climate Change” – Efforts to reduce carbon emissions appear to be starting to work, and the link between economic growth and energy consumption is breaking. For example, last year, coal consumption fell for the first time in China, by 2.9% from 2013. [SustainableBusiness.com]
Science and Technology:
¶ A redox flow battery designed at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory more than doubles the amount of energy this type of cell can pack in a given volume, allowing it to rival lithium-ion batteries. If the device reaches mass production, it could find use in fast-charging transportation and grid storage. [Gizmag]
World:
¶ German’s Federal Network Agency, a government body, announced the country’s first tender for ground-mounted solar PV systems. The full order volume for the solar tender, which will be split into 3 annual rounds will reportedly be 150 MW. The highest bid will be set at 11.29 Euro cents per kWh. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The US-based renewable energy company Pattern Energy is partnering with the Mexican construction company Cemex to form a joint venture for developing projects in Mexico, according to recent reports. The plan is to build up to 1 GW in new project capacity to be developed via the joint venture. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Ireland is aiming at 40% renewable energy by 2020, with most renewable electricity from large-scale wind farms. But some winter nights the Irish grid will have to take 75% of its electricity from renewable sources. A combined ultracapacitor & battery energy storage system could help meet that need. [ECOreport]
¶ Navigant Research has released a report stating that 696.7 MW of global energy storage projects (excluding pumped hydro) were announced in 2014–2015, with much coming in Q3 2014 to Q1 2015. North America had 436.4 MW of the total amount. There were over 800 storage projects reported. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Sweden’s state-owned Vattenfall has won a tender to build a 400-MW wind park off Denmark, with the first turbines scheduled to start supplying power in 2017. The agreed price of power is 10.31 euro cents per kilowatt-hour, 32% cheaper than in Denmark’s latest project, the ministry said. [The Maritime Executive]
¶ China’s coal consumption fell by 2.9% in 2014, according to newly released official Chinese energy data. The data confirm earlier projections of a fall in coal use and 1% reduction in Carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel burning. An initial analysis suggests that equates to a 0.7% drop in overall emissions. [The Ecologist]
¶ A report from the International Renewable Energy Agency published in January confirms that onshore wind-generation costs are competitive with those of the fossil-fuel sources. The latter are in the $45-140/MWh range, wind comes in at an average $55/MWh. Irena also confirms that costs are falling. [Windpower Monthly]
¶ The Japanese nuclear watchdog body slammed TEPCO over its failure to disclose information on the leakage of radioactive rainwater into the sea from the crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. TEPCO disclosed high levels of radiation in a drainage ditch many months after they were found. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ The Vermont House has advanced a wide-ranging bill on a Renewable Energy Standard and Energy Transformation program, or RESET. The requirement would be that utilities get 55% of their power from renewable sources by 2017, ramping up to 75% by 2032. Some have met or exceeded those goals already. [Valley News]
¶ Massachusetts utility companies are preparing to buy enough renewable energy to power 136,000 homes under the major initiative announced for Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island on Tuesday. The companies may buy up to 817 GWh of electricity per year under a request for proposals. [Boston Globe]
¶ Less than a year into providing default electricity service to residents and businesses in Sonoma County, Sonoma Clean Power contracted with Pristine Sun to build up to 12.5 MW of new solar power. The venture represents the largest floating solar project in the US, and the second largest in the world. [Sonoma County Gazette]
¶ Ohio’s clean energy economy celebrated a big win this week. The Public Utilities Commission of Ohio denied American Electric Power Company’s request for guaranteed profits to operate its aging, uneconomic coal power plants. The EDF was one of many parties opposed AEP’s proposal. [Environmental Defense Fund]
¶ NRG, one of the largest owners of fossil-fuel power plants in the US, plans to achieve “transformational growth” in its home solar customer base this year by expanding to between 35,000 and 40,000 customers from 13,390 at the end of 2014. The company had only 4,349 home solar customers in 2013. [pv magazine]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 27, 2015
World:
¶ The second Global Sustainable Investment Review report confirms that global sustainable investment reached $21.4 trillion by 2014, up from $13.3 trillion at the same time two years earlier. Sustainable investment now accounts for 30.2% of the professionally managed assets in the regions covered. [CleanTechnica]
¶ India’s renewable energy industry is likely to generate business opportunities worth $160 billion in the next five years, the Economic Survey said the day before a budget that is set to boost clean energy funding. The Prime Minister set clean-energy targets that include raising solar capacity to 100 GW by 2022. [Reuters India]
¶ BMW South Africa is considering wind and solar power options to make a production plant near Pretoria energy self-sufficient, hoping the factory will provide between 25% and 30% of its own energy needs by the middle of this year. Wind and solar power are two options for self-sufficiency. [Independent Online]
¶ Irish wind and solar energy company, Mainstream Renewable Power is set to develop a €2 billion windfarm off the Scottish coast. The company secured a 15-year contract for its 450-MW Neart na Gaoithe facility in the North Sea. The windfarm is expected to be commissioned and generating electricity by 2020. [Irish Examiner]
¶ Swift global action is needed to avoid the worst threats from a rapidly changing climate, the disasters brought by storms, floods, extreme temperatures, and their impacts on people and biodiversity, French President Francois Hollande warned during a climate change forum in the Philippines on Thursday. [InterAksyon]
¶ Three wind farms in Wales won financial support from the Government as part of the first auction for contracts for difference under the reform of the electricity market. The three are Clocaenog Forest and Mynydd y Gwair, both being developed by RWE Innogy, and Windpower Wales’ Brenig wind farm. [WalesOnline]
US:
¶ A bill in the Illinois legislature, to make changes to the state’s Renewable Portfolio Standard, might create 32,000 clean energy jobs, its backers say. The bill would support more solar power and improve energy efficiency. It would also increase the renewable energy standard from 25% by 2025 to 35% by 2030. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Energy storage capacity totalling over 1,500 kWh is be installed in intelligent energy storage/electric vehicle charging systems in five California school districts, colleges, and universities. Balancing their electricity supply will save up to $1 million over the life of their projects – with no upfront costs. [CleanTechnica]
¶ California-based Swinerton Renewable Energy is teaming with tracking solutions specialist Array Technologies to build a 104-MW solar park in Utah for Norwegian developer Scatec Solar. Power will be fed into the grid under a 20-year power purchase agreement with PacifiCorp’s Rocky Mountain Power. [pv magazine]
¶ If you haven’t installed solar panels on your roof because it’s too expensive, Google really wants to help. Google is once again boosting its investment in SolarCity’s residential solar power model by $300 million. SolarCity combined this with a new financing structure to produce a new fund worth $750 million. [ThinkProgress]
