Archive for March, 2016
March 31, 2016
Opinion:
¶ This chart shows the United States’ mind-blowing clean energy potential • The United States uses about 3.7 million GWh of electricity each year. The next time someone tries to make the argument that 100 percent renewable energy is out of reach for the U.S., show them this image: [Grist]

From the Environment America Research & Policy Center
¶ Wake up call for oil companies: electric vehicles will deflate oil demand • Major oil companies greatly underestimate the impact electric vehicles will have on their market. Trends currently underway in the auto industry are likely to have a substantial impact on oil demand. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Clear Skies From Wind Power • Over 17 million Americans have asthma. Every year it is responsible for more than 10 million doctor visits and 1.8 million trips to the emergency room. Health professionals tell us one of the biggest triggers for an asthma attack is air pollution. [Huffington Post]
World:
¶ David Cameron is to announce plans for the largest ever shipment of nuclear waste from the UK to the US. In return, the US will send a different type of used uranium to Europe, where it will be used medically. But Friends of the Earth said transporting nuclear waste across the ocean is too risky. [BBC]

The UK waste will come from the Dounreay facility in Caithness. Thinkstock
¶ Japan’s electricity market is going through a fundamental shake-up, with the introduction of greater competition for households and small businesses. Until now, regional utilities have monopolized supply. With the change, consumers can choose their electricity provider. [The Japan Times]
¶ Energy storage development in Ireland remains purposely technology-agnostic and this, together with the strong drivers behind storage in the country, is transforming the country into Europe’s energy storage lab, as highlighted a recent Grid and Storage workshop in London. [pv magazine]

The ninth regional Grid and Storage workshop shone a light on Ireland’s energy storage R&D. Pam Brophy/Wikipedia
¶ Cambodia can get 90% of its energy from wind, solar and biomass by 2050, the World Wildlife Federation found in a new report published yesterday. Renewable energy will soon be cheaper than fossil fuels, especially with their environmental damage and health costs. [The Phnom Penh Post]
¶ A new solar project in the Dominican Republic will be the largest of its kind in the Caribbean. The Monte Plata project, named for the capital city and province in which it is located, is a 33.4-MW PV array destined to churn out five times as much clean energy as the nation currently generates. [Inhabitat]

Image via Phanes Group
¶ Two solar power projects with a total installed capacity of 185 MW were commissioned in the Philippines. This includes the largest project in Southeast Asia, a 135 MW project now operational at Cadiz. Local media reports say the project’s total cost was about $200 million. [CleanTechnica]
US:
¶ Many have long speculated about fracking and its possible negative impact on drinking water. Recent research released today from Stanford scientists finds for the first time that fracking operations in Wyoming have had a clear impact on underground sources of drinking water. [CleanTechnica]

US EPA staff members sample a monitoring well for contaminants from hydraulic fracturing. (Photo: Dominic DiGiulio)
¶ Analysis of data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics and the DOE for Environmental Entrepreneurs found that over 2.5 million Americans work in the clean energy sector. Almost 1.9 million work on energy efficiency, 300,000 in the solar industry, and 77,000 with windpower. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The Virginia State Corporation Commission approved Dominion Virginia Power’s plan to build a 1,588 MW, natural gas-fired combined-cycle plant, rejecting assertions by independent power producers and environmentalists that the utility failed to fully explore cost-effective alternatives. [Platts]
¶ It might seem like a bad April Fool’s joke, but Plant Vogtle is no laughing matter to Georgia Power customers. They have already paid more than $1.4 billion for reactors that won’t be operational until 2020 or 2021. The first was supposed to be operational on April 1, 2016. [Creative Loafing Atlanta]

The first of two new reactors at Plant Vogtle were supposed to open April 1. (Georgia Power Company)
¶ HP is joining RE100, a worldwide initiative of big-name businesses committed to 100% renewables. RE100 works with companies like HP to help them transition to renewable energy sources and accelerate the shift of the global energy market to a low-carbon economy. [North American Windpower]
¶ SunEdison, the US-based solar power giant, is at “a substantial risk” of bankruptcy, ne of its own publicly listed subsidiaries says. The statement was made by one of SunEdison’s “yieldcos,” listed companies that hold renewable energy assets and have long-term power purchase deals with utilities. [GCR]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 30, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ The National Snow and Ice Data Center reported that the spread of Arctic sea ice set a new record low for the second straight year, stopping last week at 5.607 million square miles. That’s 5,000 square miles less than last year’s record low and 431,000 square miles less than the average. [CNN]

The consequences of climate change go
far beyond warming temperatures.
¶ MIT researchers demonstrated a calcium-metal-based liquid battery intended for grid-scale storage and a long cycle life. Calcium was blended with magnesium to make it usable. Use of earth-abundant materials and a scalable kind of construction are among the battery’s advantages. [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ There are renewed calls to re-examine Alberta’s deregulated power market after the announced closure of a coal-fired electrical generator. Maxim Power Corp announced the temporary shut down of the 44-year-old plant, saying it is losing money at current spot market prices. [Calgary Sun]

Power Plant northeast of Calgary. (Postmedia Network)
¶ The European Investment Bank agreed to provide £500 million for a major reinforcement of the electricity transmission network in the north of Scotland to improve connections between wind, wave and tidal renewable energy schemes and the national power network. [Your Industry News]
¶ Renewable energy developers won contracts to produce 1,720 MW of power in Mexico’s first-ever private auction. Seven wind and solar companies including Enel Green Power, SunPower Systems Mexico, and Recurrent Energy, won 15-year contracts for power beginning in 2018. [Energy Voice]
¶ Scotland’s Western Isles is preparing to run its own utility as part of a long-term plan to tap the islands’ renewable energy potential. Hebrides Energy will be a collaboration between Comhairle nan Eilean Siar and an unnamed UK energy supplier, together with representation from others. [reNews]

Fuel poverty is a major issue in islands off Scotland (Mi9)
¶ Japan’s Nuclear Regulation Authority gave TEPCO a go-ahead to freeze the soil around the reactors at the crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. The aim of the frozen soil wall is to block the flow of groundwater into the reactor buildings to prevent it from becoming contaminated. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ Wind energy reduces a variety of health-harming air pollutants, including smog-causing oxides of sulfur and nitrogen. This helps reduce rates respiratory diseases such as asthma. Electricity generated by wind in 2015 represented $7.3 billion in avoided health costs last year alone. [Green Energy Times]
¶ The Tennessee Valley Authority, in partnership with the Tennessee Valley Public Power Association, is awarding 16.7 MW of solar capacity to four local power companies who applied through the Distributed Solar Solutions pilot. The projects will generate power for over 1,300 homes. [Your Renewable News]
¶ A unique hybrid renewable energy project in Northern Nevada was celebrated by a host of dignitaries, including the Prime Minster of Italy. Enel Green Power combined 33.1 MW of geothermal capacity, 26.4 MW of PV, and 2 MW of solar thermal at a cost of $200 million. [Las Vegas Review-Journal]

Earthquakes in Oklahoma and Texas
¶ About 7.9 million people are now at risk from earthquakes scientists believe are caused by fracking, including certain regions in Oklahoma, Kansas, Colorado, New Mexico, Texas and Arkansas, the US Geological Survey said. The earthquakes don’t factor in building-code maps, but do create a hazards. [CNN]
¶ An anti-Clean Power Plan bill Colorado Senate Republicans insist has “nothing to do with climate change” prompted them to argue on the Senate floor that human-caused global warming is a myth. The bill would have the state inactive pending Supreme Court review. [The Colorado Independent]
¶ Aerojet Rocketdyne, a subsidiary of Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings, Arkansas Electric Cooperative Corporation, and Ouachita Electric Cooperative Corporation, will announce full commissioning of the 12-MW East Camden solar field, the largest solar project in Arkansas, on March 31, 2016. [EIN News]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 29, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ When a large generating plant shuts down, the grid’s frequency drops due to an imbalance between generation and load. DOE researchers are evaluating wind farms for providing frequency-responsive back-up currently supplied to the grid by conventional power plants. [Windpower Engineering]

NREL’s National Wind Technology Center is the nation’s
premier wind energy technology research facility.
World:
¶ Five years after the Fukushima Disaster in Japan resulted in three reactor meltdowns, the global nuclear industry is spending $47 billion on safety enhancements mandated after the accident revealed weaknesses in plant protection from earthquakes and flooding, according to a Platts review. [Platts]
¶ The top official in China’s northern province of Hebei, one of the country’s most polluted, has vowed to use the staging of the 2022 Winter Olympics to drive efforts to cut smog and promote clean energy. Skiing and snowboarding events will be held in the city of Zhangjiakou. [Voice of America]

Heavy haze on a severely polluted day in northern China. Reuters
¶ Chinese regulators said the windswept regions in northern China will suspend the approval of new wind projects in 2016. It is at least the fourth time in five years wind operators were ordered to slow down growth. The transmission system has to keep up with turbine installations. [InsideClimate News]
¶ During the upcoming summer, a public-private council set up in Fukushima will focus on developing market strategies for the wind and hydrogen segments. The scheme is one more step towards the fast reconstruction of the prefecture following the Fukushima nuclear disaster. [SeeNews Renewables]

Wind farm in Japan. Author: cotaro70s.
License: Creative Commons, Attribution-NoDerivs 2.0 Generic.
¶ Japan had been poised to get its nuclear plants up and running again after the response to the Fukushima Disaster shut them down. But a series of mishaps has raised doubts over the country’s ability to achieve a goal of supplying 20% to 22% of its energy needs with nuclear power by 2030. [IEEE Spectrum]
US:
¶ DTE Energy is working with the City of Detroit on “what could be one of the largest urban solar arrays in the U.S.” DTE confirmed reports that the company has a large solar energy array planned for 10 acres of a vacant 20-acre parcel on Detroit’s west side in the O’Shea neighborhood. [MLive.com]

Solar panels constructed by DTE Energy in Ann Arbor, Mich.
(Ryan Stanton | The Ann Arbor News)
¶ The Vermont Senate is due to consider legislation this week that proponents say will give municipalities a say over where renewable energy projects get built. To have that say, towns and regions would have to write energy development provisions into their regional and town plans. [vtdigger.org]
¶ Advanced Rail Energy Storage said its proposed commercial-scale gravity-based rail energy storage project has been granted a right-of-way lease by the Bureau of Land Management. The 50-MW project, on 106 acres of public land in Nevada, will help stabilize the electric grid. [AltEnergyMag]

Rail energy storage. ARES photo
¶ Rooftop solar panels could meet 74% of California’s electricity needs, and the country could get about 39% of its, according to a new study from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. In 2008, NREL estimated that the nation could get 21% of its power from solar. [The Desert Sun]
¶ Navajo utility and government officials in New Mexico will break ground on a large-scale solar project on April 23. The utility authority in December struck a two-year agreement with Tempe-based utility Salt River Project to build the 27.5-MW solar farm in Kayenta, Arizona. [Albuquerque Journal]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 28, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ A Sandia-led team, with support of the US DOE, has developed a way to make a magnetic material that could lead to lighter and smaller, cheaper and better-performing high-frequency transformers, helping adoption of more flexible energy storage systems and renewable energy. [Nanowerk]

Sandia National Laboratories researcher Todd Monson.
¶ Researchers from two Scottish universities are taking part in a project to boost the development of “meshed” offshore grids to link windfarms with the mainland. Aberdeen and Strathclyde are part of a four-year European initiative investigating high-voltage direct current technology. [The National]
¶ A research team from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel, environmentally friendly low-cost battery that overcomes many of the problems of lithium-ion batteries. It has both lower weight and lower fabrication costs. [AZoCleantech]

Schematic structure of the AGDIB
(Image by Professor TANG Yongbin)
World:
¶ In a bit of an unexpected move, the biggest heavy machinery manufacturing firm in China, the SANY group, announced that it will invest around $7.7 billion in various solar PV projects in the country over the next 5 years. A pilot project of 3.82 MW had already been tested. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Authorities in the Indian state of West Bengal were forced to suspend generation at the 2,300-MW plant because the canal carrying cooling water to it went dry. The township it was in lost water, residents had to be given bottled water to drink, and the whole area had electricity shortages. [BBC]

The canal connecting the Ganges to the power station dried up.
¶ In refugee camps and at military camps, the power supply is often a huge cost item. Three students from the University of Applied Sciences in Amsterdam have been looking into a potential solution: the use of end-of-life batteries from electric cars as a source of renewable energy. [Recycling News]
¶ A pipe stretching nearly 1.2 miles into the ground could deliver heating from the earth to the new Aberdeen Exhibition and Conference Centre and nearby homes, a report has found. A feasibility study revealed that a deep geothermal well would cost around £2.3 million to build. [Press and Journal]
¶ China is aiming to triple its solar PV generation capacity by 2020, bringing it up to 143 GW, its National Energy Administration says. The plan is to add between 15 GW and 20 GW of PV capacity a year, investing about $368 billion in types of grid infrastructure at the same time. [CleanTechnica]

Image by Aapo Haapanen (some rights reserved)
US:
¶ Power generators are resisting Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker’s plan to tap Canadian hydropower to meet the state’s energy needs. His plan, which hinges on lawmakers’ approval, calls on the utilities to import 1,200 MW to 2,400 MW of hydro-electricity. [Gloucester Daily Times]
¶ North Dakota is one of the top states in the Midwest for jobs in the clean-energy field, according to the Clean Jobs Midwest survey. It shows North Dakota has the highest percentage of clean-energy jobs, per capita, out of 12 Midwestern states, at just under 12,000. [Public News Service]

