Opinion:
¶ “Coal for water: crisis incoming”• The world’s rapidly dwindling freshwater resources could be further depleted if plans for hundreds of new coal power plants worldwide go ahead, threatening severe drought and competition, according to a new Greenpeace International report. [The Phuket News]
¶ “Mikhail Gorbachev: 30 years after Chernobyl, time to phase out nuclear power” • At 85, committed environmentalist Mikhail Gorbachev still campaigns to bring the failed nuclear experiment to an end, while encouraging a clean, efficient and renewable global energy economy. [The Ecologist]
¶ “Digitalization: Where are the German digital utilities?” • In Germany, a lot has been written about two energy megatrends of our time, liberalization of energy markets and decentralization of the energy landscape. What we think has been neglected is a third megatrend: digitalization. [EurActiv]
World:
¶ IKEA UK unveiled Solar Shops, its in-store offering to sell residential solar installations, partnering with Solarcentury. IKEA also released the results of its own survey which showed 33% of all UK homeowners would like to invest in solar panels, largely to cut their electricity bills. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Venezuela’s government has imposed a two-day working week for public sector workers as a temporary measure to help it overcome a serious energy crisis. Venezuela is in the middle of a major drought, which has dramatically reduced water levels at its main hydroelectric dam. [BBC]

Electricity Minister Luis Motta looks at the massive Guri Dam, virtually dry because of the drought. Reuters photo.
¶ Leclanché has secured a $28.9 million order for a 53 MWh battery system to be installed in Ontario. The company was founded in 1909, and began making energy storage modules for renewables in 2011. In 1987, it produced lead-acid batteries. Today, it focuses on lithium batteries. [CleanTechnica]
¶ For the upcoming Australian election, Labor is proposing two emissions trading schemes, one for big industrial polluters and one other consumers, in a climate policy that trumps the Coalition’s ambition but minimizes the hit on household power bills. Details are yet to be determined. [The Guardian]

The 9KW capacity solar system on Montague island. Photo by Binarysequence. CC BY-SA 3.0 unported. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ According to China’s National Energy Administration, the first quarter of 2016 saw the country’s solar industry add 7.14 GW in capacity, bringing its total solar capacity to 50.3 GW. China’s solar capacity includes 43.29 GW of ground-mounted solar PVs, and 7.03 GW of distributed solar PVs. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Central banks might accomplish what anti-nuclear activists have not, forcing operators to decommission almost 150 nuclear plants now sitting in limbo across the globe. In the past, many operators waited to allow growth in the cleanup funds. But the funds have been shrinking. [Taipei Times]
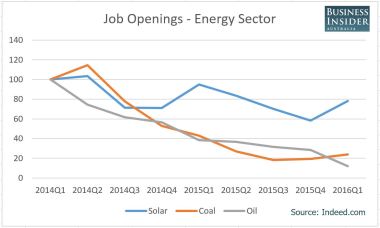
¶ Employment opportunities in Australia’s energy industry have collapsed in recent years. But while oil and coal jobs continue to decline, data from Indeed, the world’s largest jobs site, suggests solar is staging a massive comeback. Solar jobs are up 34% in the last quarter. [Business Insider Australia]
¶ Hokuriku Electric Power Co may be forced to decommission a reactor at its Shika nuclear power plant because a geological fault line beneath the building was assessed as active. A panel of five experts on active faults issued its report to the Nuclear Regulation Authority on April 27. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ When a sudden change in state policy seemed to block the solar ambitions of Minster, Ohio, the village wasn’t put off. Instead, it decided to look into battery storage. A 7-MW battery will allow the village to defer transmission and distribution costs, improve power quality, and shave peak demand. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The Senate passed a bipartisan amendment sponsored by Senators Jeff Merkley, D-Oregon, and Chuck Grassley, R-Iowa, that restores funding for wind energy research and development to $95.4 million, the same level as in FY16. The initial draft contained a $15.4 million cut. [KTVZ]
¶ An effort to bring renewable energy to Western Alaska has been recognized by the federal government. The Ocean Renewable Power Company was named the 2016 Outstanding Stewards of America’s Waters for its ability to bring hydropower to the Bristol Bay village of Igiugig. [KTOO]
¶ Some of the sunniest states in the country maintain policies that block rooftop-solar development, a report from the Center for Biological Diversity says. Ten states have over 35% of the potential in the contiguous United States, but less than 3% of the installed capacity. [Center for Biological Diversity]





April 28, 2016 at 4:18 pm
Reblogged this on nuclear-news.