¶ Two farms, a real-estate office, a jewelry maker and an animal hospital are among the latest recipients of Rhode Island state grants for new solar projects. The funds are awarded by the Rhode Island Renewable Energy Fund and were approved. Eight solar projects have received $1,137,000 in recent awards. [ecoRI news]
¶ Hints are emerging about how California’s investor-owned utilities might meet the governor’s goal of providing 50% renewable power by 2030. The CEO of California’s second largest electric utility says they want to claim rooftop solar, energy efficiencies, and electric vehicle charging stations in their portfolios. [U-T San Diego]
¶ Electricity users would have to pay a little extra to help cover costs of Exelon’s nuclear power plants under Illinois legislation. Exelon maintains the bill would save jobs and keep service steady and reliable. It would also have residential customers pay about $2 more each month to keep the nuclear plants running. [Chicago Tribune]
¶ A $3 billion deal will unite Iberdrola USA with UIL Holdings Co to create a massive power and utility company serving 3.1 million customers in New York, Connecticut, Maine and Massachusetts. Iberdrola USA will pay $52.75 per share of UIL in a deal announced after the close of business Wednesday. [Portland Business Journal]
¶ Hawaiian Electric Co was generating about 21% of its power from renewable energy at the end of 2014. The utility said that it was generating about 39% of its power from a combination of renewable energy and efficiency measures when the year ended, up about 4 percentage points from a year earlier. [Pacific Business News (Honolulu)]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 26, 2015
World:
¶ The UK’s Department of Energy & Climate Change awarded contracts worth more than £315 million to 27 projects. ScottishPower got one to build a 714-MW offshore wind farm, RWE Innogy GmbH won for three onshore wind projects totaling 166 MW, and Lightsource will build a 14.67-MW solar facility. [Bloomberg]
¶ Ground was broken for the 36.3-MW wind farm at Malvern, St Elizabeth forms part of a concerted push to reduce Jamaica’s $2-billion oil bill through the use of renewable energy. The project, at one of the most windswept points in the Santa Cruz Mountains, is being developed by BMR Jamaica Wind Limited. [Jamaica Observer]
¶ GDF Suez profits dropped last year amid falling oil prices, unusually warm weather in Europe and lower electricity prices, prompting the group to announce short-term restructuring measures. The plunge in oil and gas prices has had significant short term impact and is set to cost them €900m in 2015 profits. [Financial Times]
¶ Germany’s renewable energy production has been steadily growing, with a fourfold increase since 2000. Around 40 terawatt hours were generated with renewables 15 years ago and in 2014, the level was at 157.4 terawatt hours. But a study shows the potential of renewables is far from being fully exploited. [EurActiv]
¶ SunEdison, the world’s largest renewable energy development company, is planning to supply electricity to 20 million unserved people around the world. The initiative will be led by a company group focused on developing sustainable business models and technologies for renewable energy in rural areas. [AltEnergyMag]
¶ The European Commission has leaked a 19-page draft blueprint for an “energy union.” It is a grab bag of policies and proposals designed to transform the 28-member European Union into a more cohesive energy market. Despite its widespread appeal, the initiative shows fractures and double standards. [OilPrice.com]
¶ European transmission system operators have been preparing for an eclipse that will happen in March for several months, evaluating and attempting to mitigate risks. Some 35,000 MW of solar energy, the equivalent of nearly 80 medium size conventional generation units, will stop producing during the event. [Phys.Org]
¶ Fukushima fishermen appear to have finally run out of patience with TEPCO. They lambasted TEPCO at a meeting on February 25 over the utility’s failure for half a year to disclose the flow into the ocean of water contaminated with radioactive materials from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ Under a new plan by governors of Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island, electric distribution companies will collaborate with state agencies on a bidding process for proposals for clean energy resources including wind, solar, small hydro, biomass, fuel cells and other low-carbon sources. [Lexington Herald Leader]
¶ Iberdrola Renewables, the owner and operator of the Blue Creek Wind Farm, along with Ohio State Senator Cliff Hite presented checks to Van Wert County, Ohio for more than $2,070,000, and Paulding County for $666,000. Iberdrola pays the counties $18,000 per year for each Iberdrola turbine they have. [Delphos Herald]
¶ The Department of the Navy announced the signing of a lease with Duke Energy that will allow the development of a large-scale, ground-mounted solar array at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune. The lease grants Duke Energy access to 80.65 acres of land at Camp Lejeune to develop a 17 MW solar PV array. [Camp Lejeune Globe]
¶ In Hawaii, the Big Island’s electric utility has asked Ormat Technologies to supply it with more geothermal power. The additional 25 MW will come from a new power plant at a new location, Hawaii Electric Light Co said Tuesday. The precise location has not yet been announced, under a nondisclosure agreement. [Thegardenisland.com]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 25, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ A major new study from Agora Energiewende says the cost reduction potential of large-scale solar is still not understood. It predicts that solar PV will be the cheapest form of power within a decade, and cost less than $0.02/kWh by 2050. The study says the end to cost reductions for solar is “not in sight.” [RenewEconomy]
World:
¶ As part of its first major retrofit in 30 years, two custom-designed wind turbines have started generating power for the Eiffel Tower. Located above the World Heritage Site’s second level, about 400 feet off the ground, the sculptural wind turbines are now producing 10,000 kWh of electricity annually. [ThinkProgress]
¶ Africa’s first grid-connected biogas plant will begin supplying power by March 1. The $6.5 million Gorge Farm Energy Park anaerobic digester in Kenya will consume an annual 50,000 tons of organic waste sourced from a neighboring 1,977-acre farm owned by VegPro Group, one of the plant’s investers. [Starr 103.5 FM]
¶ The European Union will map out a plan for closer energy ties among its 28 nations, seeking to avoid supply risks highlighted by the crisis in Ukraine and to facilitate the planned shift to low-carbon economy. It will also present a plan on a global climate deal and a strategy for improving energy across Europe. [Bloomberg]
¶ The Abbott government’s efforts to scale back Australia’s renewable energy target have set the industry back 12 years in that country, its senators were told by the Clean Energy Finance Corporation in a hearing. And the government has told senators it will still pursue the abolition of the CEFC. [Sydney Morning Herald]
¶ Australia has some of the highest electricity prices in the world due to an overbuild of network infrastructure. Solar power installers there say the cost of batteries is the only thing holding back more widespread consumer grid defection in the residential sector. And household solar installations are booming. [RenewEconomy]
¶ A hydro scheme, the first in Scotland to be financially supported by a community group, has been switched on. The 469 kW development on the remote Abhainn Shalachain river near Lochaline, on the shores of the Sound of Mull, is now generating income for local residents on the Morvern peninsula. [Scotsman]