New numbers show North Dakota has the highest percentage of clean-energy jobs per capita in the Midwest. (iStockphoto)
¶ The advocacy group, Industrial Energy Consumers of America, sent a letter to ranking members of two US Senate Committees, urging them to extend the combined heat and power business energy investment tax credit, which is set to expire at year-end 2016. [Energy Manager Today]
¶ In early 2015 engineers on a brand-new submarine found that a pipe joint near the innermost chamber of its nuclear-powered engine showed signs of tampering. Defective parts, probably costing $10,000 or less, have kept the $2.7 billion Minnesota in an overhaul for two years. [NavyTimes.com]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 27, 2016
World:
¶ In India, Tata Power’s Mulshi solar plant shows how energy needs do not have to be met at the cost of the environment. Suitable plants will be grown immediately below the solar panels so that all the available land there can be utilized to its fullest, with its fertility maintained. [Daily News & Analysis]

The site of the Mulshi solar plant run by Tata Power
¶ A battery storage trial by an Australian network operator shows that the combined benefits of battery storage nearly match the costs of technology, and should exceed them with falling battery costs. The trial tested battery systems using five different types of demand management. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Morgan Stanley, which predicted a million Australian households will adopt battery storage over the next four years, says the broader Australian energy market, including incumbent coal-fired generators, the big networks and retailers, still underestimates coming market changes. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Investment in wind generation of electricity has propelled Mexico on to the list of the 10 countries that recorded the greatest spending on renewable sources of energy. That spending in Mexico in 2015 totaled $4 billion, representing a growth of 105% over the previous year. [Mexico News Daily]

Wind turbine blade en route to new Tamaulipas wind farm.
El Sol de Tampico
¶ Two large media companies, Sky and Bloomberg, have both pledged to go “100% renewable” as part of the RE100 initiative. Sky will source 100% renewable electricity by the year 2020 “where available;” and that Bloomberg will purchase only renewable electricity by the year 2025. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A mere two days after bombs in Brussels killed 31 people, a security officer who worked for a nuclear power plant was murdered and his pass stolen. A story in local newspaper Dernière Heure emphasized the security badge was de-activated shortly after the guard was found dead. [Slate Magazine]

Belgium’s Doel nuclear plant. Photo by LimoWreck.
CC BY-SW 3.0 unported. Wikimedia Commons.
US:
¶ The number of energy loans in danger of default is on course to extend above 50% this year at several major banks, including Wells Fargo & Co and Comerica Inc, according to bankers and others in the industry. Oil prices remaining at around $40 a barrel would be bad news for the banks. [morningstar.com]
¶ According to Solar Power Rocks, a website to help homeowners understand the ins and outs of investment returns on local solar panel installations, half of the top ten states where switching over to solar power makes the most economic sense are in the Northeast. [Republican & Herald]
¶ Wisconsin’s renewable energy landscape has been pretty much frozen for five years, especially for wind farms. While neighboring states have been blossoming with wind development, Wisconsin has become almost a “black hole” of development. And it shows in lost jobs. [Milwaukee Journal Sentinel]

Turbines on a We Energies wind farm near Johnsburg in northeastern Fond du Lac County in 2014. Credit: Mark Hoffman
¶ Natural gas may have become the dominant source nationally for electrical power generation in 2016, but coal remains king in Nebraska. Nevertheless, more renewable energy sources have begun to creep into Nebraska’s energy portfolio with investments in windpower. [Lincoln Journal Star]
¶ The US DOE released the agency’s first annual analysis of how changes in America’s energy profile are affecting national employment in multiple energy sectors. The inaugural US Energy and Employment Report provides a broad view of the energy employment landscape. [Imperial Valley News]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 26, 2016
Opinion:
¶ Has US Nuclear Power’s Death Spiral Begun? • Crashing prices for natural gas and accelerating market penetration of renewable energy have both contributed to dramatic drops in wholesale power price levels, leaving nuclear power with few options other than surrender. [IEEE Spectrum]

The Quad Cities nuclear plant is getting help from
a regional grid operator. Photo: Kevin Schmidt/Alamy
¶ US Chamber of Commerce Forecasts No Growth in Renewable Energy. We Disagree. • The Chamber wants to belittle both the supply and demand for renewable energy, when Main Street and Fortune 500 companies continue to make investments greatly outpacing expectations. [The Equation]
World:
¶ Investment in renewable energy hit a record $286 billion (€256 billion) in 2015, a UN report says. For the first time, over half came from developing countries. New investment in cleaner energy has exceeded $2.3 trillion since 2004, when investments totaled less than $50 billion. [Daily Sabah]

Growth of clean energy in 2015 was dominated by
solar PVs and wind. (AP Photo/Arnulfo Franco, FILE)
¶ The Indian government has a new goal. Come 2030, and every car user in India could have an electric vehicle. Under the plan, the vehicles will be given without an upfront payment and will be paid for by users over a period of time from the savings made on fuel, according to the energy minister. [Livemint]
¶ At the end of 2014, Europe had 17,240 biogas plants, with a total installed capacity of 8,293 MW. The electricity they produced stood at 63.3 TWh, enough for 14.6 million European households. The numbers are growing fast in such places as the UK, where they doubled in just one year. [Biomass Magazine]

Harvest Power’s energy garden in Orlando. Photo by Harvest Power.
¶ SSE, the UK’s second largest utility, could be forced to cut its dividend, experts warned. A currently healthy showing from SSE’s generation business results from a wet and windy winter boosting its renewables output, but low wholesale electricity prices of £35/MWh are straining it. [Telegraph.co.uk]
¶ Siemens was awarded an order to supply a link between the Dutch and Danish grids. The order covers two 700-MW converter stations for a DC voltage of ±320 kV. One will be at Eemhaven in Holland, the other in Endrup in Denmark. The cable will be 325 km long. [Transmission and Distribution World]

Siemens Holland photo.
¶ After terrorist attacks in Brussels, authorities have stepped up security at nuclear sites. Safety officials said there was nothing to suggest a specific threat against the country’s reactors or plants, but videos suggest a connection between terrorists and a senior nuclear official. [The Guardian]
US:
¶ The US DOE will participate in the Clean Line transmission project, to bring 4,000 MW of low-cost electricity from wind farms in Oklahoma and the Texas panhandle to the Southeast. The project will bring enough affordable wind power for more than 1.5 million homes. [EcoWatch]

The US DOE will participate in the Clean Line transmission project.
¶ Five years ago, Texas’ power grid operator offered up data on projected power demand and supply that convinced companies to build new power plants. Now those plants barely turn a profit. Dallas-based Panda Power Funds says the data was “seriously flawed or rigged” and is suing. [Houston Chronicle]
¶ NaturEner USA and San Diego Gas & Electric reached a settlement of a lawsuit involving Montana’s largest wind farm and protections for raptors. NaturEner USA had earlier shifted locations of some of the turbines due to concerns of Montana Audubon and the US Fish and Wildlife Service. [Great Falls Tribune]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 25, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ A colorful goop, developed at the University of Toronto, could be a real-life blockbuster. When spread on a strip of metal and subjected to an electric current, it can break apart molecules of water at about three times the rate and far more cheaply than any substance currently available. [The Globe and Mail]

The University of Toronto has developed a catalyst that could improve energy storage. (Marit Mitchell/University of Toronto)
World:
¶ India’s massive solar power capacity addition target is expected to revolutionize the Indian jobs market. According to a report by the Natural Resources and Defense Council, India may end up creating over a million new jobs in its endeavor to have 100 GW of solar capacity by March 2022. [Sustainovate]
¶ Chinese media reported that the country’s National Energy Administration ordered 13 provincial governments to suspend approvals of new coal-fired power plant projects until the end of 2017. Another group of 15 provinces was ordered to delay new construction of projects already approved. [EcoWatch]

China is stopping unnecessary new coal plants.
Photo credit: Greenpeace
¶ It is over 3 months since the Basslink interconnector failed, just as hydropower was reduced to nearly nothing by drought. Tasmania has huge wind and solar power resources, which may be key to solving its energy security woes in the long term, but the immediate situation is pressing. [Energy Matters]
¶ The UK won’t struggle to keep the lights on if EDF decides not to proceed with its £18 billion ($25 billion) plan to build a new nuclear plant at Hinkley Point, Energy Secretary Amber Rudd said. Britain has nine years to fill any gap in generation created by the loss of a 3.2-GW project. [Bloomberg]
¶ A new UN report says 2015 set a slew of new records for global investment in clean energy, with the bulk of investment in the developing world. But the report also contained a grim punchline when it came to the impact this is having on the broader climate change problem. [Washington Post]
¶ A nuclear reactor that began operating almost 40 years ago will be retired at the Ikata plant in Ehime Prefecture, western Japan, for economic reasons, Shikoku Electric Power Co announced. It would cost about ¥200 billion ($1.77 billion) in upgrades for it to pass strict new safety standards. [Asahi Shimbun]
US:
¶ A report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory is the deepest dive on solar’s potential since 2008. It examines the country’s potential for rooftop solar power. According to the report, we could get bout 39% of the country’s electricity consumption, at current levels. [Grist]

Los Angeles
¶ The mayor of Seattle announced a plan to cut city vehicle fleet greenhouse-gas emissions by 50% by the year 2025 through the use of electric vehicles and biodiesel. Seattle gets most of its electricity from hydroelectric sources, so to cut greenhouse gas emissions, it must do so in transportation. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Omaha-based Tenaska sold or managed 10% of US natural gas in 2014. Now low gas prices have pushed down profits and its CEO believes pairing renewable energy with conventional sources like natural gas “is where the future is” for Tenaska and others in the energy industry. [Omaha World-Herald]
¶ A 12-MW Virginia offshore wind demonstration project has been cleared to install and operate two 6-MW turbines in federal waters off Virginia Beach. The US Bureau of Ocean Energy management has approved the country’s first “research activities plan,” which lays out plans for the turbines and cabling. [reNews]

Virginia Beach (reNews)
¶ The US Securities and Exchange Commission told Exxon Mobil Corporation to include a climate change resolution in its annual shareholder proxy, according to Reuters. If it is approved, investors would have to be informed on how the company’s profits may be effected by climate change. [Business Finance News]
¶ The Rockefeller Family Fund announced its intention to divest from fossil fuels as quickly as practically possible. The statement singled out ExxonMobil, which has been accused of a cover-up on climate change and interfering in efforts to mitigate it. [The Maritime Executive]

Rockefeller Family Fund Divests from ExxonMobil, Fossil Fuel
¶ The Sierra Club Virginia chapter and the Center for Media and Democracy released a report on the influence that ALEC and its political allies have exerted to stymie state climate and clean energy policies in Virginia. The report focuses on ALEC’s efforts to stop the Clean Power Plan. [Augusta Free Press]
¶ LD 1649, presented to Maine’s Joint Energy, Utilities, and Technology Committee last month, would replace the state’s current retail rate net energy metering policy with a system of market-based incentives for residential solar generators. Stakeholders have been voicing opinions. [Utility Dive]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 24, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ Siemens has unveiled a new solution for the protection of offshore wind turbine rotor blades against leading edge erosion. The protection layer is designed to absorb the impact energy from rain drops and other particles and thereby protect the leading edge from fatigue damage. [reNews]

Horns Rev 2 (Dong Energy)
World:
¶ Barely a month after South Africa launched the continent’s first solar airport after Kochi India, the country has recorded another major milestone in renewable energy as it opens an additional solar PV plant in the Northern Cape province, Solar Capital De Aar 3, a 75 MW plant. [Atlanta Black Star]
¶ Scotland’s huge Longannet power station is to produce its last electricity on March 24, ending coal-fired generation north of the border. Scottish Power said the 2,400-MW power station on the banks of the Forth in Fife would burn through its remaining coal stocks by about 3:00 pm. [Financial Times]

© PA
¶ Plans for a 46-MW solar farm in Northern Ireland, moved one step closer after the country’s environment minister said they should be approved. But the site’s developer must now race against time to complete the project before the 31 March 2017 Renewables Obligation deadline. [Solar Power Portal]
¶ Pattern Energy Group and Green Power Investment announced completion of the 42-MW Futtsu Solar PV power station. Pattern Energy and GPI are joint venture partners that developed the installation in Japan’s Chiba Prefecture. TEPCO has a 20-year agreement to buy all power produced. [PV-Tech]
¶ Japanese egg producer ISE Group, French energy major Total SA and US solar firm SunPower have initiated construction work on a 27-MW PV park in Japan’s Ishikawa prefecture. It is being built on 25 ha (61.8 acres) of land and will provide enough power for over 8,900 local homes. [SeeNews Renewables]

Solar installation in Japan. Author: Official US Navy Page.
License: Creative Commons, Attribution 2.0 Generic.
¶ UK Members of Parliament grilled EDF Energy boss Vincent de Rivaz over the troubled Hinkley C nuclear plant in Somerset. He insisted that the project was definitely going ahead – but refused to say when the “final investment decision” was due. Confused? So were the MPs. [The Ecologist]
US:
¶ Fueled by tax credits and the prospect of energy savings, municipal solar-array projects are operating in five towns on Martha’s Vineyard. Oak Bluffs will soon join them; the town is now before the Martha’s Vineyard Commission seeking a permit for a four-acre solar system. [Martha’s Vineyard Times]

A solar array installed at the Tisbury landfill.
File photo by Michael Cummo
¶ US renewables, excluding hydropower plants, now hold a combined share of roughly 9.5% of the country’s total available installed generating capacity according to FERC. The country’s total wind power capacity totals 74.6 GW, while its operational solar plants are 15.6 GW. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ GE has finished building the offshore platforms for America’s first offshore wind farm. The first foundation for one of the five turbines that will eventually end up totaling 30 MW. GE hopes the wind farm will provide about 90% of Block Island’s electricity demand. [CleanTechnica]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 23, 2016
Opinion:
¶ How California got way ahead of the rest of the world in fighting climate change • Today, California can claim first place in just about every renewable-energy category. It has also attracted more venture capital investment for clean-energy technologies than the European Union and China combined. [Grist]

