Archive for August, 2017
August 31, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Harvey sparks debate over hurricanes, climate change” • The question, “Did climate change cause Harvey?” is not really the right one. A better way to frame thinking about the connection is through the question, “Does climate change make storms like Harvey more likely?” In several respects, the answer to this question is yes. [Houston Chronicle]

Flooded oil refinery (Photo: David J. Phillip, Associated Press)
World:
¶ Australian households and businesses are now generating enough electricity from solar panels on their roofs to power every home in Sydney. There are almost 2.8 million small-scale solar systems in Australia with a collective capacity of 6000 MW. It is a capacity the Clean Energy Regulator calls a remarkable milestone. [TheBull.com.au]
¶ While the disaster unfolding in Texas and Louisiana is of course worth keeping an eye on, it should be realized that there are disasters occurring elsewhere as well. More than 1,200 people have died across India, Bangladesh, and Nepal in recent days as a result of the flooding accompanying the worst monsoon season in years, according to recent reports. [CleanTechnica]

Monsoon flooding
¶ Siemens and several project partners have successfully tested a microgrid system in Germany that may help connect distributed renewable energy to consumers. The project, in Wildpoldsried, in the Allgäu region, is aimed to technically and economically optimize a smart energy system with distributed power generation, the company said. [reNews]
¶ India has barred state authorities from unilaterally cancelling or modifying solar power purchase agreements after six state governments pushed developers to lower tariffs, threatening to derail projects worth $7.5 billion. The government will impose a minimum penalty of 50% of the tariff on arbitrarily scrapped PPAs. [ETEnergyworld.com]

Solar power plant
¶ Methane leaks around oil and gas well boreholes in the North Sea may be much more common than was previously thought, according to research from the GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research Kiel and the University of Basel. Researchers say gas leaks at boreholes could constitute one of the main sources of methane in the North Sea. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Australian states and territories are powering ahead on developing policies that will meet the federal government’s internationally agreed greenhouse gas emission targets, with South Australia, the ACT and Tasmania leading the race. They are doing this despite being chastised by the federal government for unilateral action. [The Guardian]

Australian windfarm (Photo: Tim Phillips Photos | Getty Images)
US:
¶ The largest oil refinery in the US is shutting down as Hurricane Harvey causes more catastrophic flooding. The Port Arthur refinery, which is on the Texas-Louisiana border, is closing in response to worsening local flood conditions. In all, at least 12 refineries, a significant part of the US refining capacity, are currently offline. [CNN]
¶ A chemical plant near the flooded city of Houston is expected to explode and catch fire in the coming days. Forty inches (102 cm) of rainfall in the area flooded the site, cutting off its power, and back-up generators were flooded. The plant lost its ability to refrigerate chemical compounds that need to be kept cool to prevent explosion. [BBC]

Helicopter rescuing people in Beaumont (Reuters image)
¶ The flooding in the Houston area caused by Hurricane Harvey is just the latest problem for the troubled National Flood Insurance Program. After a series of major storms caused floods in the last 12 years, including Hurricane Katrina in 2005 and Superstorm Sandy in 2012, the Federally funded program is roughly $25 billion in debt. [CNN]
¶ Houston’s relaxed approach to development should not be blamed for Hurricane Harvey’s destruction, as critics are saying, but rather the unprecedented nature of a storm that dumped as much as 50 inches of rain on the city, say planning experts and engineers. Nevertheless, it is the third 500-year flood in Harris County in three years. [Washington Examiner]

Flood in Houston (AP Photo | David J. Phillip)
¶ The largest wastewater treatment agency in Rhode Island is on its way to getting all of its power from renewable sources after signing an agreement with a company building large solar farms in Coventry and Richmond. The Narragansett Bay Commission announced the deal with Green Development for 9.69 MW in two solar projects. [The Providence Journal]
¶ Cuttyhunk Island off Massachusetts is in its first summer with most of its electricity from PVs and battery backup. A microgrid system developed Solar Design Associates Inc has provided most the electricity for both Cuttyhunk residents and boats visiting its harbor. Cuttyhunk previously relied solely on diesel-powered generation. [Electric Light & Power]
¶ Engine and power firm, Cummins, has taken the wraps off its AEOS all-electric semi truck concept, beating Silicon Valley’s Tesla to the punch. Instead of a conventional 12-liter turbo-diesel engine, the standard Cummins AEOS uses a 140-kWh battery pack that gives it a range of around 100 miles (160 km) on a single charge. [CarAdvice]
¶ Southern Co and other utilities building the Vogtle nuclear expansion project in Georgia are prepared to finish the reactors but will lay out a set of assurances that must be met in a filing with state utility regulators, E&E News learned. The nuclear reactors at Plant Vogtle are the only ones under construction in the US, at least for now. [E&E News]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 30, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Conservative groups shrug off link between tropical storm Harvey and climate change” • Conservative groups with close links to the Trump administration have sought to ridicule the link between climate change and storm events, amid warnings from scientists that storms are being exacerbated by warming temperatures. [The Guardian]

Rescuing residents (Zachary West | Zuma | Avalon.red)
¶ “New solar plants now powering whole of Northern Cape” • Abengoa announced completion of Xina Solar One, its latest concentrated solar power plant in South Africa. A representative from the company said the project supplies clean electricity to 95,000 households. But utility Eskom refuses to sign power a producer agreement. [Daily Maverick]
World:
¶ Sweden recently announced that tax for renewable energy power generators over 255 kW would be reduced by 98%, and architects are innovating in response. Linköping apartment complex, located in Sweden’s Vallastaden district, generates more energy than it uses, thanks to a large roof-mounted photovoltaic array. [Interesting Engineering]

Linköping building (Kjellgren Kaminsky Architecture)
¶ Scientists from Germany and the US determined that rising temperatures due to climate change will have a dramatic impact on Europe’s electricity consumption patterns, putting strain on European power grids. Importantly, the report foresees a shift of annual peak demand from winter to summer in many countries by the end of this century. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Renault electric vehicles are providing second-life batteries for energy storage in Europe. Using them, Groupe Renault has installed two quick charging stations in Belgium and Germany with partner, UK-based Connected Energy. It’s the starting point of installing the E-STOR energy storage technology on highways in Europe. [Hybrid Cars News]

Renault charging
¶ Spanish renewable energy company Abengoa announced that it has connected to the grid the first 62 MW of PV generating capacity at the Cerro Dominador solar complex in the Atacama Desert in northern Chile. It is comprised of a 100-MW PV plant, along with Latin America’s first solar thermal plant of 110 MW capacity. [pv magazine]
¶ S&C Electric Canada and North Bay Hydro will install a microgrid at North Bay Community Energy Park in Ontario. S&C Electric will provide engineering, procurement, and contract management services for the automated microgrid. It will have solar panels, battery energy storage, and a GridMaster control system. [Power Technology]

Microgrid testing (Photo: Idaho National Laboratory | Flickr)
¶ China has reached its 2020 solar power target three years ahead of schedule. New figures published by solar industry firm Asia Europe Clean Energy Advisory revealed that China has already exceeded its 2020 target of 105 GW of installed solar capacity, after new builds in June and July pushed it up beyond 112 GW. [EURACTIV]
US:
¶ The Port of Long Beach in California has greatly reduced local air pollution levels, the most recent annual Emissions Inventory revealed. Compared to 2005 levels, it has reduced local diesel particulate matter air pollution by 88%, and nitrogen oxide air pollution by 56%. Local greenhouse gas emissions were also reduced by 22%. [CleanTechnica]

Port of Long Beach
¶ American Electric Power, Ohio Public Utilities Commission staff, the Sierra Club, and other stakeholders have reached a settlement agreement. Under its terms, AEP Ohio is to develop 900 MW of renewable energy, initiate an electric vehicle program, and protect consumers from monthly fixed-fee rate increases. [North American Windpower]
¶ In Florida, Duke Energy will build nine or more solar plants and delete a controversial nuclear charge from customer bills, according to a widely lauded plan. The utility has 1.8 million customers in 35 counties, but it has lagged behind other major utilities in solar energy, and it had drawn criticism for a pair of nuclear disappointments. [Orlando Sentinel]

Duke Energy Solar Plant (Russell Aerial Photography)
¶ Xcel Energy is asking the Colorado Public Utilities Commission to approve a plan that it hopes could lead to $2.5 billion in clean energy investments across the state. The plan, which has the support of 14 other groups, calls for shuttering two of its coal-fired power plants in Pueblo a decade earlier than planned. [Grand Junction Daily Sentinel]
¶ Amazon unveiled what the company says is the largest rooftop solar panel energy system in New Jersey on the 30-acre roof of its Carteret warehouse. The 22,000-solar-panel system will power the facility. The company said it is one of the country’s largest rooftop solar panel systems and it generates enough electricity to power 600 homes. [NJ.com]

Amazon array (Robert Sciarrino | NJ Advance Media for NJ.com)
¶ First Energy, a utility in West Virginia, wants its ratepayers to bail out a struggling coal-fired power plant. The Pleasants power plant, owned by an Ohio subsidiary, is failing to compete against less expensive sources. West Virginia’s utilities are regulated, and an ownership transfer to that state could help guarantee a positive rate of return. [Record Delta]
¶ The Kayenta Solar Facility, near the famed sandstone buttes of Monument Valley, is now producing electricity for the Navajo Nation. It generates enough electricity to power about 13,000 Navajo homes. This comes at a time when the tribe is bracing for the loss of hundreds of jobs as a nearby coal-fired power plant will close. [AZCentral.com]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 29, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Trump Rolled Back The Country’s Best Flood Protection Standards Two Weeks Before Harvey” • On August 15th, Trump signed an executive order rolling back various environmental rules in order to streamline approvals for infrastructure projects. One of them set a federal infrastructure standard to reduce the risk of flood damage. [Pacific Standard]

Waiting in a flood (Photo: Scott Olson | Getty Images)
¶ “Why We Won’t Be Ready for the Next Hurricane Harvey Either” • Houston is far from the only place in the US vulnerable to disastrous flooding as a result of bad policy. It happens in every state. And experts say sea level rise and increased precipitation related to climate change could exacerbate the problem in the coming years. [TIME]
World:
¶ A £2 billion wind farm off the coast of Scotland would create 2,000 construction jobs and more than 200 jobs every year of its lifespan, a study found. It suggests that over its 30 year lifetime, the Neart na Gaoithe project could generate an economic impact of around £827 million for the Scottish economy, equivalent to 0.6% of Scotland’s GDP in 2016. [Herald Scotland]

Neart Na Gaoithe Offshore Wind Farm
¶ A study produced by the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change shows that the percentage of PVs in the global power supply could be three times higher in 2050 than previously projected. The share of solar energy will likely range between 30% and 50%, instead of 5% to 17%, as had been suggested earlier. [Nanowerk]
¶ Saudi Arabia has issued a request for proposals to build a 400-MW wind farm at Dumat Al Jandal in the Al Jouf region of the country. The request was issued by the renewable energy project development office of the Ministry of Energy, Industry, and Mineral Resources. The project is supported by a 20-year power purchase agreement. [reNews]

Wind farm (Pixabay image)
¶ Power Ledger has launched a new form of bitcoin, a virtual currency allowing consumers to practice green energy trading in a new kind of renewable energy marketplace. The token-trading platform will enable consumers and developers to generate renewable power and trade surplus energy with their neighbors. [Energy Matters]
¶ P Squared Renewables Inc announced that Borealis GeoPower Inc has started exploration work at the Canoe Reach geothermal project in British Columbia. Borealis has initiated its Passive Seismic Reservoir Characterization program at the Canoe Reach Energy Project, one of the final steps in the project’s pre-drilling evaluation. [ThinkGeoEnergy]

Kinbasket Lake, British Columbia (flickr | Kim, Creative Commons)
¶ The cost of wind power in Tamil Nadu has fallen to ₹3.42 per unit (5.34¢/kWh), the lowest in the country. The price now is ₹0.04 lower than that quoted in the Union renewable power ministry’s wind power tender bid. In a recent auction ReGen Power Tech Company had bid for ₹3.42 per unit for a capacity of 200 MW. [Times of India]
¶ GE Renewable Energy announced an agreement to provide wind turbines for the largest wind project in Jhimpir, Pakistan. The 150-MW project is being built by Power China in the Gharo-Keti Bandar Wind Corridor. US development and energy agencies estimate that Pakistan could develop more than 132 GW of wind capacity. [CleanTechnica]

Wind farm (Sapphire Wind Power image)
US:
¶ The US Energy Information Administration published its latest “Electric Power Monthly.” It says the US renewable energy is tied US nuclear energy, with each providing roughly 20% of the country’s electrical generation. However, experts predict nuclear’s share to decrease, while that of renewables is expected to continue growing. [CleanTechnica]
¶ CNN meteorologist Dave Hennen labeled Harvey a “one-in-1,000-years type of event.” By amount of rainfall, Harvey might set a new record. The sea level is about seven inches higher than it was a hundred years ago. And the temperature of the ocean is one to two degrees higher. The combination led to more rainfall and more flooding. [CNN]

Houston Flooded by Hurricane Harvey
¶ Hurricane Harvey’s path through southeast Texas and the Gulf of Mexico hit almost half of US refining capacity and a fifth of its oil production. The drop in production is expected to cause a temporary spike in US gas prices. Analysts expect the storm’s economic impact to pass $40 billion, with direct losses of over $20 billion. [BBC]
¶ Floodwaters are expected to rise still further in the inundated Texan city of Houston, where more than 30,000 people have been forced from their homes in the wake of Hurricane Harvey. Historically heavy rains have fallen for three days and the downpour is forecast to continue. Now New Orleans is preparing for flooding. [BBC]

Rescues in action
¶ As many as 5 million commercial electric customers across the country could cost effectively reduce their utility bills by using behind-the-meter energy storage, according to a report from the DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory and the Clean Energy Group. The report analyzed over 10,000 utility tariffs in 48 states. [Utility Dive]
¶ Delaware Gov John Carney signed an executive order creating a working group to study offshore windpower technology. The executive order says the group is to examine how Delaware can participate in developing offshore wind, identifying ways to leverage the related economic opportunities of offshore wind for the state. [Delaware State News]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 28, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Cyclones and climate change: connecting the dots” • Scientists freely acknowledge they don’t know everything about how global warming affects hurricanes like the one pummeling southeast Texas. But what they do know is enough to keep them up at night. The amplifying impact of climate change is basic physics. [Phys.Org]

Hurricane Harvey’s destruction
¶ “States Dare to Think Big on Climate Change” • There is a bright spot amid gloomy news about climate change and the Trump administration’s resistance to doing anything about it. It is the determination of a number of governments of California and the states in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative to take action on their own. [New York Times]
World:
¶ The Australian city of Canberra has its first all-electric and hybrid buses, following the launch of a new 12-month public transportation fleet trial. The $900,000 trial involves leasing two all-electric buses from Carbridge and one hybrid bus from Volvo. The test buses will see their performance gauged against the existing fleet of diesel buses. [CleanTechnica]

Electric bus in the ACT
¶ The government of Zimbabwe is making efforts to boost electricity generation, with over $151 million worth of new small hydropower projects lined up and $154 million secured to repower small thermal power stations. The government is finalizing policy frameworks with the expectation of greater private sector involvement. [Bulawayo24 News]
¶ Australia’s renewable energy sector is within striking distance of matching national household power consumption, cranking out enough electricity to run 70% of homes last financial year. The first Australian Renewable Energy Index finds the sector will generate enough power to run 90% of homes with completion of current projects. [The Guardian]

Wind turbine in Australia (Photo: Bloomberg | Getty Images)
¶ Australia’s Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull is fast-tracking the Snowy Hydro 2.0 power project, with a timetable for a A$29 million ($23 million) feasibility study. He says the project will meet peak demand for 500,000 homes. The project will create 5,000 new jobs in Cooma, Tumut, and Sydney next year, when construction starts. [Sky News Australia]
¶ TenneT delivered 7.77 TWh of electricity generated by offshore wind in the North Sea in the first half of 2017, up 50% on the 5.18 TWh in the same period last year. TenneT said it currently has nine offshore grid connections with combined capacity of 5,221 MW. It plans to complete three further grid connections by the end of 2019. [reNews]

Cable laying at BorWin 1 (TenneT image)
¶ Electricity generators have rebuked the Turnbull government for delaying the introduction of a clean energy target, arguing a target will trigger new investment and bring down power bills. Now Mr Turnbull will meet bosses of some of Australia’s biggest power companies for discussions about rapidly rising power prices. [Brisbane Times]
¶ China is expected to invest $3 trillion in power generation over the next 25 years, according to a recent report released by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. Some 75% of the expected investment will flow into the renewable energy sector. The report said that the investment in the wind power sector alone will reach $1 trillion. [China Daily]