¶ The UK’s renewable sources of energy like wind turbines could soon generate more electricity than nuclear power stations. Nuclear power is in a slow decline from its peak of 25% in 1995 to its current 19%. The contribution of renewables more than doubled from 6.8% in 2010 to 14.9% in 2013, and it continues to grow. [New Scientist]
US:
¶ According to the Electric Reliability Council of Texas wind energy provided 6.2% of the state’s share of electricity in 2009, a figure which has since grown to 10.6% in 2014. In terms of annal power production, Texas windpower has grown from 19.9 million MWh in 2009 to 36.1 million MWh in 2014. [CleanTechnica]
¶ As Tulare County, California, has grown into the top dairy producing county in the United States, there’s a lot of cow poop to deal with. A new plant in Calgren is now making ethanol for blending with gasoline from all that manure. The plant’s process also extracts water that can be used by local farmers for crops. [Sustainablog]
¶ President Barack Obama, exercising his veto power for the first time in five years, rejected on Tuesday a measure green-lighting the construction of the controversial Keystone XL pipeline. It is unlikely GOP lawmakers will be able to reverse Obama’s veto, as that would require a two-thirds vote in each chamber. [CNN]
¶ Essex Capital Partners, based in Massachusetts, and Sunpreme Inc, a US-based solar cell manufacturer, completed 90 day post commissioning of a 2.6 MW ground mount solar system in Barton, Vermont. The system will generate 3,400,000 kWh of electricity annually, enough to serve over 1,500 homes. [Your Renewable News]
¶ SunEdison Inc, a US solar panel maker and project developer, expects its annual installations to more than double this year. The company intends to complete solar and wind power facilities with 2,100 to 2,300 MW of capacity during 2015. Last year it completed 1,048 megawatts of solar farms. [Bloomberg]
¶ Exelon will ask state lawmakers as soon as this week to approve a new surcharge on electric bills throughout the state to provide more revenue for low-carbon power-generation sources like its six Illinois nuclear plants. Some of its nuclear plants here are in danger of closing without a revenue boost. [Crain’s Chicago Business]
¶ In a rare move, Washington DC’s Federal US Court of Appeals will hear a landmark challenge to the continued operation of California’s two remaining reactors. They are surrounded by more than a dozen seismic fault lines. The Shoreline fault runs within 600-700 yards of the Diablo Canyon reactors. [OpEdNews]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 24, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “New Coal Plants in China: A (Carbon) Bubble Waiting to Burst” – China’s coal consumption growth has slowed down and fell in 2014. At the same time, coal-fired power generating capacity is growing rapidly. This represents an investment bubble that will burst as overcapacity becomes too large to ignore. [Energy Collective]
World:
¶ Grassroots support for energy reform is substantial in India. This was seen most recently in Aan Adani Party’s win in the Delhi state elections, a jarring reminder that the Indian masses have clout. A central election issue was making electricity both more sustainable and more affordable for the poor. [Solar Novus Today]
¶ The government of the Australian state of Victoria has made good on a pre-election promise to support the state’s first solar-powered town. Energy audits and retrofits to reduce consumption have already begun in Newstead as the first step towards a community micro-grid using 100% renewable power. [The Fifth Estate]
¶ The New South Wales Greens have unveiled a plan for a secure and clean energy future in the state. It has households and small businesses become active participants in the electricity industry. Coal and gas-fired electricity generation in NSW generates over 60 million tons of carbon emissions annually. [Energy Matters]
¶ The Director of Electricity from Panama’s National Energy Secretariat says that the recent solar bid was very successful with more tenders being put forward than ever. He says this means the country will have over 80 MW of installed capacity in solar PV and there are many opportunities for more. [AltEnergyMag]
¶ Senvion is delivering 18 wind turbines for the Nordergründe offshore wind farm in the German North Sea. Each turbine has a rated power of 6.15 MW, enabling it to supply about 4,000 households with energy. The Nordergründe offshore wind farm will be completed in the fall of 2016. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
¶ A Swedish group is building the world’s first ‘climate positive’ data center, in the famous copper mining and snow sports city of Falun. The proposed data center will work in tandem with a local energy system, using its waste heat for a variety of purposes and incorporating various renewable sources. [The Stack]
¶ Hawkins Group, of New Zealand, is developing the two new geothermal plans as part of a joint venture with Indonesian partner Banguan Cipta Kontractor. Hawkins has experience in delivering geothermal projects in New Zealand having recently successfully completed three power stations in that country. [Renewable Energy Focus]
¶ March will mark the fourth year since the crisis began at TEPCO’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, where decommissioning work continues. About 6,000 to 7,000 workers are working every day to try to bring the situation under control at the buildings and facilities still scarred by the accident. [The Japan News]
US:
¶ The US installed some 470 MW of wind and 70 MW of solar parks in January 2015, according to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. This compares to 235 MW of wind and 343 MW of solar deployed a year earlier. Total installed wind power capacity reached 65.66 GW, 5.61% of total capacity. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ A new Massachusetts state Senate report on climate change is a call for the state to set policies in the face of deepening environmental impacts. Its title is its bottom line: “No Time to Waste: Our climate clock is ticking and our natural resources, public health and the future of our economy are at stake.” [The Recorder]
¶ Gulf Power has submitted four petitions this year to the Florida Public Service Commission for solar and wind projects that could potentially power more than 68,700 homes in Northwest Florida. Three are solar energy farms at military bases, and one would purchase power from wind-rich Oklahoma. [Pensacola News Journal]
¶ Ameren Corp. has proposed an alternative to the EPA’s Clean Power Plan. The company says its proposal would achieve the same final CO2 emission reduction goals as the EPA’s own plan, while saving $4 billion in costs and avoiding grid reliability problems related to closing key coal-fired plants. [PennEnergy]
¶ In the latest sign that a Bay Area renewable energy trend is picking up steam, San Mateo County, California is taking a close look at buying its own power on the open market, instead of relying on PG&E, in a bid to lower its greenhouse gas emissions. The county is considering a community choice aggregation program. [Chico Enterprise-Record]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 23, 2015
World:
¶ Apple plans on investing €1.7 billion (£1.3 billion) into Europe, which is the biggest investment the American company has ever made on European soil. The plan is to create two new data centres in County Galway, Ireland, and Denmark’s central Jutland. The facilities will run on 100% renewable energy. [ITProPortal]
¶ An initiative to integrate more renewable energy into the Central America power system took one step forward last week as regional vice-ministers, directors of energy, and directors of climate change met in El Salvador to discuss the region’s energy future, the International Renewable Energy Agency reports. [solarserver.com]