Reuters | Steve Marcus
World:
¶ PowerStream unveiled Canada’s first of its kind virtual power plant. The virtual power plant dubbed Power House, is meant to showcase how residential customers can simultaneously generate their own clean energy and work together as a virtual power plant to augment the grid. [CTV News]
¶ Morocco is investing about $2.6 billion on the construction of the Ouarzazate complex, which forms the heart of a $9 billion strategy to harness one of the country’s greatest natural resources, sunshine. And impressively, the complex can continue to operate after the sun sets. [CNN]

Morocco’s Noor I solar plant near Ouarzazate currently
powers over 100,000 homes.
¶ Bolivia’s Hydrocarbons and Energy Ministry said it expects the country to add 411 MW of renewable energy by 2020. Bolivia plans to install a total of 2,954 MW of generation capacity by 2020, including thermal, renewable, and hydro sources, investing $5.85 billion. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ Breaking with tradition, cheap oil no longer foretells disaster for renewable energy companies. On the contrary, disillusioned fossil fuel investors are seeking high-growth opportunities, just in time to ride the renewables wave in the wake of the 2015 Paris climate talks. [GreenBiz]

Low fossil fuel prices are evolving from an omen to an opportunity for the renewable energy market. Shutterstock | nopparatk
¶ Mongolia has vast renewable energy resources. They could help boost energy security, reduce pollution, meet global climate commitments and grow the economy, according to a report prepared by the International Renewable Energy Agency and the Ministry of Energy of Mongolia. [solarserver.com]
¶ Building materials supplier Hanson UK is pioneering a demand-side response approach to energy management, with the technology being rolled out to 29 of the company’s quarries across the country. It will reduce energy consumption for de-watering Hanson’s quarries. [edie.net]

Hanson’s West Drayton Asphalt Plant in the London Borough of
Hillingdon will be used for grid balancing.
US:
¶ The Chicago-based Clean Energy Trust released its first Clean Jobs Midwest report on Tuesday, looking at the status of clean energy jobs in 12 states. The report found that Illinois had nearly 114,000 clean energy jobs and posted 9% job growth in 2015, making it the regional leader. [Chicago Tribune]
¶ Officials of St Petersburg, Florida, are taking on the seemingly daunting challenge of remaking the way the city consumes energy. It will be one of the 100 US cities to embark on the Sierra Club’s “Ready for 100” campaign, opting for 100% renewable energy for all municipal power needs. [Creative Loafing Tampa]
¶ Former Democratic Governor Deval Patrick’s three former energy secretaries offered their public support for Republican Governor Charlie Baker’s proposal to solicit long-term contracts for hydroelectric energy. A press conference gave Baker a chance to boast of bipartisan support. [MassLive.com]
¶ Over 100 Long Island community groups and local leaders hosted a rally prior to a Long Island Power Authority board meeting. They called on LIPA to invest in offshore wind energy to help meet the goal of sourcing 50% of the state’s electricity from renewable power by 2030. [The Indypendent]

Offshore wind supporters march on Monday to
a meeting of the Long Island Power Authority.
¶ The New York State Public Service Commission has announced new regulations that it says will make it faster and easier for solar energy, microgrid and other distributed generation projects to connect to the electric grid and advance renewable power development in the state. [Solar Industry]
¶ The economic viability of the Millstone Nuclear Power Station, the largest power plant in New England, is about to become a major issue. The Connecticut legislature’s Energy and Technology Committee is opening a public conversation over whether the state should act to ensure its profitability. [The CT Mirror]

Millstone Nuclear Power Station in Waterford.
Dominion Resources photo.
¶ Bloomberg has expanded its commitment to renewable energy and sustainability by committing to 100% clean energy by 2025. Bloomberg partnered with the Climate Group’s RE100 initiative, which aims to support organisations committing to 100% renewable power. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
¶ US wind farms now pay $222 million dollars a year to farming families and other rural landowners, according to new data released by the American Wind Energy Association today, with more than $156 million dollars going to landowners in counties with below average incomes. [Windpower Engineering]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 22, 2016
World:
¶ TenneT delivered 7.4 TWh of electricity from offshore wind farms in the German North Sea to the grid, an almost six-fold increase compared with 2014. The transmission operator said offshore wind farms in the German North Sea accounted for about 9.6% of Germany’s overall wind energy generation. [reNews]

Laying a cable at sea. TenneT increased offshore capacity in
German North Sea to 4.3GW last year (TenneT)
¶ Australia has added 100 MW of rooftop solar in the first two months of 2016, as Victoria overtakes New South Wales to be the country’s second biggest market. The 55 MW added in February still represented a fall from a year ago, with Queensland, the biggest market,down nearly 20%. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Tidal energy projects in the UK can be developed for nearly half the price of the proposed Swansea Bay project, according to the founder of Ecotricity. He said tidal energy projects in the region could be built for around £90/MWh, rather than the £168/MWh price-tag proposed for the project. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Together, China, India, Vietnam, and Indonesia have plans for 1,824 coal power plants, three-quarters of the total worldwide. But analysis from the Energy and Climate Intelligence Unit suggests fewer than half of those, and possibly as few as 500, will be built by 2020. [Climate Home]

Many coal plants planned in Asia will not be built, say analysts.
(Pic: Peabody Energy)
¶ Coal plants are draining a dwindling global water supply, consuming enough to meet the basic needs of one billion people and deepening a worldwide crisis, Greenpeace warned. They said newly built plants will further stress the world’s major river basins and threaten communities. [Times LIVE]
¶ Jordan has announced that its first nuclear power reactor would be ready by 2025, aimed to meet the rising demand for the country’s electricity needs, said a report. The reactor with a total capacity of 1,000 megawatts will be ready and connected to the grid by 2025. [Trade Arabia]
¶ Commercial PV developer EvoEnergy has completed the fourth largest rooftop PV system in the UK for Lyreco, a global office and workplace solutions provider. The project has a capacity of 3.811 MW and 13,860 panels. It is at Lyreco’s national distribution center in Telford. [Renewable Energy Magazine]

EvoEnergy completes UK’s fourth largest rooftop solar array
¶ An 18-month battle to discover the true cost to consumers of building the Hinkley Point C nuclear reactors is to come to a climax in London. The Information Commissioner has been blocking freedom of information requests. However, it has finally agreed to a hearing. [The Ecologist]
US:
¶ Consumers Energy says it is on track to close seven Michigan coal-fired power plants this spring. The plants have 1,000 MW of capacity. They say power will be replaced by a gas plant they bought, and they plan to continue to invest in wind power and other renewable energy sources. [Midland Daily News]
¶ The US Bureau of Ocean Energy Management has found a lease request for a floating wind project of up to 800 MW off California to be qualified and will proceed with the next step in its leasing process. It is the first formal interest in wind development off the California coast. [SeeNews Renewables]
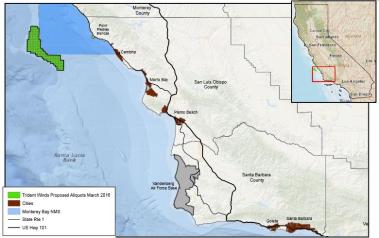
Map by Bureau of Ocean Energy Management
¶ Apple today announced that 93% of its facilities run on renewable energy, including 100% of its facilities in the US, China, and 21 other countries. Apple’s VP of Environment, Policy, and Social Issues made the announcement. Apple had set a goal of 100% renewable two years ago. [The Verge]
¶ A pioneering experiment, leveraging mass-market purchasing power on energy, promises to bring cheaper, “greener” electric supplies to Somers, New York. The lower rates are expected to make the price of so-called green energy attractive enough to encourage its widespread adoption. [TAPinto.net]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 21, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ According to NASA, February 2016 was the most anomalously warm month in 135 years of record keeping – 1.35° C (2.43° F) warmer than the 1951 to 1980 average. While the recurring El Niño event certainly drives short-term oscillation, the long-term warming trend is quite apparent. [CleanTechnica]

2010, 2014, and 2015 were all record-breaking years. Climate Central graph
World:
¶ The South African Energy Minister launched the Solar Capital De Aar 3 in the Northern Cape – the 17th solar photovoltaic plant in the province. She said the commercial operation of the 75-MW plant is a huge achievement in scaling up the deployment of renewable energy in South Africa. [AllAfrica.com]
¶ Last summer, the Mayor of London unveiled plans to test a fleet of double-decker electric buses to ply the tourist-friendly Route 16. Things must have gone swimmingly because just last week a fleet of five of the hulking EVs was announced for Route 98 to calm a pollution hotspot. [CleanTechnica]

Electric bus. Image via businesswire.com
¶ Greenpeace has challenged the case for a new nuclear power station at Wylfa Newydd, Wales. It submitted evidence to Westminster’s Welsh Affairs committee warning that the project is based on an “outdated” concept and questions whether nuclear is most effective for low-carbon power. [WalesOnline]
¶ Statoil is to deploy a 1-MW storage system at its 30-MW Hywind floating offshore wind farm off the Scottish coast. The Batwind battery is based on lithium technology and will be installed at the end of 2018. Hywind will feature five Siemens SWT-6.0-154 machines. It is due to be fully operational in 2017. [reNews]

Statoil image
¶ China plans to more than triple solar power capacity by 2020 to as much as 143 GW to help reduce carbon emissions. The country will add 15 to 20 GW of photovoltaic power annually in the next five years, the head of the National Energy Administration said in a conference in Beijing. [Bloomberg]
¶ The first four days of March saw maximum temperatures in much of the country 4° C above average, and 8° C to 12° C above average in most of southeastern Australia, a Climate Council report says. It argued that heat impacts lent urgency to climate mitigation efforts. [The Marshalltown]

Drought and heatwave affected London Plane Trees. Photo by Bidgee. CC BY-3.0 unported. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ EDF’s new nuclear power station in France faces years of further delays if tests confirm that the steel used in its reactor is flawed, the country’s atomic watchdog has warned. The flagship plant at Flamanville in Normandy has already been subject to years of delays and cost overruns over 200%. [Financial Times]
US:
¶ Additions this year to the ERCOT grid in Texas are expected to be dominated by ⅔ from wind and solar PV, according to energy research from SNL. If SNL research proves true, this will be a huge boost to the generation of renewable electricity within this historic oil-producing state. [CleanTechnica]

ERCOT control room operator. Photo by Dpysh w.
CC BY-3.0 unported. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ A renewable energy campaign has the goal of producing as much solar power energy as Ginna nuclear plant by the year 2025. ROCSPOT, a community-based organization, shows people the environmental and financial benefits of solar power and helps them through the installation process. [13WHAM-TV]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 20, 2016
World:
¶ The Spanish utility company Endesa purchased 410 GWh of solar electricity, during a recent solar energy auction for Portugal and Spain, at a price of €39.6/MWh ($43.82/MWh). The quarterly auctions relate to roughly 500 GWh of generation, varying at the various times of year. [CleanTechnica]
(This is extremely important. In this case, the wholesale price of unsubsidized solar power has fallen below to 4.4¢/kWh. Even with the price of battery storage added, it competes with electricity from natural gas at a time when the price of gas fuel is low.)

PVs in El Paso, La Palma, Spain. Photo by Rufus46.
CC BY-SA 3.0 unported. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ The province of Jujuy in Argentina will develop 700 MW of solar PV projects with the German company Photovoltaic Park, following the signing of letter of intent between the two. Three different projects, in different parts of the province, and will cost around $1.4 billion to develop. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The UK government will make a net-zero emissions goal that it agreed to at the COP21 talks in Paris the law, following advice from the Committee on Climate Change, according to recent reports. The UK’s legal target will change from an 80% emissions reduction to net-zero. [Sustainnovate]

Abandoned UK farmhouse on the edge open-pit mine. Photo by Robert Guthrie. CC BY-SA 2.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Vietnam will need around $148 billion to invest in developing the national grid and resources in the 2016-2030 period. Vietnam will accelerate development of renewable resources, such as hydro, wind, solar, and biomass, to increase the proportion of electricity that is renewably sourced. [VietNamNet Bridge]
¶ Italy’s economic powerhouse, Milan, is seeking to bring back the bicicletta by paying people to cycle to work. The move follows the announcement in December of a €35 million government fund for sustainable mobility solutions, after dangerous levels of pollution in major cities. [The Guardian]
¶ After transformer explosions caused massive power outages across Sri Lanka, German experts are coming to inspect the transformers and recommend ways of avoiding future power failures resulting from such breakdowns. They will recommend both short-term and long-term solutions. [The Sunday Times Sri Lanka]
¶ Rottnest Island is off the coast of Western Australia. Together, a new solar farm and its existing wind turbine to generate almost half its electricity, greatly reducing the amount of diesel fuel it needs. The solar farm will cost AUS$7.3 million (US$5.55 million) and will generate 600 kW. [The West Australian]
¶ The growth of cheaper renewable power is outpacing that of nuclear in India, and renewables now account for much more production. In fiscal year 2014-2015, renewable energy accounted for 5.6% of electricity generated in India, against 3.2% for nuclear power. [The Hans India]
US:
¶ Enough windpower came online last year for 19 million American homes. No region of the United States shows this progress better than the American heartland. More than 31% of Iowa’s electricity was generated by wind power last year, the first time a US state topped the 30% milestone. [DesMoinesRegister.com]

Wind turbines in Iowa. Photo by Billwhittaker at English Wikipedia. CC BY-SA 3.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Duke Energy signed agreements to buy biogas generated by swine and poultry waste and other biomass sources from a facility to be built in eastern North Carolina. It is expected to make enough methane to produce 125 GWh per year, which will power about 10,000 homes. [Charlotte Business Journal]
¶ The high cost of upgrading 40-year-old nuclear reactors is confronting Xcel Energy again. Investments in the Prairie Island nuclear power plant in Minnesota, are projected to cost more than expected – $487 million by 2020, with more spending needed in the next decade. [Minneapolis Star Tribune]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 19, 2016
Opinion:
¶ Dispelling the nuclear ‘baseload’ myth: nothing renewables can’t do better! • The main claim used to justify nuclear is that it’s the only low carbon power source that can supply ‘reliable, base-load electricity. But renewables can match grid demand continuously in a way nuclear power cannot. [RenewEconomy]