Inspecting a solar system (Song Weixiong | for China Daily)
¶ In Bangladesh, the state-owned Power Development Board signed a 20-year power purchase deal with local company Intraco Solar Power Ltd at the rate of 16¢/kWh (Tk12.80 per unit) for the next 20 years. To fulfill its target, the government wants to raise the ratio of renewable energy to 10% of the total power generation by 2020. [Dhaka Tribune]
¶ Hokkaido is the leader among Japan’s 47 prefectures in power generation using alternative sources such as solar energy, according to data compiled by the Natural Resources and Energy Agency. In fiscal 2016, Hokkaido accounted for nearly 10% of the 28.42 million MWh of Japan’s total renewable energy generation. [The Japan Times]
¶ The Sainshand wind farm in Mongolia, the country’s third privately financed wind farm, will receive a $120 million project financing package from international investors. The scheme will significantly help the government to achieve the goal of having renewable energy account for 20% of all power by 2020, and 30% by 2030. [eco-business.com]
US:
¶ Engineers at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory’s Marine Sciences Laboratory in Sequim, Washington, are working with open-source software ThermalTracker to find the best method for capturing flight patterns of winged creatures to help developers locate optimal sites for offshore wind projects. [Peninsula Daily News]

Engineering software to find flight patterns
(Eric Francavilla/Pacific Northwest National Laboratory)
¶ Two of America’s biggest telecommunication firms are being urged to use more renewable energy to power their businesses. Verizon and AT&T customers are being asked to push the providers to commit to shifting to 100% clean energy at their operations by 2025. The campaign is being led by Green America. [Innovators Magazine]
¶ Coal and nuclear industry groups are pressing the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to implement policy changes outlined in Energy Secretary Rick Perry’s new grid reliability study, which was aimed at saving their power plants from closing. The study recommends new rules to value of nuclear and coal power plants higher. [Washington Examiner]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 27, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Why Apple, Facebook, Microsoft and Google Are Flocking to Iowa” • Apple is the fourth tech giant to build a data center in Iowa, following Google, Facebook, and Microsoft. Apple CEO Tim Cook said at an event in Waukee that one of the important attractions for business is Iowa’s “world-class power grid,” which is powered 36% by wind. [TheStreet.com]
¶ “National energy plan needs a major review” • Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has begun a review of the government’s Basic Energy Plan, three years after its last update. The current plan calls for reducing the nation’s dependence on nuclear power, but also calls nuclear an “important baseload power source.” [The Japan Times]
¶ “Did global warming cause Hurricane Harvey?” • Our future may actually be one of fewer hurricanes, but they would be much stronger. Fewer hurricanes mean a lower chance that one hits the US coastline. But a hurricane that does form and heads toward the US will likely be stronger, with a more severe storm surge and higher winds. [WDIV Detroit]

Hurricane Harvey in Corpus Christi
Science and Technology:
¶ The Power to Ammonia project, a study looking at the potential of CO2-free ammonia, shows that the electrochemical production of ammonia from renewable energy is a potentially attractive alternative to current technology and that it offers a very promising solution for large-scale seasonal storage and import of renewable energy. [Advanced Science News]
World:
¶ There is no greater threat to Pakistan than climate change, Punjab’s top judge has warned, adding the South Asia country is second most vulnerable to impacts of climate changes although it is not much responsible for global warming. He advised that judicial officers should take a grip on environmental cases with a strong link to science. [Daily Pakistan]

Flooding in Pakistan
¶ An ambitious plan to build one of Australia’s first waste-to-energy incineration plants in Canberra’s south is facing hurdles, with air quality concerns and questions around receiving tariffs for feeding excess energy into the grid. Additionally, the local government has already contracted for 100% of the power it needs from solar and wind plants. [ABC Online]
¶ Western Australia’s Curtin University has shed light on the province’s energy provision, revealing that a quarter of citizens live in energy poverty. Many people are turning to solar power as the price of gas is rising. But even though solar provides cheap power, the upfront cost of installing panels is out of the reach of many Western Australians. [Business Review Australia]

Solar power in Western Australia
¶ India’s wind energy program has nearly halted as distribution companies are signing very few power purchase agreements. Many states and regulators are reluctant to sign for projects agreed upon when tariffs and costs were higher. India added 5,400 MW of wind capacity last year. So far this year, it has added less than 230 MW. [Indiainfoline]
¶ Coal-fired power has slumped to its lowest level in the UK for 135 years, according to Aurora Research analysts. In 2015 it accounted for 23% of electricity generation. From this point it dropped to 9% in 2016. This year, in July, it contributed just 2% of the total power generated, and the average could drop an even lower in August. [The Independent]

UK Coal plant
¶ Philippine retail giant SM Supermalls continues its partnership with Solar Philippines as it puts up more solar rooftops in its malls. It will end 2017 with 8.9 MW total capacity. The mall operator said it will have approximately 33,000 solar panels capable of producing that much electricity by the end of its current installation phase. [Philippine Star]
US:
¶ Apart from physical damage to facilities, hurricanes affect the energy industry due to flooding, power cuts, evacuation of workers and disruptions to the loading or unloading of tankers. Crude oil prices have actually fallen on the news, while petrol prices are up, with traders expecting refineries to be affected more than oilfields. [The National]

Hurricane Harvey (Jack Fischer | NASA via AP)
¶ Utility customers in Westby, Wisconsin, will soon receive more of their electricity from renewable energy thanks to an agreement between Westby Utilities’ not-for-profit wholesale power supplier, WPPI Energy, and Invenergy. WPPI Energy will purchase the output from Invenergy’s 132-MW Bishop Hill III Wind Energy Center. [The Westby Times]

Coventry wind farm (Rhode Island Office of Energy Resources)
¶ Rhode Island Governor Gina Raimondo said that she is committed to increasing renewable resources to 1,000 MW by 2020. Block Island Wind Farm developer Deepwater Wind is pursuing a wind farm with a 1,000 MW capacity in an offshore leased siting area. Alternative energy sources currently generate 100 MW for Rhode Island. [Block Island Times]
¶ Most owners of brownfield sites would like to make them productive. At capped landfills, the environmental and physical risks remain too high to let them be used for housing, shopping centers or industrial facilities. But even the worst contaminated sites can often be used productively by converting them for solar installations. [The Keene Sentinel]
¶ Two South Carolina power customers charge in a lawsuit that South Carolina’s state-owned utility Santee Cooper hiked rates unconstitutionally to pay for a failed nuclear power plant project. The utility and South Carolina Electric & Gas Co decided to scrap a project at the VC Summer Nuclear Station after spending nearly $10 billion on it. [Patch.com]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 26, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Here’s why oil’s future is grim” • What do the auto makers, major utilities, and oil companies have in common with Kodak, Blockbuster, and Macy’s? Their old business models are rapidly vanishing under the pressure of technology, innovation, and societal norms. Banning petroleum-powered cars may be unnecessary. [Hellenic Shipping News Worldwide]
¶ “The US coal industry is going out, not with a whimper, but with a burst of rent-seeking” • The US coal industry is dying, but not with any dignity. As the end approaches, its demands for government handouts increasingly frantic. The industry’s product is outmoded, and “picking winners” doesn’t look so bad when you’re losing. [Vox]
Science and Technology:
¶ An increasing percentage of the world’s population are living in cities, and this number is set to keep growing. A startup based in Brooklyn, Square Roots, has just raised $5.4 million in seed funding that will be used to empower food entrepreneurs and increase urban farming to give city dwellers access to locally produced, healthy food. [CleanTechnica]

Square Roots farm
¶ An international research team led by scientists at Hanyang University in South Korea and the University of Texas in Dallas has developed high-tech yarns that generate electricity when they are stretched or twisted. The researchers describe “twistron” yarns and their possible applications in the August 25 issue of Science. [Renewable Energy Magazine]
World:
¶ Those Schools around the northern Indian city of Bikaner that have no supply of electricity will soon be illuminated with power fetched through solar panels. The district administration in a recent review meeting of electrification took this decision to give schools situated at distant locations in rural areas renewable power. [Daily News & Analysis]

Indian rooftop solar power
¶ A review of India’s National Solar Mission by a committee of the Indian Parliament identified 34 solar parks in 21 states with a cumulative capacity of 20 GW. It indicated that land has been acquired to support the implementation of 71 GW. So far, 7.3 GW of capacity has been tendered, while 1.5 GW capacity has been commissioned. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Chile’s abundant geothermal potential provides a good renewable energy option to further diversify the country’s power generation mix. This is consistent with Chile’s Energy Policy, which aims for at least 70% of electricity generation to come from renewable sources by 2050. Chile has long been the Latin American renewables leader. [ThinkGeoEnergy]

Cerro Pabellon geothermal plant, Chile (source: developer)
¶ Since 2010, the UK has more than doubled its capacity for burning residual waste, but that means the waste has not been recycled. The UK is building so many rubbish-burning facilities that it may be impossible for the country to meet its recycling targets. Overuse of incinerators could be a problem for much of northern Europe. [Gears Of Biz]
US:
¶ Eight Community Choice Aggregation nonprofit agencies currently serve over 1 million customers in California. With their success, Los Angeles, San Jose, and others are implementing CCAs. According to a Public Utilities Commission estimate, 67% of California’s electricity needs may be met by CCAs in three years. [The San Diego Union-Tribune]

Solana Beach is the first city in San Diego County to move
forward with a CCA program. (Union-Tribune file photo)
¶ The US DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory has released its 2017 Annual Technology Baseline, a highly respected analysis of current and projected energy technology generation costs. The analysis compares technology costs, and it’s good news again for wind and solar, which are cheapest alongside natural gas. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Oil companies like to push the narrative that Alaskans want more oil development, but that’s not true. Construction of a few wind turbines in Arctic villages cannot undo much of the damage the fossil fuel economy has already done here, but the transition to renewable energy can provide local economies a measure of control. [YES! Magazine]

Mayor Tim Gavin of the Inupiaq village of Buckland
has backed renewable energy. (Photo: Stephen Miller)
¶ Fresh off the first American Wind Week, the DOE’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory released a report finding wind energy cost reductions of 50% are possible by 2030. That’s on top of the 66% fall in costs since 2009. NREL expects advancements in wind turbine design, materials, and controls to unlock major cost reductions. [Windpower Engineering]
¶ The US Army will add a 1-MW energy storage system to a 10-MW PV system, which recently broke ground at the Redstone Arsenal in Alabama. Through a power purchase agreement, Army will purchase 18,000 MWh of electricity from the project at a cost equal to or less than the arsenal’s current and projected utility rates. [Red, Green, and Blue]

Redstone Arsenal (Image CC by Whitney Gal on Flickr)
¶ As of 2016, natural gas accounted for the production of 34% of the nation’s electricity, passing coal for the first time, according to a new report from the US DOE. Natural gas has disrupted electricity markets by creating sustained and low wholesale prices. Some coal and nuclear power plants are now operating at a loss. [Denver Business Journal]
¶ Duke Energy is asking the North Carolina Utilities Commission to approve cancellation of the development of a new reactor project at Lee Nuclear Station in Cherokee County. Duke officials cited the recent bankruptcy filing by Westinghouse Electric Co, which would make the reactor, as the primary reason for the project’s cancellation. [GSA Business]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 25, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “This Stealth Terrorist Killed ~53,000 Americans Last Year” • An MIT study found that 200,000 premature deaths a year come from air pollution in the US Road transportation account for 53,000 of them. Electricity generation from coal and natural gas power plants accounts for another 52,000. These are real people; they are being murdered. [CleanTechnica]

Graveyard
¶ “Oops: Rick Perry may have stumbled upon solution to going 100% renewable” • Energy Secretary Rick Perry’s new grid study is filled with buried treasure, including the solution to enabling very deep renewable energy penetration: The future is smart control systems and electric cars. Clearly, that was not what Rick Perry had in mind. [RenewEconomy]
¶ “Texas oil industry boasts of near-infinite supply – but what if the world stops buying?” • With all the talk from Trump administration officials about achieving “energy dominance,” Texas’ own oil and gas industry detailed its disproof of the idea of “peak oil.” The theory of “peak demand” seems like a tougher one to disprove. [Chron.com]

Wind turbines (Photo: Michael Paulsen | Chron.com)
Science and Technology:
¶ An Australian pilot project capturing carbon emissions and storing them in building materials aims to have a full-scale production plant by 2020. Mineral Carbonation International, an Australian company developing carbon-utilisation technology is launching its technology and research program at the Newcastle Institute for Energy and Resources. [The Guardian]
World:
¶ A commercial LNG tanker has sailed across the cold northern route from Europe to Asia without the protection of an ice-breaker for the first time, carrying gas from Norway to South Korea. The specially built ship completed the crossing in just six-and-a-half days setting a new record, according to tanker’s Russian owners. [BBC]

The tanker Christophe de Margerie (Sovcomflot photo)
¶ Power generation in Lesotho is set for a major boost after the African Development Bank approved a $695,500 (M9.1 million) grant towards the development of 20-MW solar PV plant, the first utility-scale solar PV project in the country. The plant is expected to supply at least 13% of the country’s demand for electricity. [AllAfrica.com]
¶ Northern Ontario’s newest hydro-electric power source was celebrated Thursday with the opening of the Peter Sutherland Sr Generating Station. It is on the Abitibi River near New Post Creek, roughly 75 km north of Smooth Rock Falls. The new 28-MW facility was constructed on time and without overspending its budget. [Timmins Press]

Inside the Peter Sutherland Sr Generating Station
US:
¶ EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt is leading a formal initiative to challenge mainstream climate science using a “back-and-forth critique” by government-recruited experts, according to a senior administration official. This is the first time agency officials acknowledged that Pruitt has begun that process, also favored by Energy Secretary Rick Perry. [Sunbury News]
¶ Pipeline operator Energy Transfer filed a lawsuit against Greenpeace and other organizations, alleging that actions against construction of the Dakota Access Pipeline constituted “eco-terrorism.” Energy Transfer is represented by Kasowitz Benson Torres & Friedman, whose founding partner Marc Kasowitz is President Donald Trump’s lawyer. [CleanTechnica]

Pipeline protest (Pax Ahimsa Gethen, CC BY-SA 4.0)
¶ The Midcoast Regional Redevelopment Authority plans to install a 1.5-MW solar farm at the former Brunswick Naval Air Station as it develops a microgrid powered entirely onsite. ReVision Energy will soon break ground on the PV array, which is to be operating by the end of this year. The system will also have a 1-MW bio-gas plant. [Bangor Daily News]
¶ LM Wind Power is expanding its operations at the Port of Little Rock in Arkansas to accommodate the construction of longer wind turbine blades. These will reduce the levelized cost of energy. A new post-molding facility is being built, marking the second time in 12 months that the company has invested more in the site. [reNews]

Shipping wind turbine blades (LM Wind Power photo)
¶ After President Donald Trump announced that Apple CEO Tim Cook promised to build three new manufacturing plants in the country, the tech giant made public its plans to build a $1.3 billion data center in Waukee, Iowa. Cook noted in a statement on the new facility that it would be “all powered by renewable energy.” [News18]
¶ The DOE study on the reliability of the US electricity grid, ordered by Secretary of Energy Rick Perry back in April, had one overarching conclusion on the demise of coal. Cheap and abundant natural gas is the killer of coal plants, not renewables or excessive environmental regulation, as many coal proponents have claimed. [OilPrice.com]

Natural gas equipment
¶ Green Lantern has received a Certificate of Public Good from the Vermont Public Utility Commission and plans to build and sell ownership shares in a new group-net-metered Community Solar Array in Guilford. The array will have a capacity of 252 kW AC, and will be able to serve between 50 and 100 homes or the equivalent. [Vermont Biz]
¶ Families of five Navy service members who died after responding to the Fukushima nuclear meltdown have sued TEPCO, blaming the deaths on radiation illnesses contracted from the March 2011 disaster. The 7th Fleet broke off humanitarian response to the Fukushima Disaster when radiation was detected on the ships. [Gears Of Biz]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 24, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Exxon Dared Critics to Prove It Misled the Public. These Researchers Just Called the Company’s Bluff.” • Science historian Naomi Oreskes and Harvard researcher Geoffrey Supran have published the first peer-reviewed, comprehensive analysis of Exxon Mobil’s climate communications. It adds heft to charges of deceptive climate denial. [Mother Jones]
(Thanks to Tad Montgomery.)