¶ Dong Energy’s 400-MW Anholt offshore wind farm in Denmark will be offline for at last three weeks following a fault with the subsea cable connecting the project’s 111 wind turbines to land. The project’s transmission operator, Energinet.dk, said it is too early to say what the cause of the problem on the line is. [reNews]
¶ SunEdison, a US-based company, has announced it will set up 15.2 GW of solar and wind energy capacity in India over the next 5 years. India has an ambitious target of adding 100 GW renewable capacity by 2022. India’s installed renewable energy capacity currently stands at just above 32 GW. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A 12-MW biomass power plant with a dedicated plantation will rise in Bataan after Filipino-owned Cleangreen Energy Corp received its operating contract from the Department of Energy. The power plant, targeted for completion in October 2017, is expected to commence construction this year. [eco-business.com]
¶ Engineers in Norway and Sweden, two of the countries trying hardest to develop wave power technology, have announced “breakthroughs” in their methods, which the inventors believe will make wave power competitive. The latest Norwegian experiment has been installed in a redundant fishing vessel. [eco-business.com]
¶ Alternergy Wind One Corp, a company led by former Philippine Energy Secretary Vince Perez, is expected to complete a 67.5-MW wind farm project there in May. The $177.9-million project is due for completion in July 2015, Energy Department records showed, but it is likely to be completed early. [Manila Standard Today]
¶ Sensors at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant have detected a fresh leak of highly radioactive water to the sea, TEPCO announced Sunday. The sensors detected contamination levels, up to 70 times greater than the already-high radioactive status seen on the plant grounds, in water draining to the sea. [The Japan Times]
US:
¶ Floridians for Solar Choice has secured 100,000 petition signatures to obtain a place on the 2016 ballot after only one month of collecting signatures. Should the campaign secure enough signatures, Florida voters would be able to vote in 2016 to expand solar choice. (The petition needs 700,00 signatures.) [CleanTechnica]
¶ Wei-Hock “Willie” Soon, a prominent climate change denier and researcher, quietly took more than $1.2 million in payouts from the energy industry, including the Koch brothers and other oil lobbyists, for the past 14 years, newly released documents obtained by Greenpeace have shown. [eNews Park Forest]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 22, 2015
World:
¶ Electric car sales (including plug-in hybrid electric cars) in the UK surged over 300% in 2014, as compared year-on-year against 2013, according to the most recent figures from the European Automobile Manufacturers Association. EV sales in the UK rose from just 3,833 units in 2013 to 15,361 units in 2014. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In the UK, National Grid is announcing the results of a sealed-bid auction for the new Contracts for Difference mechanism to subsidise low carbon energy generation projects in the years ahead. CfDs provide a different structure than the subsidies that have moved the UK so far, and some say they are not as good. [Scotsman]
¶ The city of Munich is claiming that a giant wind farm being built off the coast of North Wales will contribute to its renewable energy targets, after it acquired a £660 million stake in the scheme. This leaves the UK with the question of how it can apply power from Gwynt y Môr to its own renewable targets. [Business Green]
¶ The IKEA Group is continuing to make progress on its path to receiving 100% of its energy needs via renewable energy sources by the year 2020, as the recent announcement that it had acquired a new wind energy project in Poland demonstrates. The specifics of the deal haven’t yet been publicly revealed. [CleanTechnica]
US:
¶ The oil and gas industry sponsors and spins research to shape the scientific debate over horizontal hydraulic fracturing, or fracking. That’s the conclusion of analysis by the non-partisan group, Public Accountability Initiative, of more than 130 documents distributed to policymakers by industry representatives. [Huffington Post]
¶ Federal regulators are close to approving construction of Michigan’s first new nuclear power reactor in more than a quarter century, although it’s an open question if it will ever get built. Changes in the energy market over the past 6½ years have dimmed the possibility of a nuclear power revival. [Detroit Free Press]
¶ A broad political coalition, from liberal environmentalists to tea-party conservatives, has banded together in Florida to press for something that ironically is in short supply in the Sunshine State: solar power. The group launched a campaign to place a pro-solar initiative on the state’s 2016 ballot. [Fox News]
¶ A new report produced by the Wind Energy Foundation, Creighton University in Omaha, Nebraska, and Washington-based consultants David Gardiner and Associates said “significant cost declines” for electricity generated by wind and solar power is spurring development in Nebraska and nationwide. [Grand Island Independent]
¶ Illinois legislators introduced a bill to spur new growth in the clean energy industry, creating an estimated 32,000 jobs annually, once proposed clean energy standards are implemented. Illinois already has 100,000 clean energy jobs. The bill is endorsed by the recently-formed Illinois Clean Jobs Coalition. [Energy Collective]
¶ In 2013, solar installations accounted for 31% of all US electric power installations, and 2014 was a breakthrough year for utility-scale solar. Growing advantages in pricing and purchase agreements have been cited. Among area projects are several in conjunction with Oneida County, New York government. [Rome Sentinel]
¶ Southern Company subsidiary Southern Power today announced the acquisition of two solar PV projects totaling 99 MW in Georgia. They are the 80-MW Decatur Parkway Solar Project and the 19-MW Decatur County Solar Project. Southern Power is acquiring them from Tradewind Energy, Inc. [Sowega Live]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 21, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “We Don’t Need New Energy Storage Innovations” – There’s been a lot of talk about energy storage being a “holy grail” for solving the problems of deeper renewables saturation in the US power grid. But it’s time to start pushing back on the rhetoric. The solutions we have now for storage are sufficient to the task. [Greentech Media]
Science and Technology:
¶ One of the biggest statements on Tesla’s last quarterly conference call was that it would be unveiling a battery storage system for home use within 1–2 months. Several competing energy storage companies are watching closely to see what the details end up being, while a bit envious of the media attention Tesla gets. [CleanTechnica]
¶ It’s been frigid in much of the US this week, and in New England for weeks on end. But nationally, the country has been going through a surprisingly warm winter. According to the National Climatic Data Center, the December 2014 to January 2015 period has been the sixth warmest on record in the contiguous US. [Huffington Post]
World:
¶ Much has been made of the competition between the United States and China for the title of world’s leading wind energy country, with the former the leading generator and the latter the leading installer. However, according to GlobalData analyst Pranav Srivastava, both titles are to be China’s as soon as 2016. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Vestas has entered into a deal with OX2 to supply 10 turbines for the 33 MW Maevaara 2 wind power plant in northern Sweden. Under the contract, Vestas will supply, install and commission the V126, 3.3 MW turbines with de-icing system. The project is the second in Sweden to feature the V126 3.3 MW. [Greentech Lead]