Wind farm in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The state runs on 100% renewable energy. Photo: Clemens v. Vogelsang via Flickr (CC BY).
¶ Five ways to power the UK that are far better than Hinkley
Point • The planned £18 billion nuclear reactors at Hinkley Point in Somerset are derided by critics as “one of the worst deals ever” for Britain. One energy policy expert has come up with five better ways of powering the nation: [The Guardian]
World:
¶ The CEO of Canadian Pacific Railway was recently quoted as saying that people need to begin realizing and accepting that fossil fuels are “probably dead,” owing to a changing climate and the environmental hurdles that are likely to be introduced in coming years to large-scale use of fossil fuels. [CleanTechnica]

Canadian rail cars carrying coal.
¶ In a record-setting year for Canadian electricity exports, British Columbia bolted to first place in 2015. Canada’s net electricity exports increased by more than 14 TWh in 2015, an overall 30% increase over 2014. More than half of the increase was an additional 7.4 TWH from BC. [Business in Vancouver]
¶ According to a report by the Lazard investment fund, the cost of electricity generated with wind power fell 61% in the years from 2009 to 2015. And the cost of solar energy fell 82%. This puts renewables into a price range that is competitive with fossil fuels, coal, or oil. [Manila Bulletin]
¶ Green energy production in the High Weald could power an entire village when plans for an anaerobic digester are submitted. The technology is off to a slow start in Britain, but hopes are high it could provide an alternative to fracking as a resource to produce power. [Kent and Sussex Courier]

A digester in Melton Ross, North Lincolnshire
¶ Solar microgrids are bringing reliable power to three remote villages in Nepal, where nearly a quarter of the population has no access to electricity. The microgrids have 35 kW of solar and battery storage, which is enough for 540 people and avoids carbon emissions. [Microgrid Knowledge]
¶ The global battery market in the telecom sector will grow 10.5% annually during the period 2016-2020, a report by Research and Markets said. Rising numbers of Telecom tower installations are built, 80% of which run on diesel generators. Solar or wind with batteries will reduce costs. [ETTelecom.com]
US:
¶ This is already turning out to be a very bad year for the “clean” image of natural gas, with earthquakes in Oklahoma, water pollution in Pennsylvania, a gas leak in California, and new federal emissions scrutiny. Now a proposed LNG export terminal on the Oregon coast failed to get approval. [Triple Pundit]

Cumulative number of earthquakes with a magnitude of 3.0 or larger in the central and eastern United States, 1970–2016. Public domain: US Geological Survey Image. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ The three biggest coal mining companies in the United States, Peabody Energy, Arch Coal, and Cloud Peak Energy, depend on federal coal for the vast majority of coal they mine each year. This is the primary conclusion from a new report published this week by Greenpeace. [CleanTechnica]
¶ For the first time since Gallup first asked the question in 1994, a majority of Americans oppose nuclear energy. The 54% opposing it is up a lot from 43% a year ago. Those favoring nuclear have declined from 51% a year ago to 44% now. Before the Fukushima Disaster, approval stood at 57%. [Greentech Media]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 18, 2016
Opinion:
¶ So … was that climate change? • While the broad trends of climate change, and our role in causing it by burning fossil fuels, have been clear for decades, it was not possible until recently to tie a specific storm, drought, flood or heat wave to long-term warming trends. Thankfully, that’s changing. [CNN]

Waterspout off the Florida Keys. Photo by Dr. Joseph Golden, NOAA. US Government image. Public Domain. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ How Cheap Oil Is Accelerating Investment In Sustainable
Energy • An increasingly unprofitable global oil market is discouraging its own investors. Cheap oil no longer foretells disaster for renewable energy companies because investors want opportunities for growth. [CleanTechnica]
Science and Technology:
¶ February smashed the previous record for the warmest February and even became the warmest month ever compared to average, according to NOAA. February temperatures averaged 1.21° C (2.18° F) above the 20th century average. The past three months hold the top three places. [CNN]

Temperature departures from normal for the
month of February 2016
World:
¶ Doubling the global share of renewable energy by 2030 could save $4.2 trillion annually, 15 times the costs. This is the primary conclusion from a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency. It examines options to boost renewable energy from its current 18% to 36% by 2030. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Japan’s energy ministry confirmed that the feed-in-tariffs for solar power will be reduced, as usual, for the new fiscal year. The rate for PV systems bigger than 10 kW will fall to ¥24/kWh ($0.22/kWh) from the current ¥27/kWh. Smaller systems have higher rates. [SeeNews Renewables]

Solar farm in Japan. Author: Haruhiko Okumura.
License: Creative Commons, Attribution 2.0 Generic.
¶ The world is expected to have about 18.4 GW of geothermal capacity by 2021, after it reached 13.3 GW, spread across 24 countries, in 2015, according to a report by the US Geothermal Energy Association. There are currently 12.5 GW of projects under development in 82 countries, according to the association. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ Two “run of river” hydro power schemes are being developed in the Scottish Highlands as part of a £4.8 million investment. Albion Community Power (ACP), said the projects would generate 2.8 GWh of renewable electricity a year, enough to power about 700 homes. [Scotsman]

ACP is also involved in a scheme near Loch Arkaig.
Picture: Contributed
¶ The Suzlon Group has bagged orders for a combined capacity of 81.90 MW of wind turbines. The orders were received from SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises) across diverse industry segments including food and agro, textiles, chemical, real estate and engineering. [Business Standard]
¶ As Abu Dhabi pursues its solar ambitions, it is weighing more cost-effective technologies. As it comes to its third anniversary, the 100-Mw Shams 1 concentrated solar power plant is not cost competitive to other available technologies, such as solar PV, whose price has been falling. [The National]

The Shams 1 plant was one of the first concentrated solar
power plants in the region. Christopher Pike / The National
¶ The £18 billion plans to build the first nuclear plant in the UK in two decades look set to go ahead after EDF secured a bailout from the French government. The French economics minister said it would be a mistake for EDF, which is 85% government-owned, not to build the plant. [Fresh Business Thinking]
US:
¶ The California Public Utilities Commission gave the 392-MW Ivanpah CSP park more time to reach the output levels agreed in its power purchase agreement. Pacific Gas & Electric has agreed to give the owners of the power plant until end-July 2016 to improve performance. [SeeNews Renewables]

Ivanpah. Author: Bill & Vicki T.
License: Creative Commons, Attribution 2.0 Generic
¶ Work began this week on one of the largest floating solar arrays in the nation, in the Borough of Sayreville, New Jersey. Along with the project development team, two local educational partners will also participate, providing valuable services to their special needs clients. [Water Online]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 17, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ Nearly a quarter of all deaths around the world are caused by living and working in toxic and polluted environments, and the worst affected are children, the poor, and the elderly, according to a new report released by the World Health Organization (WHO). [CommonDreams]

A child scavenges for coal scraps in a slum in Manila.
(Photo: Adam Cohn / flickr / cc.)
¶ NOAA’s Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii reported a spike in CO2 levels this week, 3.05 ppm, which was the largest year-to-year increase ever observed in the 56 years of recording and research done at the station. It was the fourth consecutive year that CO2 grew more than 2 ppm. [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ Ontario’s Independent Electricity System Operator awarded around 140 MW of new solar energy project contracts at a weighted average price of CAN$0.1567/kWh (US$0.12/kWh). The solar energy allocation in the tender was oversubscribed, with 1,742 MW of bids. [CleanTechnica]

Ontario. Image by Dennis Jarvis (some right reserved)
¶ Acciona Energía is providing adjustment services to the Spanish electricity system by increasing the level of generation by wind power. Traditionally, system adjustment services for the national grid have been provided by conventional technologies, such as thermal or hydropower stations. [reNews]
¶ Japan has seen a heavy shift from atomic to renewable sources since the Great East Japan Earthquake tipped the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into triple meltdown. But five years after the catastrophe, major issues need addressing for renewable energy to flourish. [The Japan Times]

Wind and solar demonstration field of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology’s Fukushima Renewable Energy Institute. | Kyodo
¶ The UK government presented Budget 2016, giving some details on the planned support for offshore wind in future years, but there was little reason to cheer for renewable energy. The government is criticized for ending renewable incentives while increasing support for fossil fuels. [SeeNews Renewables]
US:
¶ According to TransActive Grid, Brooklyn consumers can transform their homes into connected power stations. The New York startup has developed a consumer-run microgrid – a technology which its founders hope will radically transform the way electricity is bought and sold. [CleanTechnica]

Water towers in New York. Image via Shutterstock
¶ Peabody Energy Corp warned it could go bankrupt, signaling the end of an era for listed US corporate coal companies, even as their mines continue to fuel a big chunk of the country’s power stations. Arch Coal Inc, Alpha Natural Resources, Patriot Coal Corp, and Walter Energy are already bankrupt. [Daily News]
¶ ConEdison Solutions, the competitive retail subsidiary of Consolidated Edison, won a $150 million contract for a community aggregation program to provide electricity at low rates to 90,000 residential and small business customers in Westchester County, New York. [Energy Manager Today]
¶ This is likely to be the first year in which natural gas has a higher market share for electricity generation than coal does, federal analysts predict. EIA is predicting that when 2016 ends, natural gas will have generated 33% of the country’s electricity, compared to 32% for coal. [The Hill]

Please click on the image for a larger view.
¶ Federal officials dedicated over 125 square miles in waters off Long Island for wind energy development, pushing forward a renewable energy proposal created by New York utilities. Interior Secretary Sally Jewell said the state has “tremendous” offshore wind potential. [Ledger Independent]
¶ The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System, a $2.2 billion solar project in the California desert, isn’t producing the electricity it is contractually required to deliver. PG&E Corp says the solar plant may be forced to shut down if it doesn’t receive a break from state regulators. [Nasdaq]
¶ United Airlines will launch an initiative using biofuel to help power flights running between Los Angeles and San Francisco, with plans to expand to all flights operating out of LAX. It is the first time an American airline will use renewable fuel for regular commercial operations. [Independent Online]

The renewable fuel used to power United’s planes will be coming from a Los Angeles refinery operated by AltAir Fuels. AP photo.
¶ In an unusual move, Colorado state regulators verbally rejected a proposed agreement between Xcel Energy Inc and three solar power developers that would have added up to 60 MW of “community solar” power plants in Colorado. The PUC typically approves such agreements. [Denver Business Journal]
¶ A unit Dominion Resources Inc will build a 20-MW solar power facility in Virginia in partnership with Microsoft and the state. “It’s good to be moving forward but we’re not moving fast enough”, said the head of the Virginia chapter of the Sierra Club. The plant will power 5,000 homes. [Examiner Gazette]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 16, 2016
Opinion:
¶ How Google Became to World’s Largest Corporate Purchaser of Renewable Energy • The Google approach to renewable energy is not unlike how many utilities purchase power. It often enters into power purchase agreements, and its projects range from California to Sweden. [Triple Pundit]

Wind turbines. Image Credit: Flickr/naql
World:
¶ A report from the UK’s Offshore Wind Program Board outlined how investment in turbine technology has delivered significant cost benefits to the offshore wind industry. It says costs fell through 2015 and remain on track to fall to its target of £100/MWh by 2020. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Climate change efforts may be bearing fruit faster than expected. Energy-related carbon emissions stayed flat for the second consecutive year last year even though the global economy kept growing. Over 90% of new electricity generated last year was from renewables. [The Australian Financial Review]

More than 90% of new electricity generated
last year came from renewables. Fairfax
¶ Swedish energy firm Vattenfall announced this week that it has started development on the 3.6-GW Norfolk Vanguard offshore wind farm. Vanguard is 47 kilometers off the coast, and will generate the equivalent electricity necessary to supply more than 1.3 million UK households. [CleanTechnica]
¶ BusinessGreen has been told a group of about 15 of the UK’s Conservative MPs wrote to George Osborne declaring their backing for continued support of renewable energy projects. They urged the Chancellor to use the budget to extend subsidies for clean energy projects through to 2025. [Business Green]
¶ Younicos announced that it is building the world’s first “100% renewable” grid on the Azorean island of Graciosa. Wind and solar power will provide electricity most of the time, with power storage from Leclanché lithium-ion batteries. There will be fossil fuel emergency backup power. [ECOreport]

Graciosa. Photo courtesy of Younicos
¶ Germany’s highest court will hear two days of testimony on whether the government owes three utility giants, Vattenfall, EON and RWE, compensation for the 2011 decision to phase out the country’s nuclear power plants. It could take months for Constitutional Court to render a decision. [Nuclear Street]
US:
¶ The Obama administration is reversing course on opening Atlantic waters to a new generation of oil and gas drilling, after a revolt by environmentalists and coastal communities that said the activity threatened marine life, fishing and tourism along the East Coast. [Times Record]

Offshore oil rig. Photograph by Mike Peel (www.mikepeel.net).
CC-BY-SA-4.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ The Imperial Irrigation District’s board of directors approved a lease agreement with Controlled Thermal Resources, which proposed a 250-MW geothermal plant on 1,600 acres on the Salton Sea’s southern shore, in California. Hopes are raised for supporters of Salton Sea restoration. [The Desert Sun]
¶ Legislators in Tompkins County, New York, voted unanimously to allow purchase of hydroelectric power to meet the government’s power needs through remote net metering. It will purchase power from a renewable energy facility and receive a deduction on its electric bill for that power. [The Ithaca Voice]
¶ Republican lawmakers in the New York State Senate are pushing a $100 million bailout of the state’s nuclear power industry using funds from a climate change program meant to cut greenhouse gases from power plants. Nuclear plants currently provide about 30% of the state’s total electricity. [Albany Times Union]