Exxon plant (Matt Brown | AP)
¶ “Trump officials rewrite Energy Dept study to make renewables look bad, fail anyway” • Energy Secretary Rick Perry’s long-awaited grid study is finally out. Trump officials clearly rewrote the previously leaked staff draft to make it look like renewable energy is a threat to baseload power and grid resilience, but they mostly botched the job. [ThinkProgress]
World:
¶ An economic survey released by the Indian government states that by 2026 installed capacity in the renewable energy sector will match that in the thermal power sector, and it will continue to grow more important thereafter. Currently, India’s total capacity is 327 GW, of which 55% is thermal and 18% is renewable energy sources. [CleanTechnica]

Indian home solar array
¶ Electricity and water rates in Kuwait have been revised upward by 500% to encourage consumers to rationalize consumption, a spokesman for the ministry of electricity and water said in a statement. The new rates are five fils (nearly $0.16) per kWh for electricity and two dinars ($6.63) per 1,000 imperial gallons of water. [Khaleej Times]
¶ Solar PV capacity will soon match and even overtake nuclear energy’s global capacity, according to new US research. By the end of 2017, solar power plants around the world are predicted to have an installed capacity of 390 GW, according to estimates by Greentech Media. That is just shy of the 391.5 GW of nuclear capacity currently in operation. [EURACTIV]

Sunset for a nuclear plant (Shutterstock image)
¶ Canada’s National Energy Board has agreed for the first time in its history to consider upstream and downstream greenhouse gas emissions while reviewing a major pipeline project. The federal regulator will consider “indirect” heat-trapping pollution in upcoming hearings for a proposed TransCanada Energy East pipeline. [National Observer]
US:
¶ Monday’s solar eclipse offered the power sector an entirely predictable opportunity for experiments, as over 12,000 MW of solar power supplies to dropped off their systems. Many companies used the event to test software, plants, and markets that are being made ready for a time when renewable energy will become dominant. [CMFE News]

Coal-fired power plant
¶ The nine northeastern states in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative have tightened greenhouse gas emission limits on electric power plants. The group announced that the plants will face a 30% cut on maximum total emissions allowed starting in 2020. By 2030, power industry greenhouse gas emissions will be cut 65% from 2009 levels. [Albany Times Union]
¶ Grid operators and traders thought they were totally prepped for the historic US solar eclipse. But they failed to factor in human behavior. While power stations ramped up to replace lost solar power, millions of people were outdoors ogling the eclipse instead of cranking up the A/C. Spot power prices in California fell to negative levels. [Bloomberg]

Grid monitoring for the eclipse (David Paul Morris | Bloomberg)
¶ Under a settlement agreement announced by the Sierra Club, the Lansing Board of Water and Light will stop burning fossil fuels at the coal-fired Erickson Generating Station in Michigan by December 2025 and commit to specific investments in clean energy. The Sierra Club said this settles claims of Clean Air Act violations at the plant. [Solar Industry]
¶ The DOE issued a long-anticipated report stressing a need to protect the “resilience” of the nation’s power grid by valuing dependable resources such as coal and nuclear more in power markets, according to the head of a coal trade group. There is considerable controversy about the need for subsidies to protect coal and nuclear generators. [Houston Chronicle]

Cooling towers at Watts Bar nuclear plant
¶ A research team led by Dr. Mark Z. Jacobson of Stanford University published a paper, “100% Clean and Renewable Wind, Water, and Sunlight All-Sector Energy Roadmaps for 139 Countries of the World.” It provides pathways for each of 139 countries to having economies entirely free of use of fossil fuels, nuclear power, and biomass. [Green Energy Times]
¶ California could solidify its position as a global leader on the issue of climate change in the coming weeks, when the state Legislature considers a bill that would push for the state to obtain all its electricity from renewable sources by 2045. Hawaii is the only other state in America to have committed to that ambitious goal, and it is much smaller. [NBCNews.com]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 23, 2017
Science and Technology:
¶ Scientists found that some bacteria have a natural defence to cadmium, mercury, or lead that lets them turn the heavy metal into a sulfide, which the bacteria express as tiny crystals on their surfaces. These turn out to be semiconductors that the bacteria can use to photosynthesize atmospheric carbon dioxide into acetic acid, a chemical feedstock. [BBC]

“Cyborg” bacteria making and using tiny solar panels.
World:
¶ China has installed 24.4 GW of solar PV in the first six months of 2017, including an extraordinary 13.5 GW in the month of June alone, as developers rushed to complete installations to capitalize on a higher feed-in tariff that expired on July 1. The 24.4 GW is equivalent capacity to Australia’s entire fleet of coal-burning power plants. [CleanTechnica]
¶ As India’s energy needs are rising fast, the increased use of renewables could save the economy 12 times the installation costs in 2030, when environmental and health damage are taken into account, a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency said. It outlines areas that can unlock the vast renewable energy potential in India. [pv magazine]

Solar installation (Photo: Baywa re)
¶ Coal generation might have a future in Australia’s energy grid, but it may not be a long one. It is now clearly recognized, outside the imaginary world of the fossil fuel lobby, that the cheapest form of new generation in Australia – and most other places in the world – is wind and solar, and certainly not coal and gas (or nuclear). [CleanTechnica]
¶ Reliance Industries Ltd and British Petroleum Plc are planning to invest in the power-storage business to tap into the renewable energy sector, a Bloomberg report said. The oil and gas giants have plans to set up energy-storage projects near renewable energy installations. Investment decisions will be taken by year’s end. [International Business Times]

Reliance Industries facility in India (Reliance Industries photo)
¶ The company behind the huge Sapphire Wind Farm in New South Wales published plans to add a solar project. CWP said it submitted an outline of the expansion, with an assessment of the environmental impact, to the state’s Department of Planning and Environment. The solar part of the complex could have 200 MW of capacity. [Glen Innes Examiner]
¶ Victoria, Australia’s second-most populous state, has proposed a new law that would require 40% of its power needs to be generated by renewable energy by 2025. Victoria also launched a 650-MW renewable energy auction, which the government expects to spur up to A$1.3 billion ($1 billion) of investment in the sector. [reNews]

Victoria’s Macarthur wind farm (Image: Vestas)
¶ Foreign investors have filed proposals for a combined $3.6 billion to develop renewable energy projects in Iran. The Iranian government has set an ambitious target to add 5 GW of renewable power generating capacity by 2022, Iran’s Financial Tribune reports. A target of adding 1 GW of renewable capacity per year is considered feasible. [OilPrice.com]
US:
¶ When the Jiminy Peak Mountain Resort in Massachusetts installed a $4 million wind turbine in 2007, many thought the resort was taking a huge financial risk. According to the resort, the turbine paid for itself in seven years. Now, with 2.3-MW solar field and 75-kWh cogeneration unit, the resort is powered 100% by clean energy. [North American Windpower]

Skiing at Jiminy Peak
¶ Wyoming’s congressional delegation wrote a letter to President Trump urging him to ignore a proposal for a $4.5 billion federal subsidy for eastern Appalachian coal. The subsidy, proposed by West Virginia Governor Jim Justice, would provide a $15 per ton subsidy for utilities that purchase Eastern rather than Western coal. [Jackson Hole News&Guide]
¶ The US DOE issued a Final Environmental Impact Statement for the Northern Pass transmission project. It concluded that the hydroelectric system is the “preferred alternative” and will result in minimal impacts. Northern Pass Transmission is developing a 192-mile transmission line to move power from Canada to a substation in Deerfield, NH. [Utility Dive]

Transmission lines (credit: Depositphotos)
¶ Coal executives say President Trump pledged to enact an emergency order to protect coal-fired power plants, but his DOE has decided not to use its authority to offer temporary relief to the plants. This type of order is intended to protect the nation’s electricity supply and temporarily allows power plants to skirt environmental regulations. [ThinkProgress]
¶ Executives from Gulf Power and Coronal Energy joined US military officials at Naval Air Station Pensacola for a “Flip the Switch” ceremony signifying the completion of the three largest combined solar facilities on Department of Defense property. The solar arrays have nearly 600,000 PV panels with a total capacity of 50 MW. [NorthEscambia.com]

Gulf Power solar array
¶ Five recently completed Community Solar Projects were launched with a ribbon cutting ceremony at Twin Elm Farm in Mendon, Massachusetts. The solar arrays have a combined capacity of about 6.9 MW. Overall, the projects will increase the amount of power generated by Massachusetts community solar by an estimated 13%. [Stockhouse]
¶ Ohio governor John Kasich, said that he would not support a rescue plan for FirstEnergy Corp that would ensure the state’s two nuclear power plants would have viable financial futures. According to the Associated Press, he made his comments on the state’s energy future after touring a new, $800 million natural gas plant near Toledo. [Nuclear Street]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 22, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Peak Oil Demand: Time To Get Agile Or Get Left Behind In The Race To Low-Carbon Fuels” • As low oil prices persist, global oil and gas companies are undertaking some serious self-examination. “Peak oil supply” concerns have been replaced by worries about “peak oil demand.” Anxiety is not about whether the peak will come, but when. [Forbes]
World:
¶ At a briefing on profit results, AGL’s Energy CEO made a point in its presentation that the most economic option to replace the 2000-MW Liddell coal-burning plant in New South Wales would not be coal or baseload gas, but a mix of energy from wind and solar, and various load shaping and firming capacity from other sources. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A new floating solar farm went live in the Chinese city of Huainan above a retired coal mine, China Daily reported. The mine had been flooded with groundwater after it went out of service. The new solar farm generates 40 MW, which can power 15,000 homes for a year. The second biggest active floating farm has a capacity of 6.3 MW. [EcoWatch]

World’s biggest floating solar farm (Sungrow Power Supply)
¶ Electricity in Australia is some of the most expensive in the world. The cost of electricity from solar and wind is dropping so rapidly that renewables are pricing coal and natural gas out of the utility market and creating a pathway forward that will allow Australia to enjoy wide access to zero-emission power by the year 2033. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The first 7 months of 2017 has seen air quality in northern China continue to worsen at a rapid rate, going by newly released figures from the country’s environment ministry. The 13 largest cities in the northern Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region apparently saw PM2.5 levels climb 11.3% over this time period, going by the new figures. [CleanTechnica]

Air pollution in China
¶ At the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant, owner TEPCO opened valves to circulate coolant for the last remaining section of the 1.5-kilometer-long, 30-meter-deep wall around the four reactor buildings. The ice wall is designed to prevent groundwater from seeping through the facility carrying radioactive contaminants. [The Japan Times]
US:
¶ Mining giant BHP Billiton will sell its US shale assets after pressure from shareholders to offload the underperforming business. The business was considered “non-core.” BHP’s entry into US shale came at the peak of the fracking boom in 2011. A slump in oil prices slugged the business and forced a $7.2 billion write-down last year. [BBC]

Petroleum extraction (BHP image)
¶ The Trump administration has fired another shot at the scientific community, this time dismantling a federal advisory committee on climate change. The advisory committee’s big work was coming up with the release of a congressionally mandated climate report. The advisory committee was to recommend actions based on it findings. [CNN]
¶ Advanced Rail Energy Storage, based in California, has a solution to the problem of energy storage. It is to run some old trains up and down a hill. When a wind or solar farm is producing excess energy, repurposed electric locomotives haul enormously heavy railroad cars to the top of a hill. When power is needed, they generate it coming down. [Seeker]

Energy storage train (ARES photo)
¶ Over the last several years, the Arizona Public Service Company, the largest power provider in the state, has tried thwarting rooftop solar by getting utility-friendly candidates elected to the Arizona Corporation Commission, the state’s utility regulator. Now, APS is reportedly being investigated by the FBI over its political spending. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The board of the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power approved an agreement with Doosan GridTech CA to build a 20-MW battery storage system. The lithium-ion battery system is sited north of Mojave, California, in a location that will enable it to mitigate the intermittency of 600 MW of solar power and 135 MW of wind power. [Utility Dive]

Downtown Los Angeles
¶ There are only about a dozen countries on Earth that don’t recognize the right to a healthy environment. The US is one. Now, a small town in rural western Pennsylvania is asserting the legal right to clean air and water. In doing so, it’s challenging the foundation of US environmental law. Grant Township is a destination for fracking waste. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Monday’s partial eclipse statewide took a sharp, sudden bite out of solar power production in California. Shortly after 9 AM, the state’s fast-multiplying solar farms were plunged into semi-darkness, just when they would normally be revving up. And the electricity grid survived just fine. The slack was filled by hydro-power and natural gas. [SFGate]

Eclipse of 2017 (Photo: Douglas Zimmerman | SFGate)
¶ The Interior Department ordered a halt to a scientific study of the public health risks of mountaintop-removal coal mining. West Virginia officials asked the Obama administration for the study. As part of the practice, mining companies dump the rubble into the surrounding valleys and streams, in many cases leading to extensive pollution. [New York Times]
¶ The Mississippi Public Service Commission voted for the $100 million solar farm to be built near the Alabama border in Lauderdale County, by Silicon Ranch of Nashville, Tennessee. Mississippi Power, a subsidiary of Southern Power, also got approval to buy electric power under a 25-year contract from the 52.5-MW solar project. [Digital Journal]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 21, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Why solar towers and storage plants will reshape energy markets” • The 150-MW solar tower and molten salt storage plant to be built in Port Augusta has been made possible by a ground-breaking pricing and contract structure that could help completely reshape Australian power markets, including the end of “baseload” power as we know it. [RenewEconomy]

Visitors at a solar thermal power plant
¶ “How Nigeria Can Cure Its Oil Addiction” • Nigeria is addicted to oil. The oil industry contributes over 90% of export earnings and around 70% of Nigeria’s government revenue. Successive governments have sought to diversify the economy with limited success. But global moves toward electric cars and renewable energy signal the decline of oil. [Newsweek]
World:
¶ The developer of a large-scale Queensland renewable energy hub has struck a “critical” new agreement as the project powers towards production. The agreement between Genex Power and Powerlink finalizes a “vital element” in connecting the Kidston solar and hydro projects – 400 km southwest of Cairns – to the national electricity grid. [The Cairns Post]

Former gold mine to be repurposed (Photo: Marc McCormack)
¶ Powerlink is investigating plans to connect up to 2000 MW of renewable projects in North Queensland. This could make the area an exporter of wind and solar power. The state government has announced plans to connect renewable projects in five cities and towns, while Powerlink has called for expressions of interest from potential stakeholders. [Townsville Bulletin]
¶ With an expected boost from regional suppliers of coal and equipment, Vietnam plans to rely more heavily on coal-fired power plants by 2030. Unless it can be mitigated, this is not only bad news for a Southeast Asian nation already suffering from severe air pollution but also for international efforts to battle climate change. [Asia Times]

Hawking coal bricks in Hanoi (Photo: AFP | Hoang Dinh Nam)
¶ GreenWish Partners, a renewable energy company run by a former Morgan Stanley executive, is planning to invest $800 million on solar-powered telephone towers across Africa. The project could fuel economic growth by providing power for essential services. Sub-Saharan Africa has the lowest rates of energy access in the world. [Bloomberg]
¶ Panasian Power has announced the acquisition of Lower Kotmale-Oya Power Two (Pvt) Ltd to construct two mini hydro-power plants in the Sri Lankan district of Nuwara-Eliya in early 2018. The construction will have an estimated investment of 400 million rupees ($2.6 million), and envisages combined output of 7.53 GWh per annum. [Lanka Business Online]

Power grid in Sri Lanka
¶ Northland Power has reached financial close at its 252-MW DeBu offshore wind farm in the German North Sea. The total cost of the project is €1.3 billion, and a financing run was oversubscribed, the Canadian company said. MHI Vestas is supplying 31 V164-8.0MW turbines. Vattenfall will provide direct marketing for the project’s power. [reNews]
US:
¶ According to the University of Minnesota’s Energy Transition Lab, starting in 2019 the overall cost of building grid-scale storage there will be less than that of building natural-gas plants to meet future energy demand in that state. Current plans for adding 1,800 MW of gas-fired “peaker” plants by 2028 may be unnecessary. [Yahoo Finance UK]

Solar panels
¶ In late 2015, DME unveiled its Renewable Denton Plan to almost immediate controversy, as it pivoted on a $265 million investment in a new, gas-fired power plant. After management changes, a new plan is expected to identify clear steps to get 70% to 100% percent of Denton’s electricity from renewable energy by 2019. [Denton Record Chronicle]
¶ Rocky Mountain Institute has released its 2017 Micropower Database. This comes shortly after leaked drafts of Energy Secretary Rick Perry’s electric grid reliability study said renewable power does not threaten the grid, and another study to be published by federal scientists found that the US is already suffering effects of climate change. [RMI]

Global growth of micropower and nuclear power, 2000 to 2016
(Please click on the image to enlarge it)
¶ The Trump administration has decided to withdraw the official estimate of the Social Cost of Carbon and disband the inter-agency working group that developed it. Despite this, a group of prominent economists and lawyers have highlighted the metric’s continued validity for policymaking in a letter published in the journal Science. [eco-business.com]
¶ President Donald Trump’s administration has dissolved a federal panel of scientists and other experts tasked with helping create and implement new policy based on the latest climate change research findings. It is a decision that does not bode well for the future of climate change preparation and prevention during Trump’s time in office. [HuffPost]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 20, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “President Trump Has An Oil Problem” • After six months of regulatory rollback, Trump has done almost nothing that will create jobs on oil fields or offshore rigs. That’s because low oil prices, not environmental protections, are stunting job growth, and Trump’s push to nix federal regulations only makes oil cheaper. [CleanTechnica]

(Please click on the image to enlarge it.)
¶ “Montana’s fly fishing industry calls for action on climate change” • Washington politicians may deny science, but the effects of climate change can be clearly seen in Montana. The state has some of the best fly fishing in the country, but the industry already sees negative impacts from climate change on cold water fishing. [Great Falls Tribune]
Science and Technology:

“Roadkill” (The Economist)
¶ The most recent cover story in The Economist announces, “The death of the internal combustion engine… it had a good run. But the end is in sight.” The Economist reports that the end of the internal combustion engine is in sight and its days are numbered. Rapid gains in battery technology favor electric motors over internal combustion.” [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ According to a report by the UN Development Programme and the Asian Development Bank, Sri Lanka’s electricity capacity will need to increase from the current 3,700 MW to about 34,000 MW. Of this, 15,000 MW will be wind energy and about 16,000 MW will be solar energy. Balance capacity is expected to be met by other renewable sources. [Colombo Page]
¶ Masdar, a renewable energy company based in Abu Dhabi, signed an engineering, procurement and construction contract with a group of companies that include GE and Spain TSK to build a wind farm in Oman. It will be the first large scale project of its kind in the Gulf. The 50-MW Dhofar Wind Power Project will power 16,000 homes. [The National]

Offshore wind farm (AFP | Scott Eisen)
¶ Nova Scotia Power plans to install 12 fast charging stations for electric cars across the province as part of a pilot project. NSP hopes Nova Scotians will soon be able to drive electric vehicles from Sydney to Yarmouth without having to worry about where they can charge their batteries. The pilot project will be ready for use in the spring of 2018. [The Register/Advertiser]
¶ Abengoa has achieved practical completion for Xina Solar One, its third solar thermal plant in South Africa. Xina Solar One is a 100-MW plant using parabolic through technology to generate renewable and dispatchable power from the sun. The plant has a thermal energy storage system sufficient to supply power for 5.5 hours after dark. [Independent Online]

Solar thermal power plant (IOL file image)
¶ Sales of Chinese solar panels to North Koreans have soared in the past two years. It is one of the border businesses still thriving despite growing US pressure on China to limit commerce with the Stalinist regime. Last year, China exported 466,248 solar panels across the border, according to official figures from Beijing. [ETEnergyworld.com]
¶ Some day over the next two weeks, an AP1000 nuclear power plant in China’s Zhejiang Province will start loading more than 100 fuel assemblies into the honeycomb core of its AP1000 reactor with a pair of robotic arms. It is the first Westinghouse AP1000 to be finished. It is a design claimed to be meltdown-proof. [South China Morning Post]

AP1000 in Zhejiang Province
US:
¶ Increasingly, solar companies work with farmers to install solar panels on their land. In North Carolina, solar companies pay rents up to $1,400 an acre, far more than what most farmers could earn from planting crops or raising livestock. But PV arrays are low-impact, so farmers can raise livestock or grow crops on land covered with PVs. [CleanTechnica]
¶ As Monday’s total solar eclipse sweeps from Oregon to South Carolina, US electric power and grid operators will be glued to their monitoring systems in what may represent the biggest test yet of the renewable energy era. Utilities and grid operators have been planning for the event for years and have lined up standby power sources. [ETEnergyworld.com]
¶ When President Trump announced his intention to pull the US out of the landmark Paris Agreement, one thing he said stuck out to us: “I was elected to represent the citizens of Pittsburgh, not Paris.” But Pittsburgh, as well as the rest of the Mid-Atlantic region, is feeling the negative effects of the climate crisis right now. [CleanTechnica]
¶ While President Donald Trump continues to dismantle Obama-era climate policies, an unlikely surge of Republican lawmakers has begun distancing themselves from the GOP’s hard line on climate change. The House Climate Solutions Caucus, a bipartisan backwater when it formed early last year, has more than tripled in size since January. [Politico]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 19, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Staying below 2 degrees is ‘possible and practical’ says RMI” • The latest UN Emissions Gap report showed that the world would still be heading for a temperature rise between 2.9 and 3.4 °C by 2100. A report from the Rocky Mountain Institute argues that staying below 2° C is both practical and possible given trends in renewable energy. [pv magazine]

Wind and solar, sun and clouds (Public domain image)
¶ “Pushing us to the brink of climate disaster” • President Trump’s repulsive behavior drew well-deserved media attention this week, but his antics drowned out some truly troubling warnings from the scientific community on climate change. A spate of recent reports indicate we are in new territory thanks to human-driven carbon emissions. [HuffPost]
¶ “Wind and solar power are saving Americans an astounding amount of money” • The main rationale for renewable energy subsidies is that wind and solar produce benefits to society that are not captured in their market price. Wind and solar power reduce pollution, which reduces sickness, missed work days, and early deaths. [Gears Of Biz]

Please click on the image to enlarge it. (CA senate image)
World:
¶ General Electric will supply and install all of the wind turbines to the Coopers Gap wind farm project in Queensland. GE won the contract from the Powering Australian Renewables Fund. GE will provide 91 of its 3.6-MW turbines and 32 of its 3.8-MW turbines. The Coopers Gap wind farm will be the largest in Australia. [ExpressNewsline]
¶ Darwin is set to play host to an Australian solar-powered battery “giga-factory.” Energy Renaissance said it had received support from the Northern Territory government for its proposed 1-GWh lithium-ion battery plant. The company says its semi-solid state lithium-ion batteries are uniquely optimized for warm climates. [CleanTechnica]

Rendering of Australian battery factory
¶ Acer Inc, a leading PC brand in Taiwan, has inaugurated a solar power station in its Aspire Park in Taoyuan City as part of its efforts to push for the use of renewable energy, the company said. When completed, it will have an installed capacity of 2.4 MW, and be capable of generating roughly 3,520 MWh of power a year. [Focus Taiwan News Channel]
¶ Described as “a fortress for data,” developer Kolos plans to build the world’s largest data center within the Arctic Circle in Ballangen, Norway. The facility will be powered entirely by sustainable energy from hydro and wind power. The 600,000 sqare meter facility will eventually need more than 1,000 MW, although at first it will use just 70 MW. [GCR]

Proposed data center for Ballangen, Norway (Kolos image)
¶ In a European test of vehicle-to-grid technology involving 100 vehicles, the owners of the electric Nissans earned an average of $1,530 a year from the program, more than the cost of charging the vehicles. The test also showed that vehicle-to-grid schemes may actually slow the rate at which lithium-ion batteries degrade in normal use. [CleanTechnica]
US:
¶ The residents of Neptune, New Jersey know well the problems that can be created by a hurricane. Now, Neptune is one of 13 state municipalities getting money from the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities to study microgrids. One hundred fifty thousand dollars will be spent on a feasibility study to be completed by early next year. [NJTV News]
¶ The Baker-Polito administration in Massachusetts has awarded a $545,000 grant to the Franklin County Sheriff’s Department to support the installation of a 436-kW solar canopy at the Franklin County Jail and House of Correction in Greenfield. The grant is the seventh by the Leading by Example State Solar Canopy grant program. [Solar Industry]
¶ Scott Pruitt’s successor in Oklahoma as attorney general, Mike Hunter, is showing the fossil fuel industry that he cares as much about it as Pruitt did. After threatening a lawsuit against a California official over his stance on coal, Hunter is challenging plans by Public Service of Oklahoma plans to purchase the $4.5 billion Wind Catcher project. [ThinkProgress]

Oklahoma’s frequent earthquakes may be caused by fracking.
(Photo: Brian Sherrod, USGS, Wikimedia Commons)
¶ Utility company Mississippi Power and SR Meridian III have received unanimous approval from the Mississippi Public Service Commission to build a 52.5-MW solar project in Lauderdale County. The project will include approximately 570,000 PV panels, and the plant is scheduled to begin providing energy by December 2019. [Solar Industry]
¶ The Midcontinent ISO has launched a multiyear study of renewable energy integration and its impacts on grid reliability. The study aims to inform future discussions of resource needs. It will consider limitations to renewable energy integration, including where the grid might be impacted and whether battery storage is required. [Utility Dive]
¶ The Home Depot is developing mini solar farms on 50 of its store rooftops. In partnership with Current, a subsidiary of GE, and Tesla, the company is leasing its roof space to produce power through power purchase agreements in five states and the District of Columbia. This will reduce grid demand at each store by 30% to 35%. [AltEnergyMag]
¶ As South Carolina grapples with the debacle of two utilities abandoning a nuclear power project, a poll found that more than two-thirds of its voters believe the state should rely more on solar energy to generate electricity, while substantially fewer voters believe it should become more reliant on sources like coal and nuclear power. [Solar Industry]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 18, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Climate change will likely wreck their livelihoods – but they still don’t buy the science” • In 50 years, Cameron Parish, Louisiana, will likely be no more, according to newly published calculations of the Louisiana government. Cameron Parish also has the greatest percentage of Trump supporters of any county in the US. [The Guardian]

Leo Adley Dyson Sr (Photo: Shanon Sims)
¶ “What Happens to Solar Power in an Eclipse? We’ll Find Out Monday” • As the eclipse carves a long shadow over California on Monday morning, it is expected to knock offline more than 5,600 MW of solar panels at its peak, a big chunk of the 19,000 MW of solar power that currently provide one-tenth of the state’s electricity. [New York Times]
Science and Technology:
¶ Getting electricity and clean water to remote villages can make a huge difference to those who live there. Running power and water lines from a central location can be expensive, but water filtration systems and electricity generation can be provided to remote locations at low cost. An Italian startup has a $15,000 all-in-one modular solution. [CleanTechnica]

Modular electricity and water supply
¶ The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration reported that July was the second hottest month since record keeping began in 1880. At 61.89° F (16.63° C), last month was behind July 2016’s all-time record by just .09° F (0.05° C), and land temperatures in July were the hottest on record at 59.96° F (15.5° C). [The Japan Times]
World:
¶ The European Commission published tighter new standards for the bloc’s most polluting power plants, including many large coal-fired power stations, giving them four years to meet the lower emission standards. The new standards include tighter rules for emissions of nitrous oxides, sulphur dioxide, mercury and particulate matter. [EURACTIV]

Uniper coal-burning power plant near Rotterdam (Shutterstock)
¶ Germany announced the results of its second onshore wind auction this week. They show that a total of 1 GW was awarded at an average cost 25% less than the average price recorded in the first onshore wind auction just a few months ago. The accepted bids ranged from 3.5 to 4.29 Euro-cents per kWh (4.11¢/kWh to 5.04¢/kWh). [CleanTechnica]
¶ Construction is set to begin on a world-leading wind, solar, and battery storage hybrid project in north Queensland, after the company behind the 1200-MW Kennedy Energy Park, Windlab, raised A$50 million through an initial public offer. Construction of the first 60 MW of the project is due to commence over the coming few months. [RenewEconomy]

Australian renewable energy (Image: Kennedy Energy Park)
¶ Taiwan recently suffered from a massive blackout that affected millions of households and businesses. Now the government of Taiwan says that it is reaching out to Tesla to consider a solution similar to the massive 100-MW/129-MWh battery system that South Australia ordered after they had their own power outage issues. [Electrek]
¶ Latin America has the world’s cleanest electricity, having long relied on dams to generate a large share of its energy needs, according to the World Bank. Even for Latin America, Chilean officials have an ambitious goal, saying the country is on track to rely on clean sources for 90% of its electricity needs by 2050, up from the current 45%. [The Seattle Times]

Vicuas and flamingos in northern Chile (Meridith Kohut | NYT)
¶ In the basement of a three-story house in a leafy neighborhood in Tokyo, about 40 lawyers crowded together, plotting against Japan’s massive nuclear power industry. The host was Harley-riding 73-year-old Hiroyuki Kawai, one of Japan’s most colorful litigators. The end game? To close all of the country’s 42 reactors for good. [Bloomberg]
US:
¶ Members of the public have been invited to express their views on the proposed 20.7-MW Icebreaker offshore wind project in Lake Erie near Cleveland. The Ohio Power Siting Board said it will hold a public hearing on 8 November to gauge support. Last month, the board said the application is “in compliance and ready to be processed”. [reNews]

Icebreaker test project (LEEDCo image)
¶ Cummins Inc, based in Columbus Indiana, has entered into a virtual power purchase agreement with EDP Renewables North America to expand a wind farm. The expansion will add 75 MW, enough to power 20,000 average-size Indiana homes, to the existing 600-MW at the Meadow Lake Wind Farm complex in Chalmers, Indiana. [Seymour Tribune]
¶ In Minnesota, capped landfills have become hosts to solar PV installations. Of three recently built, two were established by the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. They are being used to provide power for equipment set up at the sites to collect the methane gas and leachate produced by decomposing fill. [Minneapolis Star Tribune]

Solar panels at old landfill in Minnesota
¶ Nine facilities in Oceanside, California, will soon be powered by solar energy. Oceanside, which has 320 days per year of sunshine, has a 25-year agreement to buy generated electricity from PFMG Solar at a price below utility SDG&E’s rates. In return, the company will install and maintain the solar energy systems. [Coast News]
¶ Ameren Corp and S&C Electric Co conducted a successful 24-hour islanding test at a recently built microgrid in Champaign, Illinois. The 50-kW microgrid combines 225 kW of solar and wind generation with a 250-kW/500-kWh battery system. The test proved it can provide a seamless transition from grid-connected to island mode. [Solar Industry]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 17, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “On the climb to renewable energy, solar and wind prices tumble” • When so little is getting done in Washington, it is heartening to see how much has already been accomplished. A report from the Environment New York Research & Policy Center highlights past growth of renewable energy and says it is set for more dramatic growth. [GreenBiz]

Looking at how far we have come (Shutterstock | kopov58)
¶ “US Power Companies Have A History Of Walking Away From Nuclear Projects” • William Freebairn explains how the story of the Summer project in South Carolina demonstrates the capital-intensive nature of nuclear energy and the substantial risks of cutting-edge nuclear plant design. Will the Vogtle project be abandoned next? [Platts]
¶ “Pace of renewables shift leaves city planners struggling to keep up” • Renewable energy is driving changes in cities much more quickly than expected. Networks of city decision-makers have begun adopting climate change strategies to promote renewable energy. But land use planning has seemingly been lagging behind. [One Step Off The Grid]

Suburban solar array (Image: The Conversation)
World:
¶ Xinhua News Agency said that China is halting construction of 150 GW of new coal-fired generating capacity during the 13th Five-Year Plan period, which ends in 2020. The National Development and Reform Commission will also eliminate 20 GW of outdated capacity and upgrade almost 1,000 GW of coal capacity to decrease emissions. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The gas reserves in shale rocks in the UK have been “hyped”, a geology professor has warned. Professor John Underhill from Heriot-Watt University said UK shale deposits were formed 55 million years too late to trap substantial amounts of gas. He said the government would be wise to formulate a Plan B to fracking for future gas supplies. [BBC News]

Magma under Iceland tilted UK shale basins. (Getty Images)
¶ Most Europeans can choose who they buy their power from and can choose to purchase power from renewable power plants, instead of accepting a “grey default” power offer. More and more consumers prefer to buy clean energy from solar, wind, hydro, geothermal or bio. Growth in demand for renewable power stands at 39% this year. [Press Release Rocket]
¶ Ford of Europe has linked up with Deutsche Post to build a larger version of the electric truck DHL designed itself last year. Called the StreetScooter Work XL, it is customized to be ideal for urban delivery chores and has over 700 cubic feet of cargo space. The basic battery is rated at 30 kWh and has 50 miles of range. [CleanTechnica]

DHL StreetScooter
¶ Taiwan’s President Tsai Ing-wen publicly apologized for power outages that hit more than 6 million households and disrupted some semiconductor manufacturing but defended her policies to phase out nuclear power in favor of natural gas and renewables. Outage factors included hot weather and damage from a recent typhoon. [Hong Kong Standard]
¶ In Milan, architect Stefano Boeri created two high-rise apartment blocks that are adorned with a massive number of trees and plants, including 800 trees and 16,000 other plants. Combined, the two towers can convert around 44,000 pounds of carbon dioxide into oxygen annually. They also filter dust from the air. [CleanTechnica]

Stefano Boeri’s high-rise towers
US:
¶ A partnership of Fuel cell maker Bloom Energy and Southern Company microgrid subsidiary PowerSecure have landed their biggest client to date. They have made a 37-MW fuel cell deal with data center company Equinix. Twelve Equinix data centers in California and New York will get fuel cells over the next two years. [Greentech Media]
¶ The governor of Montana is worried about climate change. The eastern half of the Montana is now in the most severe drought in the nation. July farm losses are nearly $400 million more than last year’s, according to figures from the US Forest Service. And the state’s wildfire season is costing Montanans more than a million dollars a day. [MTPR]

A difficult year in Montana (Credit: Nate Hegyi | YPR)
¶ The Nederland, Colorado, city council unanimously voted to power their city with 100% renewable electricity by 2025. The vote came shortly after Orlando, Florida, and Nevada City, California, established similar goals last week. The Sierra Club said that Nederland is the 42nd US city to commit to 100% renewables. [North American Windpower]
¶ As climate change pushes US cities to build protections against more powerful storms and more frequent floods, the Rockefeller Foundation is helping with a kind of financing that transfers some of the risk of innovative projects from cities to investors. The environmental impact bonds were pioneered by The Goldman Sachs Group Inc. [Bloomberg]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 16, 2017
Science and Technology:
¶ A new study by the National Renewable Energy Lab tabulated data collected from Proterra electric buses and buses powered by compressed natural gas. When driven on the same route, average fuel economy for the CNG buses came to 2.1 miles per diesel gallon equivalent. By contrast, the Proterra electric buses had an observed MPDGe of 17.35. [CleanTechnica]