¶ New statistics released by the UK’s Department of Energy and Climate Change has revealed that close to 22,000 households have received support under the Renewable Heat Incentive scheme, a program of grants to support domestic low-carbon heating installations. [Cogeneration & On-Site Power Production Magazine]
US:
¶ The US Navy Task Force Energy is now drawing our attention to an op-ed by a former Navy commander outlining the risks of continued oil dependency. Like another recent piece, it pulls no punches, drawing attention to the thousands of American deaths attributed to petroleum transportation in Iraq and Afghanistan. [CleanTechnica]
¶ NextEra Energy is planning to build Hawaii’s largest wind farm on the southern coast of Maui. Before the construction of the 120-MW project, NextEra will complete the acquisition of Hawaiian Electric for $4.3 billion. In addition, the wind project will also be owned and operated by NextEra Energy. [Greentech Lead]
¶ Maine’s reshaped Public Utilities Commission wants to reconsider two proposed wind projects it approved two months ago, a move critics say would damage the integrity of the regulatory process and scare off future renewable-energy investors. The commission will decide on reassessment on Wednesday. [Nashua Telegraph]
¶ More than a dozen, mostly coal-dependent, states are already raising hell about the EPA’s Clean Power Plan. The latest battle is currently playing out in Virginia, where a state representative with ties to the coal industry wants to make it more difficult for the state’s Department of Environmental Quality to comply. [Grist]
¶ Pittsfield officials have started negotiating with Ameresco a long-term solar lease and power/net metering purchase agreement. The global alternative energy company has offered to install a solar array of up to 2.9 MW of electric generating capacity that provide more than 3.86 million kWh annually. [Berkshire Eagle]
¶ A bipartisan group of almost three dozen Illinois lawmakers yesterday proposed measures that would expand the state’s energy efficiency and renewable energy requirements and establish a carbon market to help the state comply with US EPA’s Clean Power Plan to limit GHG emissions. [Environment & Energy Publishing]
¶ Two Minnesota legislators have penned energy bills this session that would lift the state’s moratorium on Xcel Energy building another reactor at the Monticello nuclear plant. Both bills are site-specific to Monticello for the construction of a single, new nuclear-powered electric generating unit on the current plant site. [Monticello Times]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 20, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ Nuclear power plants increasingly face a new enemy: the jellyfish. Screens prevent aquatic life and debris from being drawn into the power plants’ cooling systems, but more and more often, they get blocked by large volumes of jellyfish or other aquatic life, forcing reactors to shut down. Climate change is a suspected cause. [Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists]
¶ No matter how fast the cost of oil drops, it just can’t keep up with the pace of improvements in electric vehicle batteries. In the latest development, a team of researchers at the University of California, Riverside, has come up with a paper-like material that could bring in a new generation of high-range batteries. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Pumped storage has been around a long time, much longer than renewables’ intermittent nature required it. In July 1930, the magazine Popular Science ran an article announcing start of operations at the first US “ten-mile storage battery,” or pumped-hydro energy storage plant, in Connecticut. [Scientific American]
World:
¶ Private sector developers in India’s rapidly growing renewable energy will be happy to have the backing of the country’s largest bank as they get ready for competitive bidding. The State Bank of India has committed to provide $12.5 billion in debt funding to renewable energy projects over the next few years. [CleanTechnica]
¶ GTM Research has released some key findings pertaining to the PV inverter industry. One is that global shipments could reach 50.6 GW in 2015. Reaching this amount means an increase of about 30% over the previous year. The global market for inverters will increase to about $7.1 billion, despite falling prices. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In Australia, Origin Energy warned that major electric retailers were likely to choose paying a penalty price, the equivalent of a fine, rather than contracting to new renewable energy projects, now that it is apparent that the renewable energy target would not be cut as much as the power companies had wanted. [RenewEconomy]
US:
¶ Citigroup Inc said it would set aside $100 billion to fund environmental projects over the next decade, doubling the amount it had earmarked for such projects in 2007. Citigroup said it would fund projects related to renewable energy, greenhouse gas reductions and sustainable transportation. [eco-business.com]
¶ A bill before the Illinois legislature creates new standards for the state’s utilities to use efficiency measures to reduce electricity demand 20% by 2025. It also sets a higher figure for renewable energy purchased by updating the state’s regulation for the production of energy from renewables, such as wind and solar. [Northwest Herald]
¶ Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack has announced that rural agricultural producers and small business owners can now apply for resources to purchase and install renewable energy systems or make energy efficiency improvements. The resources announced today are made possible by the 2014 Farm Bill. [Imperial Valley News]
¶ The second study in a few days has been released that finds that implementing the EPA’s Clean Power Plan will not negatively affect grid reliability. The report from Analysis Group addresses the impact of ongoing changes in the energy industry for stakeholders and offers recommendations to ensure reliability. [Domestic Fuel]
¶ Environmental Working Group Executive Director Heather White said today that Monday’s West Virginia oil spill and explosion, following derailment of a train load of shale oil, shows that it’s absolutely critical for the US to reduce its dependence on oil and base our future economy on clean energy. [Environmental Working Group]
¶ BlackRock Inc closed its acquisition of half of the 200-MW Hereford project in Deaf Smith County and agreed to buy the stakes in the 200-MW Longhorn and 194-MW Spinning Spur 3 wind farms after they’re completed later this year, the New York-based firm said Thursday in an e-mailed statement. [Bloomberg]
¶ The House Energy and Power Subcommittee heard testimony from Secretary Moniz on the DOE FY 2016 budget request, which outlined over $1 billion in renewable energy program funding increases but a decrease to fossil energy research and development. (The decrease for fossil fuels, however, is tiny.) [Breaking Energy]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 19, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ Imergy Power Systems announced a new, mega-sized version of their vanadium flow battery technology. The EPS250 series will deliver up to 250 kW of power with a 1 MWh capacity. The company claims it can deliver power for a levelized cost as low as $300 per kWh, making it competitive with lithium-ion. [ExtremeTech]
World:
¶ Turkey is now aiming to get at least 30% of its electricity requirements via renewable energy sources by the year 2023, based on figures put forward in the country’s National Renewable Energy Action Plan. Of this target, the country is reportedly aiming for at least 5 GW worth to be via solar PV projects. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The UAE has inaugurated a solar photovoltaic micro grid project to bring clean energy to some of Fiji’s outer islands. Built by Masdar, Abu Dhabi’s renewable energy company, the clean energy project is the third financed by the UAE’s $50 million Pacific Partnership Fund, through the Abu Dhabi Fund for Development. [Trade Arabia]