Constellation Energy Group Inc’s Nine Mile Point
Nuclear Station. (Constellation Energy Group Inc)
¶ A group of 100 Massachusetts state representatives broke ranks with House leadership, urging that reconciliation of House and Senate bills on a net metering bill hew more closely to the Senate approach. Nearly two-thirds of the House members signed the letter. [CommonWealth magazine]
¶ A University of Delaware initiative analysed Massachusetts’ electricity costs would look like in 2020-2030 with 2 GW of wind-power off the coast. The study says the costs for the first project in a 2-GW build-out could be as low as $0.162/kWh, with costs declining so an LCOE of $0.108/kWh. [SeeNews Renewables]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 15, 2016
World:
¶ Brazil’s power sector regulator Aneel has authorized three wind energy plants, with a combined capacity of 60.1 MW, to start commercial operations. According to Brazil’s Ministry of Planning, the investment totalled more than BRL 284.7 million ($78.5 million, €70.7 million). [SeeNews Renewables]

Brazilian wind farm. Author: Carla Wosniak.
License: Creative Commons, Attribution 2.0 Generic
¶ Climate laws will be tightened to cut carbon emissions effectively to zero, the UK’s government said. Under current law, emissions must be cut of by 80% by 2050, but ministers said it is clear the UK must not increase CO2 at all because the warming threat is so severe. [BBC]
¶ Uruguay went from having virtually no wind generation in 2007 to become a double world-record holder in less than a decade. By 2013, it was receiving the largest share of clean energy investment as a percentage of GDP, and in 2014, installed the most wind per capita of any country. [CleanTechnica]

Please click on the image to enlarge it.
¶ A report from an expert panel at the Japanese Nuclear Regulation Authority says a fault beneath Hokuriku Electric Power Co’s Shika nuclear power plant can be “reasonably concluded to be active.” The fault lies directly under the plant’s Reactor 1 and may prevent its operation. [ZME Science]
¶ Mexico installed over 700 MW of new wind capacity in 2015 and is expected to add 800 MW more this year. Growth expectations for 2017 and 2018 are much more dramatic. The Mexican wind energy association says the country topped 3,000 MW of wind capacity at end-2015. [SeeNews Renewables]

Wind turbines. Author: Rex Brown. License:
Creative Commons, Attribution-NoDerivs 2.0 Generic
¶ In Myanmar, a local company says it will pursue plans to build a 50-MW coal-fired power plant at Lut Lut village, in the Tanintharyi Region, once it has secured permission from Myanmar Investment Commission. This is despite continuing opposition from the community. [Myanmar Times]
¶ Tasmania’s energy crisis drags on. Water levels in the hydro reservoirs are at a record low of 14.8%. The fault in the Basslink interconnector between Tasmania and Victoria remains. There is not enough wind power to maintain the power supply, so diesel power must be used. [Energy Matters]
¶ Workers from Peru’s state-controlled petrol company have been mopping up and scooping oil from a pipeline spill for the past month, as it stuck in ravines and on vegetation in the smaller rivers. It is the second major spill this year in the northern part of Peru’s jungle region. [BBC]

The contaminated soil is shoveled into plastic sacks
¶ Ontario’s Independent Electricity System Operator awarded 16 contracts totaling 455 MW as part of a renewable procurement. Contracts have been awarded for five windpower developments with a total capacity of 299.5 MW and seven solar projects with total of 139.9 MW. [Power Technology]
US:
¶ New US solar power installations this year are set to break all previous records. They should be more than double what was installed last year at 16 GW. The total operating solar capacity in the US is expected to reach 25.6 GW of DC by the end of the year, GTM Research said. [Computerworld]

Workers for SolarCity install rooftop solar on a house.
Credit: SolarCity
¶ Total electricity sales in 2015 fell 1.1% from the previous year, marking the fifth time in the past eight years that electricity sales have fallen. The flattening of electricity sales reflects declining sales to industry and little or no growth in sales to the residential and commercial sectors. [Energy Collective]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 14, 2016
World:
¶ Sixteen US ships that participated in relief efforts after Japan’s nuclear disaster five years ago remain contaminated with low levels of radiation from the crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, top Navy officials told Stars and Stripes. A total of 25 ships took part in Operation Tomadachi. [Stripes Japan]

Operation Tomadachi delivering supplies. Photo by Lance Cpl. Mark Stroud. Public domain photo, Marine Corps. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ The recent years have seen the demand for smart microgrids surge to unprecedented levels. This spike in demand is attributable to the growing share of renewable energy in the global energy matrix. Transparency Market Research has issued a report on the global smart microgrid market. [Industry Today]
¶ Connective Energy Holdings Limited, of Donegal, Ireland, has announced they will create 90 jobs over the next two years by using anaerobic digesters to turn manure into bio-gas. The first of six facilities is under construction at Glenmore Estate in Aghaveagh in Donegal. [Donegal Now]

Donegal company turns manure into 90 jobs
¶ The Jordanian Cabinet approved delivering electricity to single-detached dwellings in poverty pockets using solar power units, the Jordan News Agency, Petra, reported. The solar power units will not be part of the electricity grid and will cost a maximum of JD6,000 ($8462) for each house. [Zawya]
¶ Migrating trout near a Swedish hydropower plant are at the center of a long-running court case that may shape how utilities plan for a future without nuclear power. The case signals what lies ahead for utilities seeking alternative low-emission power sources in Sweden because nuclear is not profitable. [Chicago Tribune]

Water flows through the Ultra Hydroelectric power station. Must Credit: Bloomberg photo by Johan Jeppsson. (Johan Jeppsson / Bloomberg)
¶ Modelling from a group of engineers, energy analysts and IT experts in Western Australia shows that an electricity system with 85% renewable energy will be cheaper than “business as usual,” an average of A$124/MWh compared to A$127/MWh, and around the same price as current costs. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Five small off-grid solar power stations with energy storage will replace grid supply in a pilot project in Western Australia. Last year, devastating bushfires in the Esperance region destroyed hundreds of kilometers of power lines leaving customers without power for many days. [Energy Matters]
¶ Global efforts to curb the use of coal-fired power plants may provide a lifeline to Brazil’s embattled sugar cane industry. A group of companies formed a $130 million joint venture for making sugar cane-based biomass pellets that can be burned to produce electricity. [Hellenic Shipping News Worldwide]

Ecologically grown sugarcane in Brazil. Photo by A. F. Yersin.
CC BY-SA 3.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Sri Lanka today witnessed its third nationwide electricity blackout within six months. It disrupted the water supply to many parts of the island nation. The Power and Renewable Energy Ministry Secretary said the cause of the power failure could a substation trip in Biyagama. [NDTV]
¶ Kansai Electric appealed a court decision ordering two nuclear reactors shut down even though they had been declared safe under tougher rules prompted by the Fukushima meltdown. The court had ordered the No 3 and No 4 reactors at the Takahama nuclear plant to shut down. [Japan Today]

Kansai Electric Power’s No 3 (L) and No 4 (R) reactors
at the Takahama nuclear plant. AFP
US:
¶ US wind and solar electricity generation grew by 20,659 MWh in 2015, compared to the full year 2014. That’s compared to fossil fuel electricity generation dropping by 18,041 MWh. Unfortunately, in part due to terrible drought, hydroelectricity generation dropped 8,199 MWh. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The 214 turbines in the Highland Wind Farm are online in O’Brien County, Iowa, and more are coming. O’Brien Wind Farm will add 104 turbines in the the county, and Ida Grove Wind Farm in Ida County will have 134 turbines. Both are expected to be finished by the end of the year. [Sioux City Journal]
¶ The Energy Information Administration’s latest monthly report said the share of utility-scale renewable energy had increased by over 2% from 2014. Three months earlier, it predicted a decrease by 1.8% in 2015. The EIA’s record for long-term forecasts is consistently even worse. [DeSmog]
¶ Last week, a bipartisan group of 21 Florida mayors wrote to debate moderators to argue it would be “unconscionable for these issues of grave concern for the people of Florida [climate change and sea level rise] to not be addressed.” Candidates were asked and responded. [The Guardian]

Flooding in Florida community. Photo by Barry Bahler.
Public domain – FEMA photo. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Arizona Public Service vocally supports flexible grid technologies, and peers in the industry ask why. APS identified five reasons it “got off the fence” over five years ago and began implementing flexible grid technologies to respond to a transforming marketplace. [Transmission and Distribution World]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 13, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ Efforts to increase wind power mean that turbine blades are getting bigger and bigger. But a new design in the works takes the idea to levels most people can barely imagine: Blades up to 656.2 feet long – more than two football fields. Today’s longest blades are 262.5 feet. [Los Angeles Times]

Wind turbine blades in storage. Photo by Glyn Drury.
CC BY-SA 2.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ This year’s winter has been quite strange, with temperatures throughout much of the northern hemisphere being considerably higher than at any other time since high-accuracy records began over a hundred years ago. Now here is a video showing just how fast Arctic ice is declining. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Night-time temperatures are more sensitive to climate change, a study found. The nights have been warming much faster than the days over the last 50 years, worldwide. Analysis of the causes of this more rapid warming at night shows this is likely to continue in the coming decades. [News Nation]
World:
¶ A new report from the energy consultancy firm Baringa projects that the Scottish isles could see economic benefits of around £725 million (over the next quarter century) from renewable energy development. The benefits include revenues of up to £390 million for community-owned projects. [CleanTechnica]

Scottish Isles. Image by Moyan Brenn (some rights reserved).
¶ The Polish government plans to unveil legislation that could swing the country’s energy mix even more towards coal and favor biomass over the nascent wind power industry. Although Poland was one of 195 nations that backed the COP21 deal, it sought a special status for coal. [MENAFN.COM]
¶ Five years ago an earthquake off the coast of Japan triggered a tsunami and a series of meltdowns at the Fukushima nuclear plant. Kaori Suzuki’s home is nearby – determined to stay, but worried about her children’s health, she and some other mothers set up a laboratory to measure radiation. [BBC]

Mothers’ radiation lab
¶ More doubts have arisen over plans by French Energy firm EDF to build an £18 billion nuclear plant at Hinkley Point. The chairman of the House of Commons energy committee has called for the project to be re-examined. This follows a letter by EDF’s chief executive saying more funding is needed. [BBC]
¶ Faced with power blackouts lasting anything from eight to twelve hours a day, residents and businesses in Gaza are increasingly turning to the sun to supply their energy needs. Solar panels are more reliable and cheaper in the long run. And in some cases they are essential to staying alive. [Ynetnews]

Solar panels. Reuters photo.
¶ Taiwan’s President-elect Tsai Ing-wen (蔡英文) of the Democratic Progressive Party reiterated Saturday that one of her party’s objectives is to phase out nuclear power in Taiwan over the next nine years. She said it is important to promote renewable energy and efficiency. [Focus Taiwan News Channel]
US:
¶ Almost no wind turbines have been built in Wisconsin over the past five years. Widespread opposition to wind farms made Wisconsin unattractive for wind investors. But that could soon change. In southwestern Wisconsin, nearly 50 turbines could be built over the next year. [Milwaukee Journal Sentinel]

The Glacier Hills Wind Park in Columbia County, the last
wind farm built in Wisconsin. Photo credit: We Energies.
¶ Building anything at sea is never easy, but it can be easier if as much as possible is done beforehand on solid ground. So even though Deepwater Wind suspended offshore work in November, workers with the project have still been busy all winter doing the final assembly of key pieces. [The Providence Journal]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 12, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ A joint letter from more than 130 scientists refers to “lack of information,” “Misrepresentation,” and “Disregard for science that was not funded by the proponent.” Scientists condemn a flawed review process for a liquified natural gas project at the mouth of British Columbia’s Skeena River. [CleanTechnica]

Coast mountains near the mouth of the Skeena River.
Photo by Roy Luck via Flickr (CC BY SA, 2.0 License)
World:
¶ As part of a plan announced last week, Norway will invest $923 million to create 10 broad, two lane, cross-country bicycle highways in and around Norway’s nine largest cities. The plan is a key component of an effort to slash Norway’s transportation emissions by 50%. [CleanTechnica]
¶ India’s massive bet on solar power is paying off far earlier than anticipated. Indian solar prices are now within 15% of coal prices, according to KPMG. If current trends hold, the consultancy predicts electricity from solar will actually be 10% cheaper than domestic coal by 2020. [CNN]

A woman turns on a solar-powered light at her home near Mumbai.
¶ There is evidence that oil prices are stabilizing and could even begin to rise again, the International Energy Agency has said. Lower oil output in the US and other countries is curbing the glut in the oil supply. The increase in supply from Iran has also been less dramatic than first feared. [BBC]
¶ The 4,000-MW Nanticoke Generating Station ceased production in 2013 as part of Ontario’s phase-out of coal energy and was officially shuttered for safety reasons last year. But the strip of land on the north shore of Lake Erie will soon begin churning out power again, this time from solar PVs. [Solar Industry]

Ontario Power Generation’s Nanticoke Generating
Station in southern Ontario. Photo: OPG
¶ In the Philippines, five solar farms in Negros Island are producing another 139 MW of power, while the groundbreaking for a 25-MW biomass power plant is set April 6. Two other solar plants in Negros Occidental with a total output of 157.5 MW were connected to the grid. [Visayan Daily Star]
¶ It takes two years to build them. Each operator trains for a month before picking up their controls. And they get fried by radiation after working for just 10 hours. The robots sent in to search the core of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant have a very short and specialized lifespan. [National Post]

A robot developed by Toshiba Corp. AP Photo/Shizuo Kambayashi
¶ The boss of the French state-owned company behind the UK’s first new nuclear power station for 20 years has threatened to pull the plug on the £18-billion project without further backing from François Hollande’s government. He said he needed more financial support to proceed with construction. [HITC]
US:
¶ Oregon is the first state to eliminate coal from its power supply through legislation and now boasts some of the most stringent demands for renewable energy among. The law phases coal-generated energy by 2030 and requires utilities to provide half of its power renewably by 2040. [CNSNews.com]
¶ After six years and a lot of legal work, two couples won a rare $4.24 million jury verdict against a fracking company, Cabot Oil & Gas Corp. The jury found that the company contaminated their water wells with methane leaching underground from natural gas fracking sites. [CleanTechnica]