Proterra electric buses
¶ Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder claim they have invented a new passive cooling material that can reduce temperatures even in direct sunlight while using no energy and no water. The new metamaterial is a glass/polymer sheet that is 50 μm thick, just slightly thicker than a piece of household aluminum foil. [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ Soon plastic waste will no longer clog up Costa Rica’s landfills. The country announced it will have a ban on single-use plastics by 2021. Costa Rica wants to become the world’s first country to achieve a comprehensive national strategy to eliminate single-use plastics, a goal that coincides with a 2021 goal of being carbon neutral. [CleanTechnica]

Costa Rica (Photo: Foter.com)
¶ London Mayor Sadiq Khan launched plans to turn his city into the world’s first National Park City and one of the greenest cities on Earth. He will create a £9 million fund to increase the cities’ trees and green infrastructure, and proposed building more green roofs, walls, and rain gardens. The first goal is to protect London’s Green Belt. [CleanTechnica]
¶ As the world searches for clean fuels for cars, there may be a solution right under our noses. The first ‘poo-powered’ car has hit the streets of Australia. It gets power from every flush of a toilet. The electric vehicle from Queensland Urban Utilities is run on electricity generated by the city of Brisbane’s toilet waste. [International Business Times UK]

Australia’s first ‘poo powered’ car (Queensland Urban Utilities)
¶ Dutch Airports will run on 100% renewable energy generated in the country starting next year. Dutch airport owners Royal Schiphol Group made a deal with energy firm Eneco, which will provide 200 GWh of clean power annually for the next 15 years. Wind farms will be built to support the airports in the years ahead. [Innovators Magazine]
¶ French utility Engie has signed a £50-million contract with Voith Hydro to refurbish its Ffestiniog power station, part of the 2-GW First Hydro pumped storage operation in North Wales. Design, planning and component production are due to start immediately. The refurbishing is scheduled for completion by early 2020. [reNews]

Hydro facility (sxc image)
¶ The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds Scotland has applied directly to the Supreme Court for permission to appeal against the recent decision by the Inner House of the Court of Session on its Firth of Forth offshore windfarm judicial review. The appeal relates to the wind energy projects with a total of 2,100 MW capacity. [Offshore Wind Journal]
¶ Coal India Ltd, which produces 84% of the country’s total output of the mineral, plans to invest ₹8,500 crore ($1.28 billion) as capital expenditure in 2017-18, its annual report said. The mining company also planned to invest ₹6,500 crore in various coal-related projects, ranging from research to acquisition of Indian coal blocks. [The New Indian Express]
¶ China National Nuclear Power announced plans to build 20 floating nuclear power stations in a bid to reinforce its influence in the South China Sea. A new company is being setup in Shanghai for the purpose. China claims an area up to 1500 miles from its shores but the claim is contested by many other countries. [Power Engineering International]
US:
¶ Duke Energy Carolinas wants to purchase up to 500 MW of wind power by 2022, reports say. The Duke Energy unit issued a request for proposals for new or existing wind farms to deliver power to the Duke transmission grid. Duke has 35 solar power projects in the region, but this would be the utility’s first use of wind power. [Electric Light & Power]

Wind project in Idaho (ELP image)
¶ Facebook will spend $750 million on a new data center in central Ohio, the company announced. The move marks another boost for the state’s growing technology sector. The 22-acre data center will be powered exclusively with renewable energy. It is expected to employ 100 people to start and to begin providing services in 2019. [Huntington Herald Dispatch]
¶ A year or so from now, electric customers of Rochester, New York, could have easy access to 100% renewable energy at a price lower than their current rates. The mayor is preparing legislation stating the city’s intent to pursue community choice aggregation, which would let the city negotiate an energy-supply contract. [Rochester City Newspaper]
¶ A study from the University of California, Berkeley gives us more reason to move from fossil fuels to renewable energy. The study says the US wind and solar power boom has helped prevent the premature deaths of thousands of people and has saved the country billions of dollars in healthcare and climate-related costs in a single year. [AlterNet]
¶ Furthering his attack on Obama-era climate policies, President Donald Trump is expected to rescind a rule that requires federal, state and local agencies to account for rising sea levels caused by climate change and to construct buildings, highways and other infrastructure to withstand flooding, according to multiple media reports. [HuffPost]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 15, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “A bolder, better deal for all Americans” • The Democratic Party recently unveiled the Better Deal: Better Jobs, Better Wages, Better Future platform focused on an economic message. As Hurricane Trump wreaks its havoc, this jobs agenda comes not a moment too soon. But as we expand upon our message, the time has come to be bold! [The Hill]

Dawn (Getty Images)
¶ “Huge Climate Opportunity If RGGI Governors Step Up” • The governors of nine Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states are about to make a momentous decision: how much they will cut power plant pollution, and how fast they will cut it. Big carbon cuts could add $3.2 billion to state coffers and reduce air pollution. [Natural Resources Defense Council]
Science and Technology:
¶ New analysis of flow rates and precipitation suggest flooding in urban areas is intensifying while rural areas dry up. To identify links between global warming and river flow patterns, scientists at the University of New South Wales surveyed flow rate and rainfall data from 5,300 river monitoring sites and 43,000 rain gauges in 160 countries. [UPI.com]
World:
¶ The UK Government spent £6.13 billion ($9.73 billion) in 2016 on energy in developing countries. Of that amount, 46% went to supporting fossil fuels, but only 22% was put towards supporting renewable energy development, according to a report by the Catholic Agency for Overseas Development and the Overseas Development Institute. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Danish wind turbine-maker Vestas has received an order to supply 99-MW of turbines to China Datang Corp Renewable Power for its Shandianhe project. The project will be located in the Guyuan County of northern China’s Hebei Province. For the project, Vestas will supply 45 of its V110-2.2MW turbines. [CleanTechnology News]

Vestas turbines (Photo: Steve Ralston | FreeImages.com)
¶ German energy company Innogy has entered the Irish market having acquired a wind farm site in County Kerry. The 10.2-MW Dromadda Beg wind farm will have three turbines, which received planning approval in May 2014. Construction is due to begin in September, with commissioning scheduled for the second half of 2018. [Irish Times]
¶ Residents of a remote community on the central coast of British Columbia received funding to build a run-of-river hydroelectric plant. The Wuikinuxv Village, on the banks of the Wanukv River, has about 80 people in it. It is accessible only by float plane or boat, so life is challenging, and it has depended on diesel power in the past. [BCLocalNews]

Wanukv River (Photo: CCIRA)
¶ Spanish firm ACCIONA has been selected by Zuma Energía to build a new 424-MW wind farm in Mexico. The Reynosa wind farm will be the largest of its kind in the country, and will require an investment of around €510 million ($600 million). The wind farm will have 123 wind generators, each with a capacity of 3.45 MW to 3.6 MW. [Power Technology]
US:
¶ A coalition of business, environmental and community leaders has backed Governor Andrew Cuomo’s plan to make offshore wind the focus of New York’s renewable energy plan. The New York Offshore Wind Alliance voiced its support for developing green energy off the state’s coastline ahead of a series of public meetings. [reNews]

Offshore wind farm (reNews image)
¶ A partnership of the Poudre Valley Rural Electric Association, GRID Alternatives, and the Colorado Energy Office will work to develop the United States’ largest low-income community solar project aimed at lowering the electricity bills of qualifying low-income residents, affordable housing providers, and nonprofit organizations. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Southern California Edison, one of the largest US utilities, has signed contracts with solar and geothermal energy producers for more than 1,500 MW of power. Signed contracts include the purchase of more than 1,300 MW of new solar power and the re-contracting of 225 MW with an existing California geothermal energy project. [ThinkGeoEnergy]

Geothermal plant in California (Photo: ThinkGeoEnergy)
¶ NextGen America, a green energy advocacy group founded by Tom Steyer, has released a video opposing the proposed power plant for coastal Oxnard, California. They are objecting to a proposal by NRG Energy Inc to replace two existing power plants at the Mandalay Generating Station with a new gas-fired facility. [Ventura County Star]
¶ A last-ditch effort to send hundreds of millions of dollars in tax breaks to Georgia’s struggling Plant Vogtle nuclear project appears to be stuck in the US Senate. Boosters of the project hope the federal bill could throw an economic lifeline, which it needs amid major cost overruns and deep delays. The cost is estimated to be $25 billion. [MyAJC]
¶ Duke Energy Renewables has acquired the 24.9-MW Shoreham Solar Commons PV project in New York from developer Invenergy. The PV plant, which is being built on a former golf course on Long Island, is due to be completed in the second quarter of 2018 and has a 20-year power-purchase agreement with the Long Island Power Authority. [reNews]
¶ The US DOE’s recently commissioned study on the national electric grid hit a new legal road block this week when the Sierra Club filed a lawsuit against the agency to reveal the third parties consulted on the study, according to Reuters. Energy Secretary Rick Perry ordered the 60-day study in April but its release has been delayed. [OilPrice.com]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 14, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “A greener grid for East Asia” • Nine of the 10 nuclear reactors that opened in 2015 were in Asia. But declarations by South Korea and Taiwan that they will “go green” have called into question nuclear power’s viability in the region. This year may mark the end of the region’s nuclear love affair and the start of one with renewables. [eco-business.com]

Windmills in Taiwan (Image: Alexander Synaptic, CC BY-NC 2.0)
World:
¶ Enel Energy, Nissan, Mitsubishi, and PSA Groupe, have been working together to pave the way for a roll-out of vehicle-to-grid technology. The Parker Project, going on in Denmark, is using a fleet of EVs to demonstrate the technology. It supplies electricity to the grid as needed from parked electric vehicles, in a real-life setting. [Digital Journal]
¶ A tiny Tesla house is on a tour of Australia, showing off the Powerwall and educating the public on how to generate, store and use renewable energy. Oh yes, and the tiny home is towed by a Tesla Model X. The tiny home is completely powered by renewable energy courtesy of a 2-kW solar power system and a Powerwall battery. [Gizmodo Australia]

Tesla Tiny House in Melbourne (iStock photo)
¶ Pakistan’s vulnerability to climate change is well established and widely recognized. Pakistan ratified the Paris Agreement on Climate Change. But even as the rest of the world is holding down on coal consumption, Pakistan is reviving its coal industry with several new power plants and working against the country’s own well-being. [MENAFN.COM]
¶ A lack of solar auctions in India could drive solar power prices down, below the record low of ₹2.44 (3.8¢/kWh). Developers backed by private equity funds are trying hard to build their assets, even if it means sacrificing returns. Analysts believe the internal rate of returns in the solar sector have reduced from 15-16% to the range of 10-13%. [Hindu Business Line]

Solar array in India
¶ Relief is in sight for farmers and other rural people in New Zealand suffering from electricity supply problems. Electricity distributor Powerco has developed a cutting-edge unit called Base Power. The system depends on PVs and batteries with diesel backup generators. Five customers have already received Base Power systems. [New Zealand Herald]
¶ Alberta produces about 80% of Canada’s oil. But as oil prices have dropped, there have been lay-offs, and the unemployment rate in the once-booming province stands at nearly 8%. Now Alberta’s renewable energy capacity is doubling roughly every two years, and interest in green energy training has been growing swiftly. [Huffington Post Canada]

Wind turbines in Alberta (Todd Korol | Reuters)
¶ Seaway Heavy Lifting has installed the first jacket foundation at the 588-MW Beatrice wind farm off the coast of Scotland, with the vessel Oleg Strashnov on the job. The foundations are being made at yards across Europe by BiFab, Bladt, and Smulders. Beatrice will feature 84 Siemens 7-MW turbines when fully commissioned in 2019. [reNews]
¶ A proposed solar thermal power plant in South Australia’s mid-north has been contracted to supply all the state government’s power needs. Work on the A$650 million SolarReserve facility will start in 2018. The state government said the 150-MW plant, to be ready in 2020, would dispatch energy to the grid even when the sun was not shining. [The Guardian]

Solar Reserve plant in Nevada (Photo: Solar Reserve)
¶ A consortium of Chinese organizations is teaming up with state-owned China National Nuclear Power Company to develop and produce small, floating nuclear power plants. The new venture will have $150 million in funding. The plants will be able to sail to where they are needed to fill a variety of high power needs. [The Maritime Executive]
US:
¶ Last year, California’s 1.4 million dairy cows fell under a statewide mandate to find a way to curb their environmental footprint in order to achieve the state’s goal to reduce methane emissions 40% from 2013 levels by 2030. The state government says now it is receiving more applications for anaerobic digesters than it can currently fund. [Triple Pundit]
¶ Despite moves made by Ohio’s legislature to thwart large-scale wind farm development, there is still a steady demand for small installations to power factories and small businesses. Projects with just a few turbines put Ohio among the top 10 for wind capacity installed since 2003, according to a report from the US DOE. [Midland Daily News]
¶ A 121-year-old church on the edge of coal country is harnessing the sun’s energy in an effort to move into the future. Campton Baptist Church in Wolfe County with 80 solar panels on its roof, has become one of the first churches nationwide to switch to solar energy, not only for both itself but also for others in the community. [WYMT News]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 13, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Joining Forces for Honest Environmental Journalism” • News publication have for years insisted on presenting opposing points of view for balance, even if they are self-serving and unscientific. The Climate News Network was set up in 2013 to provide a daily news story, objectively written, on some aspect of energy or climate change. [Truthdig]

USGS surveyors in Alaska (US Geological Survey | CC 2.0)
World:
¶ Australia is undergoing something of an energy crisis. Growing demand combined with under-investment in the electric grid has recently led to a series of embarrassing blackouts, and at the same time electric rates are soaring. South Australia has just overtaken Denmark as the place with the world’s most expensive electricity. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Norway’s plan to ramp up oil and gas production in the Arctic threatens efforts to tackle climate change, a study said. It says 12 gigatonnes of carbon could be added by exploration sites in the Barents Sea and elsewhere over the next 50 years. This is 1.5 times more than the Norwegian fields currently being tapped or under construction. [The Guardian]

Oil platform maintenance (Photo: Marius Dobilas | Alamy Stock)
¶ The Indian government is looking at doubling the nuclear power generation capacity to about 14,000 MW, Union minister Piyush Goyal said. He has ruled out nuclear power becoming the main source of energy for India because it is too expensive, but he said the government plans to add ten new reactors of 700 MW each in the country. [citytoday]
¶ The regions of New South Wales known as New England and the North West have two more solar farms in the pipeline, with a combined investment of almost A$300 million ($237 million). Canadian Solar is building a 60-MW solar farm in Narrabri, and Photon Energy is developing a 155-MW solar farm in Gunnedah. [The Northern Daily Leader]

Australian solar farm
¶ Records are being set in the UK. There was not a single major plant generating purely solar power in 2007, but now, there are 277. The current UK target calls for 30% of electricity to be generated from renewable sources by 2020, and according to provisional figures, the number for the first three months of 2017 was 26.6%. [domain-B]
¶ Tourism tycoon Chris Morris is helping fund a scientific expedition into the northern part of the Great Barrier Reef to search for corals that can survive bleaching. He is lending Great Barrier Reef Legacy his 35.5-meter yacht Flying Fish to search for “supercorals” that have tolerated warm water temperatures during bleaching events. [The Cairns Post]

The Flying Fish
US:
¶ In Mahwah, New Jersey, a Ramapough Lenape Nation’s prayer ground now has electricity, courtesy of renewable energy technology donated by Princeton University graduates. The energy system, which arrived in a 20-foot metal shipping container, has solar panels, a small wind turbine ready to be raised, and energy storage. [NorthJersey.com]
¶ A 1-MW solar array in Tres Piedras, New Mexico, started soaking in the sun and pumping power to the grid last week. Kit Carson Electric Cooperative announced plans earlier this year to eventually provide its 30,000 members with 100% renewable energy. The Tres Piedras solar array is the first of seven the co-op plans to build this year. [taosnews]

Solar array in New Mexico
¶ With an ambitious agenda to build two nuclear reactors in South Carolina, SCE&G painted a bright picture for years about progress on the nuclear project it had undertaken with state-owned utility Santee Cooper. The result was that many people did not know the magnitude of problems that started surfacing in 2012 until very recently. [The State]
¶ The clean energy standard, developed by the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection and Executive Office of Environmental Affairs, qualifies only zero-carbon producers that became operational after December 31, 2010, for clean energy credits. The Pilgrim nuclear plant is too old to get any subsidies. [SouthCoastToday.com]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 12, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Here’s What Trump’s Team Has Gotten Wrong About Climate Change So Far” • President Donald Trump is not the only official in the government to doubt human-caused climate change. His skepticism is shared by many others in his administration. This week two new reports again prove that Trump’s team simply has it wrong. [The Weather Channel]
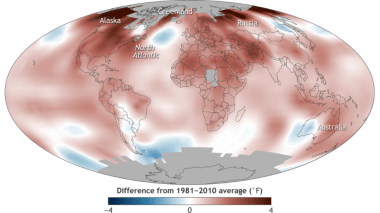
Global surface temperature changes (NOAA)
¶ “As Massachusetts Unveils New Climate Rules, More Progress Needed on Transportation Emissions” • Massachusetts has issued new regulations to reduce the emissions causing climate change. They are a positive step, but the state needs to go further, and this includes working across state lines to cut transportation emissions. [Union of Concerned Scientists]
World:
¶ Northern Adelaide Waste Management Authority is set to host a combined solar and methane power plant at a landfill, believed to be an Australian first. South Australia gets 57% of its electric power from renewable sources, meeting a 50% target eight years early. Over the last nine months reported, solar power met 7.6% of demand. [pv magazine]