¶ Egypt is looking to add 4.3 GW of solar capacity as it targets a total boost of 8-GW in the next 10 years. The government said the extra power is needed to meet the needs of the nation’s expanding economy and it expects to start signing deals for PV projects at the Egypt Economic Development Conference in March. [reNews]
¶ ITM Power PLC on Wednesday said it has successfully delivered the power-to-gas PEM electrolyser system it sold to German power company RWE Deutschland AG within ten weeks of receiving the order. The system is the third rapid-response power-to-gas energy storage system ITM installed in Germany. [London South East]
¶ A new hydroelectric dam, set to be built on the River Allt Coire Chaorach, near Crianlarich, is set to be yet another instalment that will help push Scotland to the 100% renewable energy mark by 2020. The £8.5 million investment is set to generate up to eight GWh of electricity per year, also creating jobs and growth. [Click Green]
¶ Japan has relied heavily on fossil fuels since shutdown of the country’s nuclear fleet following the Fukushima Disaster. In 2013, more than 86% of Japan’s generation mix was composed of fossil fuels. With no nuclear plants online since 2013, the Japanese government anticipates starting a few up in 2015. [PennEnergy]
¶ The UK’s Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs was informed by the CAP Direct Payments Team that solar farms do not have a “serious” impact on the UK’s agricultural output. This information came ahead of its controversial decision to remove CAP payments for solar farms. [Greentech Media]
¶ Jordan’s Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources is collaborating with the Ministry of Islamic Affairs to implement plans to power all of the country’s mosques with solar energy by the end of 2015. Mosques currently pay as much as $1,400 a month for the air-conditioning and lighting. [Global Construction Review]
US:
¶ An NRG Energy subsidiary, NRG Renew, will join Kaiser Permanente, a major US health provider serving over 9 million people, in creating one of the top three on-site commercial solar portfolios among all US companies. The California project will also be one of the world’s largest vehicle-parking solar projects. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Last week, Rolling Stone published a blockbuster climate change article complete with the incendiary title, “The Pentagon & Climate Change: How Deniers Put National Security at Risk.” Now, the US Navy has posted a response with a forceful declaration of support for the Rolling Stone article. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Origin Energy provided further details of its impending major push into the domestic solar market. It expects rooftop solar to grow five-fold over the next 15 years, with battery storage coming also. It will install and maintain rooftop solar systems, and charge the homeowner a fee to use the solar electricity. [RenewEconomy]
¶ SunEdison Inc, the world’s largest renewable energy development company, announced the successful start of operation of the Regulus solar facility in Kern County, California. The 81.6 MW(DC) facility expected to provide almost $184 million in revenue to local businesses, governments and households. [SCVNEWS.com]
¶ PSEG Solar Source joined with El Paso Electric and juwi solar to formally dedicate the PSEG El Paso Solar Center. The 13-MW facility is El Paso’s largest, producing enough renewable energy to power more than 3,800 homes. PSEG Solar Source currently has 10 facilities in operation, totaling 109.7 MW. [PennEnergy]
¶ Green Mountain Power announced that for a third year, thanks to power generation at its Kingdom Community Wind Farm, five Northeast Kingdom Towns will receive Good Neighbor Fund payments. This year, GMP will distribute more than $188,000, an increase of $62,000 over last year. [vtdigger.org]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 18, 2015
World:
¶ Australian firm Carnegie Wave Energy Ltd announced it has officially put on stream its Perth wave power station at Garden Island. The plant has three 240-kW CETO 5 wave energy devices. It is the world’s first multiple wave unit power station. Its output is going to the Western Australia grid. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ US carmaker General Motors said on Tuesday it has signed a deal with Enel Green Power to purchase 34 MW of wind power for its production facilities in Mexico. The power purchase agreement is tied to 17 wind turbines the Italian company will be erecting in Palo Alto, starting in the second quarter of 2015. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ The first renewable energy tender issued by Jordan had encouraging results, with a total of 200 MW awarded to project developers, including a 52.5-MW solar PV project. The tender is the first among several that the government plans to conduct to set up 1.8 GW renewable energy capacity by 2020. [CleanTechnica]
¶ EDF Energies Nouvelles has confirmed that it will use 68 Vestas 3.3-MW turbines at its 224.4-MW Nicolas-Riou wind farm in Quebec. The company got a 25-year power purchase agreement with Hydro-Quebec last year following a competition tender. The plant is expected to be commissioned by mid-2017. [reNews]
¶ The three-day ‘First Renewable Energy Global Investors Meet and Expo (Re-Invest)’ concluded in India on Tuesday with commitments of 266,000 MW of renewable power, including 10,000 MW from state-run NTPC. This makes it the “take off” conference towards revolutionising India’s energy sector. [Web India]
¶ As an island nation, Japan controls large swaths of ocean territory, about the sixth-greatest expanse of any country in the world. So it makes sense for Japan to look to the seas for renewable energy. The government is teaming up with two major industrial companies to start field testing marine power generation. [Wall Street Journal]
¶ Canadian Solar has secured six solar power projects worth 46 MW in the United Kingdom. They will together generate around 50,183 kWh of electricity annually. Four projects, totaling 40.5 MW, are under construction and should be connected to the grid in March, with the others following in the second quarter. [Greentech Lead]
¶ Taking a cue from Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision, Union Minister Piyush Goyal today said efforts will work to create a federation of 50 solar power-rich nations and also make India the world’s renewable energy capital. They plan to work with the World Economic Forum in the near future. [Economic Times]
¶ Mainstream Renewable Power announced the launch of a pan-African renewable energy generation platform, Lekela Power, which it has formed along with Actis, a global pan-emerging market private equity firm. Lekela Power will provide between 700 and 900 MW of wind and solar power in Africa by 2018. [Your Industry News]
¶ Siemens announced it has secured a contract in South Africa with an order for 157 wind turbines for three projects in the South Africa province of Northern Cape. The 2.3-MW machines of the Siemens G2 platform will be installed at the wind power plants Khobab, Loeriesfontein 2 and Noupoort. [Windtech International]
US:
¶ Fires continued to burn for hours Tuesday after a train carrying 109 tankers of crude oil derailed in a snowstorm alongside a West Virginia creek, threatening the nearby water supply. Cars carrying volatile Bakken crude from North Dakota’s shale fields had left the tracks Monday afternoon, and 19 caught fire. [AOL]
¶ Duke Energy, which already owns or purchases 600 MW of solar capacity in North Carolina, announced that it is seeking to acquire up to an additional 50 MW. Duke has solar and wind facilities in 12 states, and expects to increase its solar generating capacity to 110 MW over the next six years in South Carolina. [Politic365]