Fracking Site in Warren Center, PA.
Photo by Ostroff Law. CC BY-SA 3.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ The Vermont Senate Committee on Natural Resources and Energy unanimously approved a bill aimed at reforming Vermont’s energy siting process. State Senator John Rodgers said the Public Service Board still makes the final call despite increased local participation. [Watchdog.org]
¶ Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker announced on Friday that Holyoke will receive $1-million in grant funding to expand eco-friendly projects. The Department of Energy Resources awarded grants money to cities and towns with active or decommissioned coal generation facilities. [wwlp.com]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 11, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ Scientists have discovered a novel way to make plastic from carbon dioxide and inedible plant material, such as agricultural waste and grass. The new technology could provide a low-carbon alternative to plastic bottles and other items currently made from petroleum. [Futurity: Research News]

“Our goal is to replace petroleum-derived products
with plastic made from CO2.” (Credit: iStockphoto)
¶ Japanese scientists discovered a type of bacteria that can eat plastic, a finding that might help solve the world’s fast-growing plastic pollution problem. The species fully breaks down one of the most common kinds of plastic, Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), often used to make beverage bottles. [CNN]
¶ According to a new study published by researchers from the University of Queensland and Griffith University in Australia, global warming could occur much more quickly than previously thought. The model forecasts an increase in the global average temperature by 1.5° C as early as 2020. [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ After a run in with Donald Drumpf, the European Offshore Wind Deployment Center has seen the beginning of offshore works start this month. The European Offshore Wind Deployment Centre is being developed by a partnership of Vattenfall and Aberdeen Renewable Energy Group. [CleanTechnica]

Vattenfall Image
¶ More than 80 organisations from across northern England have called on the Chancellor ahead of the Budget to “Keep it Clean” and back renewable energy. The North of England led the Industrial Revolution, and they say it should be at the forefront of this new, global, clean energy transformation. [Rochdale Online]
¶ President Barack Obama welcomed Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau to the White House as the two leaders sought to join forces to combat climate change. Trudeau and Obama have both described the warming planet as among the world’s most pressing challenges. [Midland Reporter-Telegram]

Prime Minister Trudeau and President Obama.
(AP Photo / Susan Walsh)
¶ EDF’s £18-billion project to build nuclear reactors in Britain is potentially risky for the state-owned utility, whose foreign investments in recent years have proved disappointing, France’s top public auditor has said. EDF’s cashflow and high debt limit its capacity to invest abroad. [The Guardian]
¶ A consortium comprising Italy’s Enel Green Power SpA, Morocco-based Nareva Holding, and Germany’s Siemens Wind Power have won the preferred bidder status in a 850-MW wind power tender in Morocco. There are five wind parks involved ranging from 100 MW to 300 MW. [SeeNews Renewables]

Sunset in the Sahara by Christopher L. on flickr.com CC BY 2.0
¶ While an area within 12.5 miles (20 km) of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant remains an exclusion zone, it is still unclear how many people have succumbed to or suffer from radiation-caused cancer diseases directly linked to the crippled plant. Almost 10% of people still live in temporary housing. [RT]
US:
¶ Array Technologies, Inc, a provider of solar tracking systems, announced the commission of that the 45 MW Sandstone solar PV project in Florence, Arizona. Sandstone is owned and operated by sPower. It is a ground-mounted single-axis tracker photovoltaic installation. [solarserver.com]

Sandstone Solar has more than 182,000 JinkoSolar PV modules mounted on ATI’s trackers. Image: Salt River Project
¶ In 2015, Minnesota generated 21% of its electricity from renewable energy, including wind, solar, hydro and biomass. A decade ago, it was at just 6%. The state is well on pace to exceed its Renewable Energy Standard of 25% by 2025, according to its Department of Commerce. [Hometown Focus]
¶ Colorado regulators approved Xcel Energy’s $91-million plans for two battery test sites. The projects, part of the company’s Innovation Clean Technology demonstration project program, will be used to test the use of batteries and solar power for microgrids. [Utility Dive]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 10, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ Estimates from the Oxford Martin Future of Food Program published in The Lancet say changes in diets and bodyweight from reduced crop productivity could kill more than 500,000 adults in 2050. Reduced fruit and vegetable intake could cause twice as many deaths as under-nutrition. [CleanTechnica]

‘What do I water next…’ by Dennis Jarvis, via Flickr
World:
¶ SkyPower and Sachigo Lake First Nation have collaborated to develop a multitude of utility-scale solar photovoltaic projects in Ontario. The partnership is in line with the Ontario Ministry of Energy’s mandate to involve First Nation and Métis communities in new projects. [Power Technology]
¶ The International Renewable Energy Agency says 45% of China’s power plants rely on fresh water and are located in areas of high water stress. Scaling up renewable energy and introducing improved plant cooling technologies can reduce water-intensity by up to 42% in 2030. [pv magazine]
¶ Siemens announced an agreement with the government of Morocco to build a €100-million-plus ($110 million) wind turbine rotor blade factory in the North African country. Siemens expects to begin construction work on the facility as early as the spring of 2016. [SeeNews Renewables]

Siemens wind turbine blades.
Source: Siemens. License: All rights reserved
¶ Global clean energy research firm Mercom Capital Group said India will add nearly 4,000 MW of solar power in 2016, up from 2,133 MW it added in 2015. Mercom’s CEO said, “The Indian solar sector is finally coming out of hibernation.” This follows increases of 142% in 2015 from 2014. [Livemint]
¶ France closed 2015 with 421 biogas-fired plants, with a total of 365 MW of electricity generation capacity, recently published data of the ministry of energy shows. Last year, France added 40 MW of new capacity, confirming the steady growth levels observed from 2011 to 2014. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ High Wind has highlighted the role its Boom Lock technology, with reduced sensitivity to weather, can play in reducing the cost of energy for offshore wind. The company said its component lifting system could contribute to LCOE savings due to reduced vessel use and earlier power generation. [reNews]

The Boom Lock in action (High Wind)
¶ France is to begin closing the Fessenheim nuclear power plant this year. The French Government’s decision following criticisms from the Swiss and German governments over the plant’s safety. Reports had indicated a 2014 incident was worse than the French Government claimed. [Power Technology]
¶ In the UK, threatened animals need all of the habitat they can get, even if it’s under solar panels. That’s the idea behind a joint project by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds and alternative energy firm Anesco that aims to create and restore natural habitats at solar farm sites. [TakePart]

Solar panels in England (Photo: Getty Images)
¶ More than 10,000 (and perhaps as many as 66,000) excess cases of cancer are expected among residents of the Fukushima area and elsewhere in Japan, because of radiation exposure from the March 11, 2011 Fukushima Disaster, according to the report, 5 Years Living With Fukushima. [Medscape]
US:
¶ Twenty-one teenagers appeared in an Oregon courtroom to challenge the federal government over what they claim is a failure to protect them from the impacts of climate change, while several hundred schoolchildren protested outside. The case is just one of a large group of similar cases. [The Guardian]

Children protesting outside the courthouse in Eugene, Oregon. Photograph: Matthew O Berger for the Guardian
¶ Three of Nevada’s largest casino companies have recently announced plans to use more renewable energy. Twenty acres of sun-catching glass sit atop the Mandalay Bay convention center, and when new installations are complete, it will become the biggest rooftop solar array in the US. [edie.net]
¶ Burlington has been named one of three finalists in the Earth Hour City Challenge by the World Wildlife Fund, based on Burlington Electric Department’s 100% renewably-sourced generation accomplishment. It will compete for the title of US Earth Hour City Capital this spring. [Vermont Biz]

Burlington waterfront
¶ A proposed New York state subsidy for nuclear power will come too late for the James A FitzPatrick plant near Oswego. An Entergy vice president told the state Public Service Commission that the subsidy will not affect company plans to shutter the plant by January 2017. [Albany Times Union]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 9, 2016
World:
¶ Scotrenewables is trying out a turbine that looks like a yellow submarine. The 35-meter-long device was built at the Harland and Wolff shipyards in Belfast, best known as the birthplace of the ill-fated Titanic. The device is considered to be unlikely to have effects on sea life. [Deutsche Welle]

Scotrenewables turbine
¶ Until recently, virtually the only choice available to developers looking to build under the Australian government’s renewable energy target was wind energy. That is now changing. Within a year or two, large-scale solar farms may be able to compete with wind energy on costs. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A new 767-kW solar power project was recently completed in the Pacific nation of Vanuatu, marking the latest undertaking performed by the United Arab Emirates-Pacific Partnership Fund. The fund is a $50 million initiative managed by Masdar, Abu Dhabi’s renewable energy company. [PV-Tech]

The Vanuatu project will help displace 896 tonnes of CO2 emissions. Image: Masdar
¶ Kokam Co Ltd, has announced the deployment of two Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide Energy Storage Systems in Korea. One of the two systems is 24-MW, and the other is 16-MW. They will provide storage capacity for grid frequency regulation. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
¶ Edinburgh tidal developer Nova Innovation deployed the first 100-kW turbine that forms part of the Shetland Tidal Array. The M100 turbine is now delivering power to the Shetland grid following operations and testing. Plans for the array include a total of five turbines. [reNews]

M100 tidal turbine (Nova Innovation image)
¶ According to estimates published by the International Hydropower Association earlier this month in its latest briefing, the world’s total installed hydropower capacity reached 1,211 GW, thanks to 2015 installation figures of 33 GW of hydropower and 3.2 GW of pumped storage. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The death rattle of coal industry grew a little louder when JPMorgan Chase announced they will no longer finance new coal operations in the developed world. The bank joins a growing list that are cutting ties with coal, including Bank of America, Citigroup, Morgan Stanley, and Wells Fargo. [Grist]

Coal plant in china. Shutterstock image.
¶ A Japanese court ordered Kansai Electric Power to shut down two nuclear reactors in Takahama, after complaints by local residents about the safety of the plant. This is the first ruling issued in Japan against an operating nuclear plant, according to media. The company says it will appeal. [BBC]
¶ Threatened wildlife including turtle doves and skylarks could benefit from a scheme which has been launched to create natural habitats at solar farm sites. Wildlife charity RSPB and clean tech company Anesco aim to boost wildlife at the firm’s solar farms across England and Wales. [Yorkshire Post]

A skylark
US:
¶ Nearly 18 GW of electric generating capacity was retired in 2015. More than 80% of the retired capacity was conventional steam coal. The coal-fired generating units retired in 2015 tended to be older and smaller in capacity than the coal generation fleet that continues to operate. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Liquid Light is a startup company pioneering a process to convert carbon dioxide into chemicals that can be used to make consumer products. The company developed a catalyst that can combine carbon dioxide with water and electricity, to make liquid fuels and chemicals to replace petroleum. [CNN]

Emily Cole, co-founder and chief science officer of Liquid Light.
¶ The developer of a planned $1.6 billion offshore wind farm in Hawaii waters is moving ahead with its project after federal regulators accepted the 400-MW project’s lease application this week. Progression Hawaii Offshore Wind Inc plans to develop the project 10 miles off West Oahu. [Pacific Business News]
¶ Renewable energy firms SolarCity and NRG Energy plan to install rooftop solar on 184 stores and distribution centers of major grocery chain Whole Foods Market. A senior solar analyst at GTM Research told PV Tech that SolarCity would likely install lat least 15-MW, while NRG will account for 13.8MW. [PV-Tech]

Whole Foods has already piloted solar projects with SunEdison. Credit: SolarCity
¶ In Schuyler County, New York, sheriff’s deputies made 57 arrests Monday morning at the gates of the Crestwood Midstream facility. Environmental activist Bill McKibben was among those arrested. They were protesting intended storage of liquid petroleum gas in a salt dome. [Finger Lakes Times]
¶ After 116 days, the Fossil Free MIT sit-in has ended with the announcement of a deal on climate action. The longest ever sit-in for fossil fuel divestment concluded when an agreement was reached between student activists from Fossil Free MIT and MIT’s Vice President for Research. [CleanTechnica]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 8, 2016
Opinion:
¶ The Block Island Offshore Wind Project is Just the Beginning • Offshore wind and Block Island are a match made a heaven. But the island isn’t so unique. Many of the circumstances that make offshore wind so perfect for Block Island are also true up and down the Atlantic Coast. [Huffington Post]

Offshore wind farm. Photo: Stanford University
Science and Technology:
¶ A joint research team from Los Alamos National Laboratory and the University of Milano-Bicocca in Italy has a fresh approach to solar power. Working with quantum dots, the team achieved a breakthrough in solar-concentrating technology that can turn windows into electric generators. [Energy.gov]
World:
¶ A report tracks the technological advances and innovative business models which have emerged to transform the lives of millions through affordable modern solar energy services. It shows that the off-grid solar industry is benefiting from a wave of development partners, and investors. [CleanTechnica]

Image via Lighting Global
¶ More than half a million plug-in electric vehicles were delivered to buyers globally in 2015 – just under 540,000, to be nearly exact. These new numbers represent a roughly 70% increase over the figures for 2014, and that’s after the 2014 figures represented a roughly 50% increase on the 2013 ones. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Developers Vattenfall and ScottishPower Renewables are eyeing over 5 GW of offshore wind farm projects off the UK coast. The Crown Estate has signed off on final plans for Round 3 offshore wind farms. SPR has committed to two new projects of up to 800 MW in the East Anglia zone. [reNews]