Solar site at NAWMA landfill (NAWMA image)
¶ India installed an impressive 4.8 GW worth of solar in the first half of 2017, according to new figures published by Mercom India Research. This fact is all the more impressive when you consider that the country only installed 4.3 GW in all of 2016. Utility-scale solar accounted for 4,290 MW and rooftop solar 475 MW. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Capital investment in global oil and gas supply fell by 38% between 2014 and 2016, the IEA said, but still comprises around 40% of the total. This drop has allowed spending on low-carbon energy supply, including electricity networks, to reach a record 43% of the global, total spend last year. This is a rise of 12% from 2014 levels. [Petroleum Economist]

Children near a wind farm
¶ India’s renewable energy program is proceeding at such a rapid pace that its contribution to total power generation will equal that of coal in 2026 and surpass it the following year, according to projections made in the second volume of the Economic Survey. At present, coal provides 55% of India’s installed power capacity. [EnergyInfraPost]
¶ Canadian Solar Inc. and EDF Energies Nouvelles announced a partnership in the 92.5-MWp Pirapora III PV project in Brazil, through the sale of 80% interest in the Project by Canadian Solar to EDF EN do Brasil. The Pirapora III project has started construction and is expected to reach commercial operation in the fourth quarter of 2017. [solarserver.com]

Canadian Solar PV array (Canadian Solar image)
¶ JSW Energy will invest up to ₹40 billion ($623 million) to build electric cars, batteries and charging infrastructure, part of the power company’s diversification plans to drive future growth, its chief executive said. JSW plans to roll out its first electric car by 2020, making it the first non-automotive company in India to enter electric car business. [News18]
¶ Growth in the deployment of offshore wind in Europe must triple if countries are to have any chance of meeting the goals of the Paris climate agreement, a study said. Research by a joint team from Ecofys and parent company Navigant found that 45% of Europe’s power requirements would need to come from offshore wind to meet the target. [reNews]

Offshore wind farm (reNews image)
US:
¶ North Carolina’s HB589 included an amendment to set an 18-month moratorium on developing onshore wind power. In the wake of its passing, 50 small businesses, community groups, environmental organizations, and elected officials sent a letter to Governor Cooper urging him to embrace offshore wind for the state’s energy plan. [North American Windpower]
¶ Last month, the New York Independent System Operator’s CEO told a House subcommittee that it planned to integrate a price on carbon into its market dispatch within three years after the Brattle Group published a report on potential impacts. The Brattle Group has released the report, so the clock has started on carbon pricing in the state. [Utility Dive]

New York City
¶ Utility customers in Waterloo, Iowa, will soon receive more of their electricity from cost-effective renewable energy. Waterloo Utilities’ not-for-profit wholesale power supplier, WPPI Energy, has entered an agreement with Invenergy. WPPI Energy will buy the output from Invenergy’s 132-MW Bishop Hill III Wind Energy Center. [hngnews.com]
¶ Sandia National Laboratories is testing whether one of the largest and most polluted lakes in California can be transformed into one of its most productive and profitable. The 350-square-mile Salton Sea has high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural runoff. Some algae that thrive on these elements may be used to make biofuel. [Biomass Magazine]
¶ South Miami has a new “Solar Requirements” section in its Land Development Code. The city enacted its new residential solar mandate, making it the only municipality between California and Florida to enact a law mandating that solar power be installed in newly built homes or those subject to major renovation. [Miami’s Community Newspapers]
¶ Millions of customers who have been footing the bill for a now-abandoned nuclear power project for years may get a temporary reprieve from rising bills, as South Carolina’s state-owned utility dropped plans for two rate hikes. Santee Cooper’s board canceled the approval process for average increases of 3.5% in 2018 and 3.9% in 2019. [Santa Cruz Sentinel]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 11, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Renewable Energy Sources Get Thumbs up from Corporate America” • The double benefit of an environmentally friendly energy source at a low cost is hard to pass up, and corporate America is starting to take notice. Many of the multinational conglomerates are putting up investment money to cash in on the alternative energy boom. [Newswire]
¶ “The wise man Trump should listen to” • My unsolicited advice to our President: Listen to George Shultz, who held cabinet positions under Presidents Nixon and Reagan and has a wealth of knowledge. Speaking of what worries him, he said, “Well, there are two things that can wipe us out. One is nuclear weapons and the other is climate change.” [CNN]
Science and Technology:
¶ The records highlighted in the “State of the Climate in 2016” report from the NOAA sound ominous. Global land surface temperatures last year were highest in 137 years of record keeping. Sea surface temperatures were also at their highest. Sea levels were at record highs. Scientists worry that the report will be buried. [CNN]
World:
¶ India has auctioned the largest capacity of rooftop solar power projects in history. The results are extremely promising and could provide a boost to the rooftop solar power market. In an auction of just over 503 MW of rooftop solar capacity, bids ranged from $1.01/W to $1.166/W with tariffs ranging from 3.4¢/kWh to 7.1¢/kWh. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Origin Energy will underwrite one of Queensland’s largest solar farms through a power purchasing agreement with the 150-MW project. Origin has bought all the output and renewable energy certificates from the Daydream solar farm until 2030 and the deal brings its commitment to solar to 1200 MW since March 2016. [Courier Mail]

Australian solar farm
¶ Saudi Arabia’s Electricity & Cogeneration Regulatory Authority has approved the “Small-Scale Solar PV Systems Regulations,” a new net metering scheme for residential PV. The new rules will apply to PV systems not exceeding 1 MW. The program will also allow some projects with a power range of 1 MW to 5 MW to be put online. [pv magazine]
¶ India’s total installed solar power generation capacity grew over threefold to 13,652 MW over the past two fiscal years, the country’s energy minister said. He also stated the government has revised the National Solar Mission target of Grid Connected Solar Power projects from 20,000 MW by 2022 to 100,000 MW by 2022. [ETEnergyworld.com]

Solar array in India
¶ A bomb dating to World War II was found buried in a parking lot of the crippled Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. The Self-Defense Forces said the 50-kilogram dud was likely left by the imperial Japanese military and is in no danger of exploding. A radius of 200 meters was cordoned off while the SDF worked to recover the bomb. [Asahi Shimbun]
¶ A dairy farm in southern Manitoba will soon boast the largest solar energy installation in the province. Hans Gorter is getting 540 panels, each with an area of 1.4 to 1.6 square metres, installed on his 130-cow dairy farm in Otterburne, about 45 kM south of Winnipeg. The system will generate close to 200,000 kWh of energy annually. [CBC.ca]

Gorter’s dairy farm in Otterburne (Pierre Verriere | CBC)
US:
¶ Rhode Island Governor Gina M. Raimondo signed a handful of bills aimed at expanding the state’s clean energy industry. Among the bills was a 10 year extension of the renewable energy growth program. Among several other bills signed into law were some streamlining the permitting processes and for expanding net metering. [Utility Dive]
¶ US retailer Target has agreed to buy 100 MW of electricity from Infinity Renewables’ 474-MW Solomon Forks wind farm in Kansas. Target will use the energy to power about 150 stores in the region, Infinity said. Construction of the project will start in early 2018, with commercial operation scheduled for the fourth quarter of that year. [reNews]

Wind power in Kansas (Pixabay image)
¶ Vermont Governor Phil Scott’s Climate Advisory Commission hasn’t even held its first meeting, but it’s already taken a step that may alienate a broad swath of Vermont’s environmental community. The commission’s Technical Advisory Group will have Annette Smith, vociferous critic of wind turbines, as its co-chair. [Seven Days]
¶ The Wyoming Mining Association recently asked lawmakers for a tax break for uranium mines until prices rise. Without it, they couldn’t build up production, and they would be faced with increasing layoffs, companies argued. That request was denied. Now their hope is for new nuclear power plants in Asia to increase demand. [Casper Star-Tribune Online]

Uranium leaching mine wellheads (Alan Rogers | Star-Tribune)
¶ Wind power started in California in 1981, when the Altamont wind farm was built as a reaction to the Arab Oil Embargo of the 1970s. But now, as a map from the American Wind Energy Association shows, the industry is spreading rapidly across the US, with more than 52,000 large-scale turbines now operating in 41 states. [The Mercury News]
¶ Oil and gas operators are positioning for potential growth in US offshore wind projects. The US could generate more than 2,000 GW of offshore wind power, Stephanie McClellan with the University of Delaware said at Renewable Energy World’s inaugural Offshore Wind Executive Summit. Statoil and DONG may invest in the US. [Offshore Oil and Gas Magazine]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 10, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Global Fossil Fuel Subsidies Still Total More Than $5 Trillion Annually” • A study by four economists at the International Monetary Fund – not exactly a liberal outfit – and published in the journal World Development finds that direct and indirect subsidies to fossil fuel companies amount to about 6.5% of global GDP. [CleanTechnica]

Sun setting on a nodding donkey
World:
¶ Since oil prices collapsed in 2014, Canada has lost more than 40,000 jobs in oil, gas and related industries, according to data released last year by the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers. Thousands of employees of fossil fuel businesses left jobless following a plunge in oil prices are finding work with solar or wind energy. [ETEnergyworld.com]
¶ Aela Energía, a joint venture of Actis and Mainstream Renewable Power, has sealed $410 million in project financing for two wind farms in Chile totaling 299 MW. The finance will allow Aela to proceed with the construction of the 170-MW Sarco and 129-MW Aurora projects. Both projects will have turbines made by Senvion. [reNews]

Senvion turbine (Senvion image)
¶ GE Renewable Energy booked a turnkey contract with Star Pumped Storage Ltd for the 344-MW Kokhav Hayarden pumped storage station in Israel. GE Renewable Energy is responsible for the design, manufacture, supply and installation of all electro-mechanical and hydro-mechanical equipment for the two 172 MW pumped-storage units. [Your Industry News]
¶ Wildfires can happen even in Greenland. They are very rare there, but unfortunately they are becoming more common. This year has been unprecedented far as numbers of fires go. This is particularly bad, as wildfires release soot, and soot that has been deposited on ice sheets or snow greatly increases the speed at which the ice melts. [CleanTechnica]

Greenland wildfire (Photo: Pierre Markuse, some rights reserved)
¶ Sri Lanka’s cabinet has given the go ahead to install PV systems to generate solar power on the roofs of all public institutions. About 3% of Sri Lanka’s energy demand is currently met by renewables such as wind and solar. Solar power has the potential to meet 32% of Sri Lanka’s annual power demand of around 10,500 GW. [Lanka Business Online]
¶ An Australia trial to demonstrate the ability of wind farms to provide crucial grid stabilizing services, traditionally supplied by “baseload” coal and gas plants, is set to begin in October. The trial will test the ability of Hornsdale 2 to provide frequency control and ancillary services and subsequently to participate in the grid markets. [RenewEconomy]

Hornsdale wind farm
¶ Two parallel announcements have given shape to the planned 424-MW Reynosa III Wind Park set to be developed in Mexico. Three state-owned development banks will provide $1,072 million in financing, and Vestas is to supply 120 of its V136-3.45 MW wind turbines. The wind farm is expected to be completed by 2019. [CleanTechnica]
¶ In the last two years, Indian coal consumption has slowed to its lowest level in two decades, even though the economy has been growing at a steamy 7% annual pace. Thermal power plants have been running well below full capacity for years and as of June were operating at only 57% of their total capacity, the lowest level ever. [PennEnergy]

Illegal coal scavengers (AP Photo/Kevin Frayer, File)
US:
¶ When construction was halted on two nuclear power plants in South Carolina spiraling costs were blamed. But another equally important reason was that the demand for electricity has not increased as expected when the project was proposed in 2008. In fact, a report shows that US residential demand has declined from what it was ten years ago. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The US has over 20 offshore wind projects in the pipeline, with over 24-GW of potential installed capacity, according to the US DOE. Most projects are planned for the northeast Atlantic, but schemes are also in the pipeline in the southeast Atlantic, Pacific, Gulf of Mexico and Great Lakes, DOE said a report it released on wind energy. [reNews]

Block Island offshore wind farm (Deepwater Wind image)
¶ AES is to supply two batteries to Arizona Public Service for an 8-MWh energy storage project. The batteries will be installed at the community of Punkin Center. The new project will be built to avoid rebuilding 20 miles of power lines over rough terrain to the community, the company said. The facility expected to be operational in early 2018. [reNews]
¶ The wind energy industry reached an important milestone in 2016 when it passed the generating capacity of hydroelectric power for the first time to become the nation’s top renewable generating source. The total amount of wind capacity in the queue represents 34% of all generating capacity waiting to connect to the grid. [ThinkProgress]

Dry Lake wind project in Arizona (DOE photo)
¶ The total solar eclipse on Monday will obscure the sunlight at 1,900 utility-scale solar-power plants in the country, the Energy Information Administration said this week. Though there will be a reduction in solar output, relatively little solar-power capacity lies directly on the path of totality and no reliability issues are expected in the US, the EIA said. [MarketWatch]
¶ The city commission in Orlando, Florida, unanimously approved a resolution to commit to a goal of 100% clean and renewable energy for the city by 2050. According to the Sierra Club, Orlando has joined a growing movement of more than three dozen cities nationwide that have committed to a 100% clean energy future. [North American Windpower]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 9, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Switching from coal to natural gas will not save our planet” • If as little as 3% of natural gas leaks in the course of fracking and delivering it to the power plant through a pipe, then it’s worse than coal. And, sadly, it’s now clear that leakage rates are higher than that. Aerial surveys of one fracking area found leak rates as high as 9%. [The Seattle Times]

Natural gas well (Ralph Wilson | The Associated Press)
Science and Technology:
¶ Researchers at Rice University have developed a simple water filter that has been shown to remove up to 99% of the toxic heavy metals in treated water samples, including copper, cadmium, lead, mercury, and nickel. A single gram of it can treat up to 83,000 liters of contaminated water, after which it can be washed with vinegar and reused. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Ineratic, a spinoff of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, has cooperated with Finnish partners to develop a mobile chemical pilot plant that can be used decentrally to produces gasoline, diesel oil, and kerosene from regenerative hydrogen and carbon dioxide from the air. The pilot plant is so compact that it fits into a shipping container. [domain-B]

Pilot plant (Image: VTT)
World:
¶ Irizar e-mobility has been awarded the contract to supply Madrid with its first 15 electric buses, and to supply Barcelona with its first 4 electric articulated buses. The city of Valencia will also buy its first electric bus from Irizar, and the city of Bilbao will buy two. These units are expected to all be delivered before the end of 2017. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Belectric has built and commissioned a 16-MWh battery storage plant for Eins Energie in Saxony. The €10 million ($11.7 million) project provides primary reserve of 10 MW to the power market, Belectric said. The German state of Saxony funded the project, together with €1 million from the European Regional Development Fund. [reNews]

Belectric storage project (Credit: Belectric)
¶ The Queensland Government introduced a new program to support renewable energy investment and storage projects. Known as Renewables 400, it is part of the government’s A$1.16 billion ($919 million) Powering Queensland Plan. It aims to aid companies to develop large-scale renewable and battery storage projects. [Power Technology]
¶ Australian funds manager Impact Investment Group has committed to fund the construction and operation of a new 19-MW solar farm in Victoria’s Swan Hill. The Swan Hill Solar Farm is expected to produce 37,700 MWh in its first year of operation, enough to power the equivalent of about 6,300 Australian homes. [The Urban Developer]

Solar array
¶ Shell Energy Europe announced plans to enter the UK power market. It has applied for a licence to supply electric power to industries and businesses in Britain. The oil giant plans to start signing them up now to start providing them with electricity early next year. The company offtakes renewable power from wind farms and solar parks. [Energy Live News]
¶ A project that will test whether South Australia’s excess solar and wind power can be used to produce cheap hydrogen, both as a means to supplement Australia’s gas supply, and as a long-term energy storage option, has been backed by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. The agency is funding a pilot project with A$5 million. [RenewEconomy]

Snowtown II wind farm
¶ Homes across the Northern Tablelands of New South Wales will receive a second boost of locally-generated renewable electricity, with a 400,000 panel solar farm soon to be built in the region. The state government approved the 100-MW Metz Solar Farm. Construction is scheduled to begin early next year. [The Guyra Argus]
US:
¶ Goldwind Americas is to supply One Energy Enterprises with turbines totaling 60 MW for several wind projects in the US. The first 20 GW87/1500 machines are scheduled for immediate delivery, Goldwind said. The first four turbines will be installed at wind for industry projects to supply power to Whirlpool Corp facilities in Ohio. [reNews]