¶ Donald Moul, vice president of commodity operations for FirstEnergy Solutions, says distortions in the energy market are hurting FirstEnergy’s fleet of nuclear reactors, making it hard to compete. He places the blame on policies that have eaten away at the value of its coal and nuclear fleet. [Pittsburgh Post Gazette]
¶ In Vermont, after three weeks of deliberation, the House Natural Resources and Energy Committee voted 10-1 to pass H.40, a bill requiring utilities to sell renewable power. According to the bill, 55% of a utility’s electricity must come from renewables such as wind, solar or hydro power by 2017, and 75% by 2032. [vtdigger.org]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 17, 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ A number of studies investigating the effect of wind turbines on birds have found that the actual impact wind turbines have on avians is relatively low. However, according to this new research, published in the European Journal of Wildlife Research, wind turbines’ effects on bats cannot be ignored. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Israeli alternative energy company Brenmiller Energy has solved one of the biggest issues with solar technology: how to generate electricity when the sun sets. The company says it will build a 10-MW solar facility that will generate electricity 20 hours per day through a proprietary energy storage technology. [Inhabitat]
World:
¶ In Geneva, Switzerland just three weeks after the US Senate’s 98-1 vote that climate change is not a hoax, the first round of the 2015 United Nations talks among 194 nations produced the first-ever universally agreed negotiating text on how to limit global warming to 2°C (3.6°F) above preindustrial temperatures. [CleanTechnica]
¶ If you hate that persistent smell of diesel fumes and you live in France, you’ll probably be happy to learn that the government has begun an aggressive initiative to get older, heavily polluting diesel cars off the road, by offering owners up to €10,000 to switch to a plug-in hybrid electric or 100% electric car. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The Philippines is one of the world’s leading producers of geothermal energy. Located atop the Pacific Ocean’s so-called Ring of Fire, the country has used volcanic heat to produce electricity for decades. Now there is a new project underway to use this renewable resource to power an entire island. [Voice of America]
¶ Indian Prime Minister Modi’s 100 GW solar energy goal by 2022 could create as many as one million jobs, says the Natural Resources Defense Council and the Council on Energy, Environment and Water. Additionally, a proposed target of 60 GW of wind energy could generate another 180,000 jobs in the country. [Energy Matters]
¶ Romania installed 363 MW of new solar PV in 2014, according to the country’s transmission company and electricity system operator. Wind power systems added 346 MW of new capacity in 2014. Cumulative capacities for solar PV and wind technologies stand now at 1223 MW and 2953 MW respectively. [pv magazine]
¶ The UK Green Investment Bank and the Strathclyde Pension Fund are to plow £60 million into community-scale renewable energy projects through Albion Community Power. ACP builds, controls and operates community-scale schemes and has identified a project pipeline in which it will invest capital for the duo. [reNews]
¶ US power companies struggling with the escalating costs of building nuclear plants are closely watching similar efforts with similar problems in China. The first plants using Westinghouse Electric Co’s AP1000 reactor design are having problems there, and US executives and safety regulators are learning what they can. [PennEnergy]
US:
¶ The sun is shining on solar power in Illinois. A new report ranks the state 12th nationally for the number of people employed in the solar industry, up from 20th in 2013. According to The Solar Foundation, 1,700 solar jobs were added last year, bringing the total to 3,800 in Illinois, up over 80% in one year. [Public News Service]
¶ To store power from Washington State solar and wind generators, the Klickitat PUD has begun applying for a license from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to pursue a pumped storage project, which will cost an estimated $2.5 billion. When completed, the project would have a capacity of 1200 MW. [Yakima Herald-Republic]
¶ Solar power brought 3,500 new jobs to Nevada in 2014, a 146% increase over 2013 that pushed the state to number 1 in the nation in solar jobs per capita, according to a report released Thursday by the Solar Foundation. It ranked Nevada seventh nationally with 5,900 total jobs in the solar industry. [Las Vegas Review-Journal]
¶ The cities of San Mateo County, California would have the option of banding together to sell cleaner energy to their ratepayers under a community-choice aggregation plan advocated by two county supervisors. The program could put power costs from renewable sources such as wind and solar below utility rates. [San Francisco Examiner]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 16, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “Neil Sheehan: Decommissioning Vermont Yankee” We have seen the end of an era for Vermont Yankee’s workforce and for the surrounding community as power production halted. But now another phase in the facility’s life will begin as the first steps in what will be a lengthy decommissioning process get under way. [vtdigger.org]
World:
¶ Nippon Paper Industries and Mitsubishi have started operation of a 21-MW solar power plant in Japan. The plant is located in Komatsushima-shi, Tokushima Prefecture, which is claimed to have the country’s highest annual sunshine hours. It is Nippon Paper’s second solar project. [Clean Technology Business Review]
¶ Some of the world’s most environmentally efficient and profitable green energy technologies are being specifically tailored to the needs of the beef, poultry, pork, rendering, and stock feed industries. The high-temperature thermophilic anaerobic digestion technologies typically operate at 55° C. [Impeller.net]
¶ Chinese and Indian Solar Energy industry recently met under the aegis of FICCI for a business roundtable to explore partnerships between the companies of both the countries on the eve of the upcoming RE-INVEST. The Chinese delegation was led by the China Photovoltaic Industry Association. [Moneycontrol.com]
¶ China raised its total grid-connected solar power capacity to 28.05 GW in 2014, up 60% on the year, and aims to raise the total by more than half this year. The figure is equivalent to about 2.1% of China’s total power capacity of 1,360 GW at end 2014, while wind power is about 7% of the total. [Business Recorder]
¶ India is all set to have world’s largest solar power plant in Rewa district of Madhya Pradesh. It will be completed next year on Independence Day. The 750 MW will be constructed and operated as a joint venture of the state government and Solar Energy Corporation of India. It will occupy 1,500 hectares of land. [indiatvnews.com]
¶ The Durham York Energy Centre in Clarington, Ontario began burning its first haul of curbside garbage as part of a month-long testing phase before the facility opens for good. The facility will generate about 17.5 MW of renewable energy, but has faced opposition from locals. The final price tag is $286.56 million. [Toronto Star]
¶ South Korea’s LG Chem Inc says it will supply energy storage systems for four solar plants under construction in Japan in a deal worth over $272.7 million. The battery maker said it won a contract to supply storage systems, each with a capacity of 31 MW, to the Green Power Development Corporation of Japan. [The Korea Bizwire]
US:
¶ California’s Senate President Pro Tem Kevin de León proposed legislation last week to increase the amount of electricity California derives from renewable sources, excluding from what counts as “renewable” any power generated from burning household trash, with the exception of one specific plant. [Sacramento Bee]