Kentish Flats offshore wind farm (Vattenfall image)
¶ In the Philippines, Renewable energy company Citicore Power today inaugurated its 18-MW solar power project in Bataan. The start of the new solar station comes on the heels of the inauguration of the first phase of its other 25-MW solar facility in Silay, Negros Occidental in late February. [Rappler]
¶ After battling radioactive water leaks for five years at Japan’s crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant, the utility that ran it says it will need another four to finish the job. The contaminated water, now exceeding 760,000 tons and still growing, has been a major challenge. [Business Standard]
US:
¶ A Nevada-based data center operator, Switch, would convert a pyramid-shaped building that once housed a research center near Grand Rapids into a data center that operates 100% on renewable power. The Michigan Public Service Commission will review the contract. [Crain’s Detroit Business]

Data center operator Switch will open a super green facility in Grand Rapids.
¶ An amendment to the Energy Modernization Act of 2015 introduced by US Senator Susan Collins, a Republican from Maine, defines forest bioenergy is carbon neutral and biomass as renewable. The amendment does not address a number of details relating to the issue. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Businesses made deals to acquire 3.4 GW of renewable energy in 2015, equivalent to half of North Dakota’s entire power capacity. Of that amount, two-thirds came from first-time buyers, according to figures from the nonprofit Rocky Mountain Institute, which facilitates such deals. [National Geographic]

More companies are relying on wind farms, such as these near Sweetwater and Abilene, Texas, for their electricity.
¶ Southern Power announced acquisition of its second solar project in Texas and its 35th generating facility overall, the 120-MW East Pecos Solar Facility. It will be located on about 1,000 acres in Pecos County and is expected to consist of approximately 1.2 million thin-film PV modules. [Power Online]
¶ The Florida Supreme Court is set to weigh in on a controversial ballot measure that purports to strengthen the legal rights of homeowners with rooftop solar panels. But the measure was created by an organization financed by the major electric utilities and groups with ties to the Koch brothers. [Grist]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 7, 2016
Opinion:
¶ Australian coal v renewables: how much will it cost to bring electricity to India’s poor? • The Australian government continues to claim that coal from such sources as Queensland’s Galilee Basin will play a vital role in bringing cheap energy to developing nations. But is that really the case? [EconoTimes]

Renewables could be a better answer to India’s power problems.
¶ Lessons from Fukushima • Five years on, the 3/11 master narrative is still under construction. The response to the triple disaster in 2011 showed the world the best of Japanese society: orderly, humane and resilient. It also exposed the governance deficit, and that needs to be fixed. [East Asia Forum]
¶ Is the Hinkley Point C nuclear plant project about to unravel? From the outside looking in, EDF’s bid to build a nuclear power station at Hinkley Point in Somerset seems to lurch from the ludicrously improbable to the absurd. Given typical overruns at Hinkley, EDF would be in trouble. [ITV News]
Science and Technology:
¶ Researchers from the Quantum Wave Microscopy Unit at Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University published a proposal for a submerged marine turbine that could harness the energy of the Kuroshio Current, an ocean current in the North Pacific Ocean. [CleanTechnica]

Ocean turbine proposed by Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology
World:
¶ Daimler AG will put €500 million into the creation of a second lithium-ion battery production facility in Germany, according to recent news from the company. The facility will produce lithium-ion batteries to be used in electric vehicles and hybrids under the Mercedes-Benz brand. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In the survey about plans for Japan’s future energy policy conducted before the fifth anniversary of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident, 44.6% sought cuts in Japan’s dependence on nuclear power and 21.0% requested the eventual abolishment of nuclear power generation. [Japan Today]
¶ Japan’s prime minister revealed a plan to make Fukushima Prefecture a center for development of hydrogen technology. Facilities will be developed in the prefecture to fuel 10,000 fuel-cell cars by 2020. The hydrogen would be generated by renewable energy. [The Japan News]

Nunobiki Plateau Wind Farm. Photo from Nunobiki Wind Farm. CC BY-SA 2.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Myanmar’s Ministry of Electric Power signed a wind power deal with China Three Gorges Corporation last week. The two parties signed a memorandum of agreement for a wind turbine project in the Chaungtha area of Ayeyarwady Region, which will generate 30 MW of electricity. [Myanmar Times]
¶ The Federal College of Agriculture in Akure, capital of Nigeria’s Ondo State, is ready to support farmers seeking help to use gasses from cow manure to generate renewable energy. It will help bridge the gap in power shortage with biogas technologies in rural and semi-urban areas. [The Nation Newspaper]
¶ Wind power generation in Scotland was enough to meet 41% of the country’s entire electricity needs for the month of February, WWF Scotland said today. Scotland’s wind turbines supplied 929,417 MWh of electricity last month, enough to power 109% of Scottish households. [SeeNews Renewables]

Wind farm in Scotland. Author: Neil Williamson. License: Creative Commons, Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic.
¶ The nuclear disaster has cost Japanese taxpayers almost $100 billion despite government claims TEPCO is footing the bill, according to calculations by the Financial Times. Almost five years after the disaster, the figure shows how the public have shouldered most of the disaster’s cost. [CNBC]
US:
¶ One of the reactors at the Oconee Nuclear Station was shut down after a fire and explosions damaged a transformed on site. The operator declared the incident “unusual” but emphasized there was no threat of radiation release. Emergency crews contained the fire. [RT]
¶ A NOAA study shows that by building new high-tech transmission lines, the US could cut energy sector global warming emissions by 80% within 15 years, while keeping consumer costs low and meeting increased demand. The idea came from studying the national weather map. [PRI]

High-voltage direct current transmission lines could help transfer electricity over long distances. Credit: Chris Hunkeler/Flickr
¶ Rooftop solar and distributed energy champions have advanced a ballot initiative to restore Nevada’s retail-rate net metering policy. However, they are facing legal challenges from a utility-backed PAC. If nothing else, a lot of time and money will be spent on this challenge. [CleanTechnica]
¶ SUN DAY Campaign, a non-profit focusing to sustainable energy, says the renewable energy (biomass, geothermal, hydropower, solar, wind) growth in the US has been promising, but the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has failed in their forecasts on the industry. [Greentech Lead]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 6, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ The National Snow and Ice Data Center reports that Arctic sea ice extent is running not only well below average, but also below levels seen during 2012, which went on to set the all-time record for lowest Arctic ice extent (which occurs in the late summer or early fall). [Bowling Green Daily News]

Icebergs float in a bay off Ammassalik Island,
Greenland. (AP photo / John McConnico)
World:
¶ Electrification has been done in 6,000 of the 18,500 villages in India that had been without electricity, and the renewable energy capacity has reached 39.5 GW, a meeting chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi was told. Progress of the initiative is being tracked in real-time. [The Hindu]
¶ South Africa has ramped up its green credentials by unveiling the continent’s first solar-powered airport. George Airport will meet 41% of its energy demand from a solar system with 3,000 PV modules. Power is being turned on incrementally and will finally deliver 750 kW of power. [CNN]

The George Airport is located along South Africa’s
Garden Route, an area of outstanding natural beauty.
¶ In the Philippines, many solar players are participating in the race to qualify for feed-in tariff incentives. Recently, three more solar projects are joining the race ahead of a government-imposed deadline, adding at least 200 MW of supply to the country’s power grid. [Philippine Star]
¶ Dam building on the lower Mekong River appears to be accelerating at a dangerous speed. People who live on the Mekong and its tributaries know that electricity is not the only product of the mighty river. The river’s many valuable assets include the world’s largest inland fishery. [Chiang Rai Times]

Boats on the Mekong River near the proposed Pak Beng Dam
site, downstream of Chiang Khong district, Chiang Rai.
¶ To respond swiftly to increasing demands of EV batteries, the LG Group’s battery unit is ramping up the production while mulling a plan to build an additional overseas production bases. The company has plants for lithium-ion batteries in Holland, Michigan and Nanjing, China. [The Korea Herald]
¶ In the early 1970s imported oil supplied 92% of Denmark’s energy. Today Denmark’s electric grid is over 40% renewably powered, and the country is aiming to reach 100% renewable electricity by 2035. It has a goal of 100% renewable energy in all sectors by 2050. [The Ecologist]

Wind turbines in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Photo: CGP Grey via Flickr (CC BY).
¶ Ontario Progressive Conservative Leader Patrick Brown says he favors putting a price on carbon to help deal with climate change. In his keynote address to more than 1,600 convention delegates, Brown said he became a Progressive Conservative because of the environment. [National Observer]
US:
¶ This winter was a no-show throughout most of Alaska, forcing officials in charge of the iconic sled dog race known as the Iditarod to bring seven rail cars of snow from Fairbanks to Anchorage, where the race starts. A tarp will cover the snow in Anchorage in case it rains. [Mashable]

Iditarod start in Anchorage, 2008. Photo by David Weekly
from Cupertino, CA. CC BY-SA 2.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ A scuba diver is suing Florida Power and Light after he became the second person to be sucked into an intake pipe at the St Lucie Nuclear Power Plant. He saw a yellow buoy, but no indication of any danger, so he went into the water to investigate it. The pipe led to a reservoir, where he resurfaced. [TheBlaze.com]
¶ In 2007, Minnesota lawmakers adopted aggressive renewable energy goals, calling for the state to produce 25% of its electricity from renewable energy by 2025. Now, a report by the Minnesota Commerce Department says the state could beat its renewable energy goals. [TwinCities.com-Pioneer Press]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 5, 2016
World:
¶ Alberta plans to issue its first competition for renewable electricity projects in late 2016. The provincial government has asked the Alberta Electric System Operator to develop a renewable electricity incentive program. Engagement with interested parties will start immediately. [reNews]

The Oldman 2 wind farm in Alberta (Mainstream image)
¶ Germany demanded that France close down its oldest nuclear plant, Fessenheim, near the German and Swiss borders. It is just one of several ageing atomic plants that are unsettling France’s neighbours. Reports claimed a 2014 incident at Fessenheim was more serious than earlier reported. [The Daily Star]
¶ A parliamentary committee in Sweden proposed a way to bring the nation to carbon neutrality by 2045. It would achieve this huge goal by reducing domestic emissions by 85% from 1990 levels. The rest could be offset by investing in international projects that cut carbon emissions. [CleanTechnica]

Image by Holgar Ellgard (CC BY-SA 3.0 unported license)
¶ The Indian Railways has announced plans to install 150 MW of solar PVs. Of this, 50 MW would be in rooftop solar projects on railway stations. The remainder would be 100 MW of PVs in utility-scale arrays. The move is part of a goal to have 100 GW of solar in India by March 2022. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Eon’s German networks were home to 32 GW of renewable capacity at the end of 2015, more than one-third of the country’s installed renewables. In total, Germany has 96 GW of installed renewables capacity, 34% of which is connected to Eon’s networks. Renewable installation varies by region. [reNews]

Eon image
¶ China may miss its goal of 58 GW of nuclear capacity by 2020 because too few reactors are being built, the chairman of China General Nuclear Power Corp has said. The country may start seven new reactors this year and its domestically designed model will be ready for export in three years. [Daily News]
¶ British Columbia may have surplus renewable power to sell to Alberta, but the premier of Alberta said her government won’t be buying it unless it can get an oil pipeline to the coast. BC’s Energy Minister said he didn’t have a problem with linking a potential power deal to pipeline support. [Calgary Herald]
US:
¶ Actions by two separate state legislatures could lead to the future closure of all four coal-fired power plants at Colstrip, Montana. On Wednesday, Oregon’s legislature passed a bill to eliminate use of coal-fired electricity within 20 years. Washington state followed suit on Friday. [KTVQ Billings News]

Colstrip power plant.
¶ Supreme Court Chief Justice John G Roberts Jr rejected a request to stay the Mercury and Air Toxic Standards rule, which was adopted by the EPA three years ago to tighten restrictions on a class of harmful pollutants, that are byproducts of burning coal. [Washington Post]
¶ Critics insist the latest version of what is called the “Rocky Mountain Power” bill at the Utah Legislature would mean lights out for rooftop solar development in the state and pull the plug on existing solar power generation. The bill passed the Utah Senate and awaits action in the House. [Deseret News]

Brandy Smith, with Utah Clean Energy, speaks at
a solar advocates rally. Tom Smart, Deseret News
¶ Entergy customers in New Orleans will begin paying their share of the $948 million purchase of an Arkansas natural gas power plant starting this year. The typical New Orleans customer will see their monthly bill increase by about $5 when the new charge kicks in later this spring. [NOLA.com]
¶ The offshore wind industry has hopes for establishing itself in the US after years of disappointment. European offshore wind companies are increasingly committing to projects along the East Coast. That, industry leaders said, is evidence a US offshore wind industry is finally on its way. [Eagle-Tribune]

First foundation jacket installed at Deepwater Wind,
near Block Island. (AP photo / Stephan Sevoia)
¶ The New England Clean Power Link transmission line has got two of the three key permits needed to begin construction. TDI New England’s proposed $1.2 billion transmission line would carry 1,000 MW of Canadian hydro and wind power into Vermont. [Corporate Knights Magazine]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 4, 2016
World:
¶ The Canadian province of Ontario will invest $100 million into “green energy” projects in its push to reduce greenhouse gas emissions 37% by 2030. Ontario’s premier said this will help the province cut greenhouse gas emissions while improving local business prospects. [CleanTechnica]

Ontario wind turbine. Image via Shutterstock
¶ German utility E·ON will partner with Solarwatt GmbH to develop and release modular energy storage systems based on Solarwatt’s MyReserve battery. The first models are expected in the next few months. E·ON’s domestic marketplace has over 1½ million private rooftop PV systems. [CleanTechnica]
¶ India gave a big clue about how serious it is about energy transformation policy when it doubled a national tax on coal. The increase, to ₹400 per tonne ($6/tonne), applies to all domestic and imported coal. The coal tax represents 30% of the wholesale price of domestic coal. [Corporate Knights Magazine]
¶ Indonesia’s importance as a solar market looks set to grow following the announcement of a 5-GW goal. At the Bali Clean Energy Forum, the Minister of Energy and Mineral Resources launched a program for a national energy mix with up to 23% renewable energy by 2025. [Solarplaza]