View from the top of a wind turbine (Goldwind image)
¶ US diplomats should sidestep questions on what it would take for the Trump administration to re-engage in the global Paris climate agreement, a diplomatic cable seen by Reuters said. The cable was sent to embassies by Secretary of State Rex Tillerson. It also said diplomats should make clear the US wants to help other countries use fossil fuels. [HuffPost]
¶ The DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory released its annual Wind Technologies Market Report. It confirms that US wind energy costs continue to fall, technology continues to advance, and performance continues to improve. This has helped the wind industry sell energy at historically low prices to electricity customers. [Into the Wind]

American wind power
¶ Eagle Creek has acquired the 19-MW Abenaki and the 9-MW Anson facilities located on the Kennebec River in Maine. The two facilities had provided power to a mill until it closed in 2016. Under Eagle Creek’s ownership, they will now provide about 150 million kWh per year of electric energy to the New England power grid. [POWER magazine]
¶ When the South Carolina utilities decided to stop construction of the VC Summers nuclear plant, their move came “without warning,” Westinghouse said in a document filed with the bankruptcy court. The project owners did not give Westinghouse any notice before dismissing its subcontractors and vendors on the job. [PowerSource]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 8, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “The red state with an energy blueprint” • Iowa didn’t become an energy powerhouse by accident. Back in the 1980s, the state enacted the nation’s first law incentivizing utilities that bought more renewable power. Last year, nearly 37% of Iowa’s power came from wind. It has given the state jobs and the country’s most reliable and inexpensive energy. [The Hill]

Wind turbines (Getty Images)
¶ “Censoring climate change won’t stop global warming” • The United States Department of Agriculture has decided to combat the threat of global warming by forbidding the use of the words. The terms “climate change” and “climate change adaptation,” are to be replaced by “weather extremes” and “resilience to weather extremes.” [The Guardian]
World:
¶ Potent, climate warming gases are being emitted into the atmosphere but are not being recorded in official inventories, a BBC investigation has found. In just one example, Swiss air monitors detected large quantities of one gas coming from a location in Italy. However, the Italian submission to the UN records just a tiny amount. [BBC News]

Air monitoring station at Jungfraujoch
¶ Cumulative installed PV power has reached 237 MW in Brazil as of the end of June, according to provisional statistics provided by the country’s Minister of Mines and Energy. It said in the report it expects another 530.4 MW of PV plants awarded in the auctions to come online by the end of 2017 and 1.34 GW to be connected to the grid in 2018. [pv magazine]
¶ A German public works department, Stadtwerke Heidelberg, has broken ground on a new type of energy storage center. Solar and wind energy generated on site will be used to heat up the water inside the tower. The heat will then be sold. The heat storage center will also provide a sustainable energy knowledge hub to the community. [The Urban Developer]

Rendering of heat storage tank in Heidelberg
¶ The UK government has given the green light for an offshore wind farm that could meet the power needs of 890,000 homes. The 1.2-GW East Anglia Three offshore wind farm, 40 miles off the coast of Suffolk, will have up to 172 huge, wind turbines, of up to 12-MW each, bigger than any turbines currently available. [Aberdeen Evening Express]
¶ Lightsource, a UK-based solar energy developer, has applied to the Meath County Council in Ireland for planning permission to build a 70-MW solar farm. If granted, the plant would be by far the largest single solar array in Ireland, and also the largest in the British Isles. The expected investment cost is likely to reach €60 million. [pv magazine]

Castle in County Meath (Image: Andrew Parnell | Wikipedia)
US:
¶ The average temperature in the US has risen rapidly and drastically since 1980, and Americans are feeling the effects, according to a sweeping federal climate change report awaiting approval by the Trump administration. Scientists say they fear that the administration could change or suppress the report. A draft of it is available. [New York Times]
¶ Farmers Electric Cooperative serves 605 households and businesses in Kalona, Iowa, and its surrounding villages. It generates 3,719 watts of solar power per subscriber, 76% more than any other utility. The cooperative offers a look at how community-minded thinking can shape energy policy and reinvent the local economy. [CleanTechnica]

Farmers Electric solar array (Farmers Electric photo)
¶ After taking in orders for the US wind industry worth 632 MW during the second quarter of this year, Vestas has in the past two weeks announced 348 MW worth of new wind turbine orders for the United States alone. This brings the total number of wind turbine orders from the United States for the year up to 1,776 MW. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Alger Delta members in the Michigan’s Upper Peninsula will soon receive even more of their electricity from cost-effective renewable energy. Alger Delta’s not-for-profit wholesale power supplier, WPPI Energy, entered an agreement with Invenergy, to purchase the output from a 132-MW wind energy center that Invenergy owns. [UPMatters.com]

Wind turbines at sunset
¶ Only a day after the EPA was sued by 16 Democratic state attorneys general, Scott Pruitt and the EPA announced that they would forego delaying the designation of areas currently impacted by high levels of ground-level ozone, also known as smog. A press release heralded the EPA’s willingness to work with states. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Software giant Salesforce, in San Francisco’s largest employer, is switching two of its high-rise office buildings in the City by the Bay to 100% renewable wind and solar energy through a local community choice aggregation program. The company is the largest business yet to opt into the SuperGreen level of the not-for-profit CleanPowerSF initiative. [GreenBiz]

San Francisco (Shutterstock image)
¶ Low-income customers in New York City and nearby areas will have access to solar starting in 2018. A plan for Consolidated Edison to put solar panels on its buildings and properties in the city has been approved. The initial installations, totaling 3 MW, will be installed on properties including in the boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens. [pv magazine USA]
¶ An article in the Wall Street Journal says South Carolina Governor Henry McMaster is looking at ways to revive the abandoned project to build two new nuclear reactors at the V.C. Summer Nuclear Station. One is the idea to sell the state-owned utility, Santee Cooper, or sell the Santee Cooper’s 45% ownership in the construction of the reactors. [WLTX.com]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 7, 2017
Science and Technology:
¶ Climate change may have contributed to 59,000 suicides committed by Indian farmers over the last 30 years, a research paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences said. It suggests India will see more such tragedies as climate change brings hotter temperatures that damage crops and exacerbate drought. [Gears Of Biz]

Farming in India
¶ Over the coming decades, a number of new diseases spread into Europe as the continued warming of the climate allows them to expand, a study from the University of Liverpool’s Institute of Infection and Global Health said. Among them may be Lyme disease, malaria, sleeping sickness, cholera, liver fluke infection, and anthrax. [CleanTechnica]
¶ At China’s Yunnan Agricultural University, researchers have developed a perennial rice by crossing Oryza sativa, the short-lived Asian rice, with a wild African perennial O. longistaminata. The cross, a possible help for climate change, “apparently lasts at least five years and gives 10 seasons of grain twice a year with yields comparable to seasonal rice.” [NewsX]

Perennial rice
¶ There is now only a 5% “chance” that anthropogenic climate warming will be limited to under 2° Celsius, the goal set at the 2015 Paris Climate Change conference, a study published in the journal Nature Climate Change said. It said there is a 90% likelihood that temperatures will rise between 2° Celsius and 4.9° Celsius by 2100. [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ The head of Egypt’s New & Renewable Energy Authority announced that Egypt will begin to make solar panels soon, and the project will pave the way to other initiatives. According to the state-run newspaper, the solar panels will be set up on buildings that are being already established in Egypt’s New Administrative capital. [Egypt Independent]

New solar array
¶ Some of the world’s largest petroleum companies are investing in renewable energy. That is partly due to public concerns over climate change and uncertainty about the future. Statoil’s Senior Vice President of Sustainability told an international oil congress in Istanbul that his company would spend 20% to 30% of its resources on alternates. [Gears Of Biz]
¶ Plans for a major solar energy farm on a 27-hectare site in Ireland have been approved by Wicklow County Council. Ireland must meet a binding target of generating 16% of energy from renewable sources by 2020, or face a penalty of up to €120 million that will be imposed by the EU for every 1% the State falls below target. [Irish Times]

Solar panels in Ireland
¶ Taiwan’s first offshore wind farm has begun generating power with 6.5 MW coming from its first two turbines. The capacity is expected to grow to 120 MW by 2019, lead developer Swancor Renewable Energy Co Ltd (上緯新能源) said. The Ministry of Economic Affairs’ Bureau of Energy has a goal to install 1,000 wind turbines by 2030. [Taipei Times]
¶ Last week’s tender for the Wind Energy Renewable Energy Resource Area project in Turkey resulted in a world record feed-in-tariff, offered by Siemens-Türkerler-Kalyon consortium. The feed-in-tariff went down from 10.3¢/kWh to below 3.5¢/kWh, setting a new world record. This price is calculated to be 50% below the current incentive price. [Daily Sabah]

Wind power
¶ Latvia’s state-owned power utility Latvenergo has launched a program to support development of residential PV installations of up to 10 kW under net metering. Latvenergo also offers solar panels on the basis of interest-free hire-purchase with a term up to five years. The PV systems are to be installed by a partner company. [pv magazine]
Latvia (Photo: Flickr | Kārlis Dambrāns)
¶ TuNur Limited, a private company incorporated in the United Kingdom is seeking to set up a 4.5 GW concentrating solar power system in Tunisia. The power would be sent through three submarine cables to Europe. The first link, sending up to 500 MW of electricity through Malta, could be finished as soon as 2020. [Malta Independent Online]

Cable routes from Tunisia to Europe
¶ Engie Australia has begun the pre-construction work of the 119-MW Willogoleche wind farm near Hallett in South Australia. The $A250 million ($198 million) project, to be built on Willogoleche Hill about 160 km north of Adelaide, will include 32 turbines that each produce between 3.4 MW and 3.8 MW of power. [FutureFive NZ]
US:
¶ As more Hawaii residents use PV systems to power their homes and new large renewable energy sources come online, Hawaiian Electric Co. and its subsidiaries continued to see the islands’ old grid systems unable to effectively handle renewable energy sources. Now the utility is mounting a major push to modernize its electrical systems. [Maui News]

Hawaiian PV system (Photo: Matthew Thayer | The Maui News)
¶ There are a few more than 50,000 coal miners working in the US. That is slightly more than last year, with President Trump taking credit for the change, but coal mining is not secure work. By contrast, the wind industry added 15,000 workers last year and the solar industry added 50,000. The question is whether miners could take the new jobs. [Gears Of Biz]
¶ Billions of dollars have been lost on US nuclear power. Most of the 18 nuclear projects pending before the NRC a decade ago have been aborted or suspended indefinitely. The NRC licensed seven, but none of them is operational. Only one in Georgia is still being built, at a cost of $100 million a month, and in the end it could cost $25 billion. [The Augusta Chronicle]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 6, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Reality check: We can’t turn back time on Alberta’s climate policy” • The environment is not the partisan issue it’s often made out to be. Outside of a vocal minority who object to any action on climate change, leaders across the political spectrum recognize this is the critical economic and environmental challenge of our times. [Calgary Herald]

Oilsands extraction facility (Mark Ralston | AFP | Getty Images)
¶ “How SC lawmakers passed a 2007 law that failed SC power customers” • A 2007 law put SC power customers on the hook for financing nuclear reactors. The law, which was promoted as protecting South Carolina ratepayers, “basically allowed the utilities a blank check at the ratepayers’ expense,” according to one state lawmaker. [The State]
¶ “Dirty energy’s quiet war on solar panels” • With rooftop solar power, you can help address climate change, grow the renewable energy economy, create jobs, and save money. Win-win-win, right? Well, not if you’re in the fossil fuel industry – or one of the politicians who owe them favors. And that’s where things get messy. [The Hill]
World:
¶ Solar has become the world’s favorite type of new electricity generation. Global data show that more solar PV capacity is being installed than any other generation technology. Across the world, 73 GW of net new solar PV capacity was installed in 2016. Wind energy came in second place with 55 GW. Coal was third with 52 GW. [finder.com.au]
¶ Global movement toward clean energy sources is a boon for Canada’s mining industry, according to Mining for Clean Energy: Tracking the Energy Revolution 2017, a report from Simon Fraser University’s Centre for Dialogue. Solar panels, wind turbines, electric vehicles, smart grids, and LEDs all require Canadian metals and minerals. [The Reminder]

Zoro Lithium Project
¶ An academic who is a critic of the cost of renewable power is to lead an independent review of the cost of energy amid concerns about rising bills in the UK. He was chosen by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy to carry out the inquiry which he said will “sort out the facts from the myths about the cost of energy.” [The Times]
¶ The tiny Orkney island of Eday is working on an initiative that could revolutionize the world of sea transport. With shipping under pressure for producing high levels of emissions, islanders are developing a project that could pave the way for pollution-free roll-on/roll-off vehicle ferries powered by locally produced hydrogen. [The Times]

Tidal power project (LCHAM | SIPA | Rex | Shutterstock)
US:
¶ President Donald Trump has made no secret of his desire to roll back environmental regulations and change the playing field for the fossil-fuel industry. His administration’s actions over its first six months have been following that lead, including what many scientists say is a full-fledged battle against research and facts. [CNN]
¶ Manufacturers choosing where to expand may see electricity costs as vitally important, but experts say last week’s decision to scrap construction of two new reactors at the VC Summer Nuclear Station due to high costs is not expected to have a long-term impact on statewide economic development efforts in South Carolina. [Charleston Post Courier]

Boeing 787 assembly plant (Charleston Post Courier file photo)
¶ The “flash drought” that came out of nowhere this summer in the US High Plains, afflicting Montana and the Dakotas worst, has already destroyed more than half of this year’s wheat crop, going by some recent field surveys. Flash droughts are expected to become more common over the coming decades as the climate continues warming. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Citing Appalachia’s need to compensate for losing thousands of megawatts worth of coal-fired power during the last few years, developer Pike Island Energy hopes to build a $200 million hydroelectric plant at the Pike Island Locks and Dam in the Ohio River. The 48-MW plant would generate enough electricity for about 22,000 homes. [The Review]
¶ News from Arizona is a mixed bag. As the shutdown of the 2,250-MW Navajo Generating Station is still moving forward, the 27.3-MW Kayenta Solar Project has gone online, and some of its power going to Navajo homes that have never had electricity before. But Arizona utilities are doing what they can to oppose rooftop solar power. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A growing opposition in the executive branch comes as the White House’s legislative agenda has stalled in Congress and Trump turns to his Cabinet agencies to change course in several policy areas. It is emanating from career staffers whose resistance to Trump has at times been rooted in deep opposition to the president’s agenda. [The Hill]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 2 Comments »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 5, 2017
Science and Technology:
¶ A finger of ice spilling out of the Chugach Mountains marks Alaska’s rapidly warming climate – almost literally. The path approaching Exit Glacier, the most accessible of the 500 square miles of ancient ice covering Kenai Fjords National Park, is a timeline of retreat. The glacier lost 252 feet last summer. Visitors notice the change. [Alaska Dispatch News]

Glacial terminus of 1917 (Marc Lester | Alaska Dispatch News)
¶ Extreme weather could kill up to 152,000 people yearly in Europe by 2100 if nothing is done to curb the effects of climate change, scientists say. The number is 50 times more deaths than reported now, a study in The Lancet Planetary Health said. The study also said heat waves would cause 99% of all weather-related deaths. [BBC News]
¶ The North Atlantic Ocean is home to a “warming hole” that has enthralled scientists, but a new study on it in the journal Nature Climate Change is troubling. The study is part of a growing chorus of research that suggests the cold patch shows a major ocean current system may be slowing down, and melting Arctic sea ice could be the culprit. [The Weather Channel]

Observed temperature trends, 1900 to 2012. (NOAA image)
World:
¶ The Trump administration has taken another step towards exiting from the Paris climate agreement. It has notified the United Nations of its decision to leave the deal. The actual withdrawal process will prove lengthier and cannot be initiated until 2019 at the earliest. The administration still pledges to stay engaged on the issue of climate change. [CNN]
¶ In early July, the world’s first ever hybrid hydro-solar plant began full-scale operation in Portugal. Now floating on the surface of the dammed river at the Alto Rabagão Dam are 840 solar panels that work together with the dam’s hydroelectric generators. Energias de Portugal’s project the first of its kind. [Renewable Energy Magazine]

Alto Rabagão Dam
¶ Plans to promote electric vehicles in the UK do not go far enough to tackle air pollution, a leading government adviser said. Writing in the Guardian, Prof Frank Kelly said fewer cars, not just cleaner ones, were the key to cleaner air. Electric cars produce particulates from their tires and brakes, and these are linked to serious health problems. [BBC News]
¶ ABB has won a $30 million contract from TenneT to supply grid stabilization technology to help increase the uptake of renewable energy in Germany. The work will involve delivery and installation of a hybrid static compensator at the Borken substation in Hessen in central Germany to provide dynamic voltage support. [reNews]