¶ SunEdison completed a 677-kW ground-mount solar PV system, providing energy for the AT&T materials distribution facility in Lancaster, Texas. It is not the first plant SunEdison worked on with AT&T. Their solar power arrays have generated over 8.6 GWh of power, cutting CO2 emissions by 13 million pounds. [AZoCleantech]
¶ Imergy Power Systems and Growing Energy Labs Inc are collaborating on a microgrid project for Chabot-Las Positas Community College District in Livermore, California. The project will add renewable energy sources, reduce peak power, and allow the district to be more energy independent.[CleanTechnica]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 15, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “Arthur Berman: Why Today’s Shale Era Is The Retirement Party For Oil Production” – Podcast guest Arthur Berman, a geological consultant with 34 years of experience in petroleum exploration and production, sees the recent US oil production boost from shale drilling as short-lived and somewhat desperate. [peakprosperity.com]
¶ “Did Obama Just Waste $907 Million Trying to Save Nuclear Power?” – The power of the atom has started to give way to cheaper energy sources with more favorable public opinion. But President Obama’s proposed budget for 2016 set aside $907 million for the US DOE to invest in nuclear energy technologies. [Motley Fool]
World:
¶ A contract for two offshore wind parks in Japan has been won by Marubeni Corporation. The site is off the coast of Akita Prefecture, in the northern part of Honshu, Japan’s largest island. The turbines will be 5 MW. One site will have 13, and the other will have 16. Both parks should be operating in 2021. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Indian prime minister Modi inaugurated the first Renewable Energy Global Investors Meet. On the first day of the three-day event, 293 companies committed to set up plants to generate 266 GW of renewable energy in 5 years, while banking major SBI said it will finance 15,000 MW renewable energy. [India.com]
¶ Mr Piyush Goyal, Union Minister for Power, Coal and Renewable Energy, told a group of industry executives, “India will be power surplus in 2019, and we are taking all necessary steps. From the current one trillion units of energy generation, we can double the power generation and become power surplus.” [SteelGuru]
¶ A report due out in Scotland this month aims to identify the ways to jump-start the stalled maritime wind sector, by enabling price cuts of a third, to £100 per MW/h. Power from less productive onshore wind farms costs £85 per MW/h average. This means offshore wind can be competitive with onshore. [Herald Scotland]
¶ Renewable energy firm Welspun Renewables today said it will set up 11 GW solar and wind projects across India. The 11 GW capacity will be developed as 8,660 MW of solar and 2,341 MW of wind power projects, the company said in a statement. It will commission over 1 GW of solar and wind this year. [Business Standard]
¶ US-based SunEdison and First Solar committed to build more than 20,000 MW of renewable capacity in India, boosting India’s renewable energy targets. SunEdison will build 15,200 MW of solar and wind power capacity by 2022, while First Solar made a commitment to develop 5,000 MW of solar by 2019. [Times of India]
US:
¶ The White House has backed solar and wind power projects and touted the benefits of the country’s surging production of natural gas, which burns about 50% cleaner than coal, still the largest source of electricity in the US. It had backed clean coal, but now, the US DOE is beginning to withdraw that support. [Bloomberg]
¶ One thing energy companies leave out of their talking points for expanding pipelines in New England is an effort to deliver natural gas to Canada for export. Developers are already moving to send natural gas through Massachusetts to Nova Scotia, where it would be converted to liquefied natural gas and exported. [ecoRI news]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, photovoltaic, renewable power, solar power, wind power
February 14, 2015
Opinion:
¶ “What Snow and the US Army Tell Us About Coal vs Renewable Energy” Coal vs renewable energy is central to two current debates about energy in official arenas. Interestingly, one very important supporter of renewable energy in the debate is the US Army. [The Equation: Blog of the Union of Concerned Scientists]
Science and Technology:
¶ As bad as recent droughts in California, the Southwest and the Midwest have been, scientists say far worse “megadroughts” are coming, lasting for decades. Unprecedented drought conditions, the worst in more than 1,000 years, are likely to come to the Southwest and Central Plains after 2050. [Huffington Post]
World:
¶ A 42-MW geothermal power station is being planned by Electric Power Development Co for a site in northern Japan. It should be operational by May 2019. Financing for about $221 million will come from a number of banks and 80% is guaranteed by Japan Oil, Gas & Metals National Corporation. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Leaders of the UK’s three main political parties pledged a cross-party fight against climate change. David Cameron of the Conservatives, Ed Miliband of Labour and Nick Clegg of the Liberal Democrats agreed to “seek a fair, strong, legally-binding global climate deal which limits temperature rises to below two degrees celsius”. [reNews]
¶ Pattern Energy has entered into a 25-year power purchase agreement with Hydro-Québec for the 147-MW Mont Sainte-Marguerite wind project. The facility will have 46 of Siemens 3.2 MW wind turbines. Construction is expected to begin in the third quarter of 2016, and commercial operation in December 2017. [Greentech Lead]
¶ French and Spanish power grid operators have completed a long-awaited power line across the Pyrenees that will allow export of excess Spanish renewable energy and ease one of the worst network bottlenecks in Europe. They will inaugurate a 1,400-MW cable that will double French-Spanish interconnection capacity. [Reuters]
¶ Interest in building a 100-MW plus solar thermal plant in Western Australia’s Goldfields region has been revived, as more miners turn their interest to solar and other renewables as a means to deflect volatile diesel costs. Two solar developers are considering plans for large solar thermal plant near Kalgoorlie. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Ontario has issued the all clear to NextEra Energy Canada’s 102-MW Goshen wind farm, the seventh project in an eight-part 615-MW feed-in tariff portfolio in the province. The municipality of Bluewater, a host community, and a local resident failed to prove the wind farm would cause serious harm to human health. [reNews]
US:
¶ The American Wind Energy Association released a new report, “Wind energy helps build a more reliable and balanced electricity portfolio,” answering 15 frequently asked questions, basing answers upon lessons learned from grid operators’ experiences reliably integrating wind energy into the existing grid. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Procter & Gamble and Constellation Energy announced this week that they are moving ahead with the development of a biomass-fueled plant that will generate up to 50 MW and provide power to P&G’s Albany plant, one of its largest US facilities. The plant is expected to begin commercial operation in June 2017. [The Albany Herald]
¶ Inverter load rejection overvoltage tests completed by the US DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory as part of a cooperative research agreement with SolarCity have proven so successful that a testing partner, Hawaiian Electric Companies, has proposed to double its hosting capacity for solar energy. [Phys.Org]
¶ New York ratepayers will subsidize operation of the Ginna nuclear facility near Rochester, under terms of an agreement with the plant’s operators, Exelon. The Ginna Nuclear Generating Station will be allowed to charge customers above-market rates until 2018, because the plant has been losing money. [Capital New York]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »




