Solar PVs in Indonesia
¶ Dulas has begun construction on two medium-scale run-of-river hydro schemes in central Scotland. The projects have a total capacity 1.3 MW and are being developed for existing clients seeking to expand their clean energy portfolios ahead of Scotland’s 2020 targets. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
¶ Many British companies are missing out on the benefits of the switch to renewable power, according to a new report from energy supplier SmartestEnergy. The report highlights how businesses can secure multiple currently overlooked benefits from procuring clean electricity supplies. [Business Green]

SmartestEnergy report outlines the gains businesses can enjoy from switching to a cleaner electricity supply
¶ In a first ministers’ summit, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau won agreement from the premiers on a broad strategy to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions and build Canada’s clean economy, but could not gather enough support for a national minimum carbon price. [The Globe and Mail]
¶ China plans to set up a market for renewable energy certificates to increase the use of cleaner energy and reduce its reliance on coal. Power suppliers will be able to trade “green certificates” that represent the proportion of non-hydro renewable energy that they generate. [Reuters]

Workers install solar panels on the rooftop of a company in Shangrao, Jiangxi province, China, October 11, 2015. Reuters / Stringer
¶ Greenpeace said the environmental impact of the Fukushima nuclear crisis on nearby forests is just beginning to be seen that after five years, and they will be contaminated for years. Radiation forced tens of thousands of people from their homes, many of whom will likely never return. [Malay Mail Online]
¶ Almost 50,000 homes in Canberra will be powered by renewable energy thanks to a new wind farm contract awarded by the Australian Capital Territory Government. The Sapphire Wind Farm will have 32 wind turbines. The project is expected to be complete by 2018. [Australia Network News]

A new wind farm will provide power to Canberra.
US:
¶ A group of engineers in the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission say they have identified a design flaw in nearly all nuclear reactors in the country that should result in their mandatory shutdown unless operators fix the problem, Reuters reports. The issue became known in 2012. [Utility Dive]
¶ The US energy storage market grew a phenomenal 243% in 2015, the largest year on record, according to new figures from GTM Research. The US energy storage market deployed 112 MW in the fourth quarter, bringing the full year 2015 to a record 221 MW. The figure for 2014 was 65 MW. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Xcel Energy completed a $39-million high-voltage transmission project in Texas, allowing more wind and solar onto the grid. The new Bower-Howard transmission project on the Panhandle power grid would meet growing electricity demand in the area. The 115-kV was energised on Wednesday. [reNews]

Grid infrastructure. Image: Arteche
¶ Nearly 49% of electricity provided to the Big Island by the Hawaii Electric Light Co in 2015 came from renewable energy, according to a statement from HELCO’s parent company, Hawaiian Electric. Maui County reached 35% renewable and Oahu is at nearly half that level. [Honolulu Civil Beat]
¶ A bird dropping appears to have caused the temporary shutdown of part of the Indian Point nuclear plant in upstate New York. A report issued by the plant’s owner, Entergy, said a bird “streamer,” a long stream of excrement from a large bird, was the cause of a three-day shutdown in December. [CNN]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 3, 2016
World:
¶ The six-turbine Coonooer Bridge wind farm in the Australian state of Victoria has become the first operational wind farm from the Australian Capital Territory’s wind auction process. The 20-MW wind farm is expected to become fully operational this month. [SeeNews Renewables]

Wind farm in Australia. Author: Steven Caddy. License: Creative Commons, Attribution 2.0 Generic
¶ According to a study led by the University of Leeds, about 80,000 air quality-related deaths are prevented each year as a direct result of the introduction of European Union policies and new technologies. They led to a 35% reduction in fine particles in the atmosphere since 1970. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In Scotland, 70% of those polled want to see more renewable energy such as wind, solar, wave and tidal, and two-thirds agreed that the next government should “continue to take forward policies that tackle greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.” Only 19% would prioritize fracking. [RenewablesBiz]
¶ Australian firm Genex Power Ltd’s 150-MW solar PV and 330-MW pumped-storage hydropower project in North Queensland has been named a “Prescribed Project,” streamlining its approvals process. The scheme, with a 185-km transmission line, will cost $424 million (US). [SeeNews Renewables]

The project will be at the site of the historical Kidston Gold Mine. Source: Genex Power.
¶ Changes in UK government energy policy have chased off investors and may have added £120 a year to household bills, according to a parliamentary report. Funding U-turns on windfarms and energy efficiency schemes have reduced investor confidence and increased funding costs. [The Guardian]
¶ Indian automobile manufacturer Tata Motors Ltd has joined RE100, a global initiative of businesses committed to 100% renewable electricity. Tata Motors is the second Indian company to join the campaign, after Infosys. This brings the total number of RE100 members to 54. [SeeNews Renewables]

Good Energy has unveiled a revised design for the Big Field Wind Farm.
¶ Plans were unveiled for a community-owned Cornish wind farm that could be the first in the UK to operate without government subsidy. New plans have the same number of turbines of the same height as an earlier scheme, but new technology allows a 50% increase in output. [Windpower Engineering]
¶ Geneva is taking legal action over a French nuclear reactor for “endangering lives and polluting water.” Some 70 km from Geneva as the crow flies, Bugey, in the Ain department, is one of France’s oldest nuclear power plants, having come into service in 1972. It supplies about 4.5% of French electricity. [The Local.ch]
¶ A geological fault running directly beneath a nuclear reactor at the Shika power plant may be active, a panel of geological experts for the Nuclear Regulation Authority said. If that assessment is accepted, the utility will be unable to restart the unit, the No 1 reactor at the plant. [The Japan Times]
US:
¶ Massachusetts House Speaker Robert DeLeo made it official that the omnibus energy bill scheduled to come up for a vote in April will include provisions to encourage the development of offshore wind power and create a competitive procurement process for renewables. [CommonWealth magazine]

Wind turbines in Gloucester, Massachusetts. Photo by Fletcher6. CC BY-SA 3.0 unported. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ Mississippi Power, Hannah Solar and the US Navy have broken ground on a 23-acre solar project of over 3 MW at Seabee Base, in Gulfport. Two other projects approved by the state commission include a 50-MW solar station in Hattiesburg and a 52-MW solar project in Sumrall. [Solar Industry]
¶ The Oregon Assembly passed a bill setting a target of 50% renewables by 2040 and ending coal-fired power supply in the state by 2035. The House passed Senate Bill 1547, also known as the Clean Electricity and Coal Transition plan, and the Senate repassed it the next day. [SeeNews Renewables]

Solar panels. Author: Oregon Department of Transportation. License: Creative Commons, Attribution 2.0 Generic
¶ A Japanese-owned company has received construction financing and has started work on a 27.6-MW solar energy farm in Oahu. The project, which is scheduled to be completed and operational by the end of the year, will be one of the largest solar PV projects in Hawaii. [Pacific Business News (Honolulu)]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 2, 2016
Science and Technology:
¶ After seven months, Solar Impulse 2 has returned to the sky as it prepares to resume its record-setting round-the-world flight. The huge, sun-powered plane, which smashed the longest solo record last summer from Japan to Hawaii, flew a 90-minute maintenance and equipment-checking flight. [ABC 57 News]

After seven months, Solar Impulse 2 has returned to the sky as it prepares to resume its record-setting round-the-world flight.
Opinion:
¶ “Base load” power: a myth used to defend the fossil fuel
industry • At a conference in Houston, leaders of the global fossil power industry were shocked to hear the chairman of the biggest network owner in China dismiss the importance of coal, oil, and “base load” power. [RenewEconomy]
World:
¶ The Government of Western Australia will commit $300,000 to investigate building a micro-grid powered by renewables for the coastal town of Kalbarri. The town has experienced several extended and costly power outages, caused by problems with long transmission lines. [ABC Online]

A wind turbine at Kalbarri that would be used to power the proposed electricity micro-grid planned by the State Government.
¶ Oil giant Shell is being sued in London for the second time in five years over spills in the Niger Delta. Two communities are claiming compensation and want Shell to clean up their land. The Ogale community of about 40,000 people, who are mainly farmers or fishermen, are some of the claimants. [BBC]
¶ The Clean Energy Canada’s annual Tracking the Energy Revolution report found that renewables excelled in a complex economic environment, with 2015 marking the first time developing countries invested more money on clean energy than developed countries did. [edie.net]

The report said developing countries spent $167 billion on clean energy in 2015 compared to developed countries’ $162 billion
¶ China, the United States, and Japan are set to lead the way in terms of solar PV installations in 2016, as the EU solar industry slows. Additionally, by the end of 2016, cumulative global installed solar PV systems will surpass 310 GW, compared to only 40 GW at the end of 2010. [CleanTechnica]
¶ China is surging ahead in switching to renewables and away from coal. Officials say this will allow it to surpass its carbon emissions targets. The country’s solar and wind energy capacity soared last year by 74% and 34% respectively compared with 2014, according to government figures. [New Scientist]

China installed a whopping 32.5 gigawatts of wind energy
capacity last year. Xu Yu / Xinhua Press / Corbis
¶ Scientists have written an open letter to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and the premiers saying spending on fossil fuel infrastructure may not be the most productive use of resources. Trudeau and the premiers will start talks on a national climate-change strategy this week. [Huffington Post Canada]
US:
¶ The US Energy Information Administration has forecast additions to the US power grid for 2016. They say it will see the first new nuclear power in 20 years, with 1.1 GW. But that will be dwarfed by renewable power sources, which will account for nearly two-thirds of 2016’s new capacity. [Ars Technica]

¶ A lot of new utility-scale solar being built is not required under state Renewable Portfolio Standards. GTM predicts that more than 6 GW of non-RPS utility-scale solar will come online in 2016. The entire solar sector saw 4.1 GW installed in 2015, and that was a record-breaking year. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Hydropower, long the leading source of renewable energy in the United States, is slated to be overtaken by wind generation by the end of 2017, Generation Hub reports. At the end of 2015, wind accounted for 6.33% of the US power mix. Hydro made up 8.41%, but wind is growing quickly. [Utility Dive]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
March 1, 2016
World:
¶ Work is nearing completion on what will soon be Europe’s largest floating solar power farm. But few are likely to see the 23,000 solar panels on the Queen Elizabeth II reservoir near London. It is invisible to all but Heathrow passengers and a few flats in neighbouring estates. [The Guardian]

Divers fix anchors onto the bed of the reservoir.
Photograph: Martin Godwin for the Guardian
¶ SunEdison and a subsidiary of the state-owned Chinese company Jinneng Group, Jinergy Clean Energy Technology Company, are partnering for the creation of a 1.5 gigawatt integrated N-type mono-crystalline hetero-junction solar cell production facility in Shanxi, China. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The 56 MW Moree Solar Farm is feeding electricity into Australia’s National Electricity Market network. Spain’s Fotowatio Renewable Ventures developed and constructed the project. It deploys single axis tracking and is the largest solar project using crystalline silicon PV modules. [pv magazine]
¶ The 63.3-MW Calatagan Solar Farm is the largest solar facility completed in the Philippines to date. Solar Philippines, a renewable energy firm led by 22-year-old entrepreneur Leandro Leviste, developed, financed and constructed this solar farm at a cost of $120 million. [Inquirer.net]

A 160-hectare farm in Calatagan, Batangas, Philippines.
Contributed photo
¶ A group of prominent business leaders, including Ottawa’s growth guru Dominic Barton, is urging Canada to accelerate the transition to a cleaner, lower-carbon economy by pursuing a society-wide game plan. The leaders will introduce a virtual think tank called Smart Prosperity. [The Globe and Mail]
¶ 70% of Scottish voters polled wanted to see more renewable energy such as wind, solar, wave and tidal. Respondents had been asked whether there should be continued development of renewables, the extension of the life of fossil fuel plans, use of shale gas or building new nuclear plants. [Energy Voice]
¶ Wind farms in Spain produced 6,091 GWh in 2015, up by 2.4% year-on-year, and helped reach a total renewable energy share of 54.6% for February. Despite a lack of new capacity additions, Spanish wind power accounted for 30.2% of the country’s total power for the month. [SeeNews Renewables]

Wind farm. Author: TraumTeufel666.
License: Creative Commons, Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic.
¶ ScottishPower has plans to more than double the size of its 440-MW Cruachan hydro power station, though development is dependent on Government guaranteed pricing. The estimated £400 million development would need a floor price on its use in return for a cap on profits. [Scottish Daily Record]
¶ Construction of Britain’s first nuclear power plant in 20 years should be delayed until 2019 so problems with a similar reactor design in France are solved, the CFE-CGC Energy Union said. Unions occupy six of the 18 seats on the board of EDF, which is yet to vote on a final investment decision. [BBC]
US:
¶ The US produced over 190 million MWh of wind power in 2015, more than any other country in the world, even as China has nearly double the capacity, the American Wind Energy Association said. More than 31% of Iowa’s in-state electricity generation came from wind. [SeeNews Renewables]

Source: American Wind Energy Association
¶ A wide coalition of utilities, solar installers, consumer advocates, and environmentalists in Maine have introduced a bill in the state legislature to advance solar growth in the state and replace the net metering policy with a market-based “pay for production” program. [Utility Dive]
¶ Owing to the very harmful effects of common air pollution on fetal and childhood development, a large group of pro-life Christians in Texas, through the Evangelical Environmental Network, will be participating in the Pro-Life Clean Energy Campaign, according to a press release. [CleanTechnica]

Brazos Wind Farm, Texas.
Photo by Leaflet via a Wiki CC BY-SA 3.0 License
¶ The New York State Common Retirement Fund lost at least $5.3 billion over the last three years by remaining invested in fossil fuel holdings, instead of reinvesting in green companies. These are the findings according to a new report from Corporate Knights, an investment research company. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Two Wisconsin utilities announced projects that will roughly double the state’s solar capacity. Dairyland Power Cooperative agreed to purchase almost 19 MW from 12 new solar arrays. Xcel Energy has agreed to purchase up to 3 MW from community-owned solar gardens. [Chippewa Herald]
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power




































































































































