Statcom system (ABB image)
¶ More than $2 million in funding from the state of Victoria and the Moreland Council has been committed to kickstart the construction of a hydrogen refueling station. The council has partnered with hydrogen utility company H2U for the project and international vehicle manufacturer CNH Industrial is set to develop the hydrogen fuel cell trucks. [Herald Sun]
US:
¶ Allete Clean Energy is planning to refurbish 385 turbines at three wind farms in Minnesota and Iowa. The work will include replacing select blades, gearboxes and generators at the 104-MW Lake Benton project in Minnesota and the Storm Lake 1 and 2 wind farms in Iowa, which have capacities of 109 MW and 79.5 MW, respectively. [reNews]

Iowa farm (Image: Pixabay)
¶ President Donald Trump came to the heart of coal country and told a large and cheering crowd what they wanted to hear: that Obama’s war on coal has ended. But in fact, Kentucky coal jobs and production continued down in the second quarter of the year. In eastern Kentucky, employment in the second quarter dropped 5.3 %. [The Independent]
¶ Toyota and Mazda will be partnering to develop a new $1.6 billion assembly plant in the US, as well as to develop electric vehicle technologies. The new assembly plant will reportedly be capable of producing around 300,000 vehicles a year and will employ around 4,000 people. Operations are expected to begin by 2021. [CleanTechnica]

Toyota Prius Prime (Image: Zach Shahan)
¶ In Utah, like many places in the US, the growth of rooftop solar panel systems is being thrown some shade. Rooftop solar has been booming, with the number of installations increasing by an estimated 900% in six years. But the state’s largest power utility is pushing to raise the rates on rooftop solar customers who tie into the electrical grid. [St. George Daily Spectrum]
¶ South Carolina Attorney General Alan Wilson is opening an investigation and state Senate leaders are calling for a special legislative session following the abandonment of construction of two nuclear reactors at the VC Summer plant in Fairfield County. The $9 billion failure of the plant prompted the multi-pronged response. [Charleston Post Courier]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 4, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Nuclear power as we know it is finished” • South Carolina Electric and Gas Co and partner Santee Cooper abandoned work on two new nuclear reactors this week because the only way to pay for them was to overcharge customers or bankrupt both companies. Nuclear power has a hard time competing in a competitive market. [Houston Chronicle]

Control room at Three Mile Island (AP Photo | Matt Rourke, File)
¶ “How To Get Past Climate Despair To Take Climate Action: Advice From Experienced Activists” • When the news gets bad, it is only natural to feel afraid, even when you know gloomy headlines are just one side of the story and the solutions we need are in our hands today. So the question is: how do you get past the fear and start fighting? [CleanTechnica]
¶ “On Healing Sick Ecosystems” • Many creatures are in danger because we are unintentionally destroying their homes. Whether by pollution, climate change, or clearing habitats for our own reasons, we have made much of the world less habitable. There are compelling moral and practical cases for preserving healthy ecosystems. [Union of Concerned Scientists]

Ecosystem in need (Photo: lgnc.org | conservation)
Science and Technology:
¶ Part of the bad news on climate change is that New England may become a hotspot for invasive plants and animals. That was the pressing subject on the minds of around 100 experts from academia, conservation organizations and government agencies who gathered at a symposium on invasive species and climate change in Amherst. [Amherst Bulletin]
World:
¶ IKEA has teamed up with LG Chem and Solarcentury to offer residential storage battery solutions to its customers in the UK. Solar-plus-storage solutions from IKEA will start at around $9,000 with LG Chem supplying batteries between 3.3 kWh and 6.5 kWh. Battery-only packages begin at under $6,000 after a 15% IKEA family discount. [CleanTechnica]

IKEA store in Sweden
¶ Since 2014, the RE100 initiative has been working behind the scenes with businesses and organizations of all sizes and sectors to negotiate transitions to 100% renewable electricity. The reason is simple: shift to 100% renewable electricity and you massively reduce the amount of carbon pollution you produce as a company. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Nexans Norway has started installing the subsea power cable for the 1.4-GW NordLink interconnector between Germany and Norway. Starting at Vollesfjord in Vest-Agder, cable ship Nexans Skagerrak is installing the wires, which weigh 70 kg per meter, while offshore vessel Polar King will carry out subsea burying operations. [reNews]

Nexans Skagerrak (Nexans photo)
¶ Equis Energy has secured approval to begin constructing one of the largest solar farms in the world, a 1-GW installation in the Australian state of Queensland. The Western Downs Regional Council has approved the plans submitted by renewable energy developer Equis Energy to build the project. It will cost A$1.5 billion ($1.2 billion) to A$2 billion. [pv magazine]
¶ Two of the world’s largest energy companies, French giant Engie and American conglomerate GE, have announced plans to build a 119-MW wind farm in South Australia, 160 km north of Adelaide. The 32 wind turbines at the Willogoleche Wind Farm add yet another project to a state already shooting above 50% renewable energy. [RenewEconomy]

Wind farm in the Netherlands (Source: GE Renewables)
US:
¶ A study on the economic effects of climate and clean energy policies in California’s Inland Empire estimates a net benefit of $9.1 billion in direct economic activity and 41,000 net direct jobs from 2010 to 2016. With spillover effects of these benefits, the net value jumps to $14.2 billion and the jobs to over 73,000. [North American Windpower]
¶ Dominion Energy Virginia signed an agreement with DONG Energy to build two 6-MW turbines about 27 miles off the coast of Virginia Beach in a federally leased site. The companies are ironing out engineering, procurement and construction details. The Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind project is expected to be installed by the end of 2020. [Marine Log]

Offshore wind power
¶ Green energy companies have submitted dozens of bids to bring more hydropower, wind and solar to Massachusetts to help keep the lights turned on and cut carbon emissions. In total, at least 46 bids were submitted to the state Department of Energy Resources by last week’s deadline. Winning bids are set to be announced next January. [Eagle-Tribune]
¶ US power supplier WPPI Energy made a deal with Invenergy to buy electricity from the 132-MW Bishop Hill 3 wind energy center in Illinois. The agreement will supply electricity to WPPI Energy’s 51 member utilities and customers in Wisconsin, Michigan and Iowa. The project is scheduled to start commercial operations by mid-2018. [reNews]

Wind turbine (Image: Invenergy)
¶ Alliant Energy is seeking approval from the Iowa Utilities Board to add up to 500 MW of wind energy in Iowa. A decision is expected in early 2018. The company received approval in 2016 for a similar expansion. The combined projects would represent a $1.8 billion investment and add up to 1,000 MW of new wind generation. [PR Newswire]
¶ The Trump Administration, despite public pronouncements vowing support for US nuclear energy, gave little or no response after executives with both Santee Cooper and South Carolina Electric & Gas made pleas to save the construction of two units at the now abandoned VC Summer Nuclear Station, according to recent testimony. [Electric Light & Power]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 3, 2017
Science and Technology:
¶ A study led by Harvard University reveals that the damage to crops from climate change will be worse than anyone previously expected. Based on data gathered from experiments conducted on staple crops that were exposed to projected atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, the team found reductions in protein levels. [IFLScience]

Indian harvest (Photo: Zvonimir Atletic | Shutterstock)
World:
¶ The state government of Queensland announced that it is going to install a network of 18 charging stations along a highway stretching more than two thousand miles. It runs along the east coast of Queensland from Cairns to Coolangatta and then turns west to Toowoomba. The exact type of charging system has not been announced. [ExtremeTech]
¶ The Press and Communications Manager at WindEurope said offshore wind energy is “rapidly moving from being a niche technology to a mainstream supplier of low-carbon electricity.” He confirms that there is currently 12.6 GW of offshore wind operating in Europe. The sector started with eleven 450-kW turbines in 1991. [Maritime Journal]

Offshore wind turbines
¶ NTPC, India’s largest power utility, is increasing its bets on solar power as tariffs keep falling on the back of decline in prices of cells and modules in the global market. The shift in business strategy of India’s largest coal-fired generator cannot be ignored. NTPC’s chairman said that his company would focus especially on adding solar capacity. [EnergyInfraPost]
¶ Millions of people living in South Asia face a deadly threat from heat and humidity driven by global warming according to a new study published in the journal Science Advances. Most of India, Pakistan and Bangladesh will experience temperatures close to the limits of survivability by 2100, without emissions reductions. [BBC News]

Indian farmer (Photo: Noah Seelam)
¶ In a dramatic U-turn, Sri Lanka’s energy regulator approved a new long-term electricity supply plan that rejects construction of any new coal plants to 2037. Coal power’s fall from grace in Sri Lanka has in large part been driven by public opposition to pollution from the country’s only coal plant, the Norochcholai Power Station. [RenewEconomy]
US:
¶ The US renewable industry is set for long-term growth as generating costs are falling and the industry is becoming more resilient, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance’s Head of America. He noted that problems always develop as young industries mature, but renewable energy’s falling costs add to its resilience. [Energy Matters]

Solar array (Image: Pixabay)
¶ Oregon-based energy storage company Powin Energy Corp will install software and infrastructure to seven Hawaiian sites, including the Boy Scouts of America’s Honolulu headquarters and the Aqua Kauai Beach Resort, to maximize their bottom lines through storing solar energy not used during daylight hours. [Pacific Business News (Honolulu)]
¶ The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority announced plans to convert its entire 2,200 bus fleet to zero-emission buses by 2030. It is awarding contracts for 95 electric buses and charging infrastructure for two of its bus service routes, as Southern California Edison expands its electric vehicle charging system. [Utility Dive]

Proterra bus (Image: Proterra)
¶ New York energy giant Con Edison is proposing a partnership with a group of energy developers called Maine Power Express LLC to deliver wind power from northern Maine to Boston markets. MPX would build a 630-MW wind facility and deliver its power via an underground power line on an existing energy corridor. [Press Herald]
¶ The mayor of White Plains, New York, announced support for a goal of powering White Plains entirely with clean and renewable energy by 2035. He joins a growing coalition of more than 120 Mayors for 100% Clean Energy who have goals of powering their communities with 100% renewable energy, such as wind and solar. [Hudson Valley News Network]
¶ Oregon legislators failed to renew solar panel incentives during this year’s legislative session. The Residential Energy Tax Credit, which gave as much as $6,000 for installing solar panels, will expire at the end of the year. A push to replace RETC with reimbursements through 2019, after which they would decline, also failed. [The Corvallis Advocate]
¶ Vestas is to deliver turbines totalling 148 MW for Southern Power’s Cactus Flats wind farm in Texas. The Danish turbine manufacturer will supply and commission 43 V126-3.45MW machines. Delivery is expected to start in 2017, to be followed by commissioning in 2018. The deal also includes a 20-year service agreement, Vestas said. [reNews]

V126-33MW turbines (Credit: Vestas)
¶ The recent decisions of South Carolina energy companies to abandon construction of two unfinished nuclear reactors over their high costs could affect whether Virginia goes forward with a pricey new reactor of its own. Dominion Energy is considering whether to move forward with North Anna 3, projected to cost about $25 billion. [WSET]
¶ Southern Company, a utility based in Georgia, released a preliminary estimate that indicated overall costs for its Vogtle Electric Generating Plant have risen to at least $25.2 billion. The latest estimate raises new questions about whether the sole remaining nuclear facility under construction in the US will get built. [Fox Business]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | 1 Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 2, 2017
Science and Technology:
¶ An interdisciplinary team of researchers funded by the National Science Foundation concluded that bacteria in a lake 800 meters (2,600 feet) beneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet may digest methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, preventing its release into the atmosphere. The team published its results in the journal Nature Geoscience. [Laboratory Equipment]

Monitoring the WISSARD borehole
¶ The impact of climate change on the emergence and spread of infectious diseases could be greater than previously thought, according to research by the University of Liverpool. The study, published in Scientific Reports, is the first large-scale assessment of how climate affects bacterium, viruses, and other pathogens in Europe. [EurekAlert]
World:
¶ Australia’s power utilities and grid operators, under threat from the world’s fastest take-up of home solar panels, are rushing to come up with ways to stay relevant and protect long-term revenues. They are starting a push to cash into the millions of solar panels on the roofs of homes around the country, rather than lose out on them. [ETEnergyworld.com]

Solar array
¶ The monsoon season in India brings with it very high wind speeds, especially in the southern states. This year it has enabled record wind power generation in Tamil Nadu, which produced more than 5,000 MW of it at one point. The high wind energy generation forced the state utility to shut down 1,020 MW of thermal power capacity. [CleanTechnica]
¶ An analysis of Chinese development on the solar energy front from sector consultant group Wood Mackenzie finds that, when counting all planned and announced projects, solar power capacity will more than double by 2020. For wind power in China, Wood Mackenzie estimates capacity will increase by 40% by 2020. [UPI.com]

Chinese renewable energy (Photo: Stephen Shaver | UPI)
¶ The Indonesian Government plans to launch an auction for six geothermal projects in September this year. The projects will have a combined capacity of 255 MW and will involve a total investment capital of $1.02 billion. The auction aims to expand Indonesia’s renewable energy capacity, according to the Jakarta Post. [en.vietnamplus.vn]
¶ NB Power is proposing a maintenance project to ensure its 660-MW Mactaquac Generating Station can operate to its intended 100-year lifespan. The run-of-river hydro facility supplies about 12% of New Brunswick homes and businesses with power. The Mactaquac Generating Station began producing electricity in 1968. [HydroWorld]

Mactaquac Generating Station
¶ According to predictions by Eirgrid, Ireland’s transmission system operator, Irish solar power will reach grid parity in less than a decade, and this is despite its having no large scale ground mount solar currently installed. The prediction was in Eirgrid’s Future Energy Scenarios document, Tomorrow’s Energy Scenarios 2017. [Solar Power Portal]
¶ Some of Australia’s iconic beer brands will be brewed using 100% renewable energy. This is because Anheuser-Busch InBev has committed to buy all of its electricity from renewable resources by 2025, including on-site solar. Anheuser-Busch InBev is the parent company of Foster’s Group and Carlton United Breweries. [One Step Off The Grid]

Beer, to come from solar power
¶ The Spanish government says it is closing the country’s oldest nuclear power station because of lack of support among stakeholders to keep it open. Production at the 46-year-old Garona was halted in 2012 when its operator, Nuclenor, objected to a new tax. Its board has failed to reach agreement on keeping the plant open. [PennEnergy]
US:
¶ Tesla and wind farm developer Deepwater Wind plan to team up to create the largest project in the world that combines an offshore wind farm with large-scale electricity storage, the companies announced. The Revolution Wind Farm, about 12 miles off the shore of Martha’s Vineyard, would be able to store power in Tesla batteries. [RenewEconomy]

Block Island Wind Farm (Photo: Climate Central)
¶ The environmental impact study for the Keystone XL pipeline assumed that the price of oil would never fall below $100 a barrel during its useful life. Today, oil is selling for half that amount. Finding customers willing to sign up for oil shipments in 2020 may be harder than expected. And without customers, the pipeline will languish. [CleanTechnica]
¶ American Electric Power, which is based in Ohio, is applying for regulatory approval to build transmission lines for Wind Catcher, a massive wind farm under construction in Oklahoma. It will be the second largest in the world. AEP, once a leading coal-fired power plant operator, has a building program for renewable energy. [WKSU News]

Wind farm in Oklahoma (Invenergy image)
¶ The US government awarded $4.6 million in aid to retrain hundreds of Montana coal workers, many of whom will soon be out of jobs because of a partial closure of the coal-fired Colstrip power plant. President Donald Trump has declared that the “war on coal” was over, but coal industry workers’ jobs are still under threat. [Observer-Reporter]
¶ Utility customers in South Carolina may end up spending the next 60 years paying billions for two nuclear reactors that will never get built, based on a proposal that Scana Corp filed with regulators. Scana is seeking state approval to collect $4.9 billion from customers to cover the costs of scrapping two half-finished reactors. [Bloomberg]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
August 1, 2017
Opinion:
¶ “Why Court Victories for New York, Illinois Nuclear Subsidies Are a Big Win for Renewables” • A federal judge ruled that New York’s plan to subsidize nuclear power plants “is constitutional” and “of legitimate state concern.” It is a big win for Exelon, but the ramifications go well beyond the legality of New York’s nuclear program. [Greentech Media]

Indian Point nuclear plant (Greentech Media image)
Science and Technology:
¶ By the end of the century, the global temperature is likely to rise more than 2° C (3.6° F). This rise in temperature is the ominous conclusion reached by two different studies using entirely different methods published in the journal Nature Climate Change. One study put the chance that Earth will warm more than 2° at over 95%. [CNN]
¶ “Ghost forests,” stands of dead trees along coastlines invaded by rising seas, are something scientists call one of the most visible markers of climate change. The process has occurred naturally for thousands of years, but it has accelerated in recent decades as polar ice melts, sea levels rise, and salt water pushes farther inland. [Charleston Post Courier]

Ghost forest (AP photo, Stephen B Morton)
World:
¶ In Australia, the declining cost of renewables means it will soon be cheaper to build new renewables than to refurbish an existing coal plant even if it is fully depreciated, according to Kobad Bhavnagri at Bloomberg New Energy Finance. This means baseload coal power will gradually become a liability. [The Australian Financial Review]
¶ Convert is a solar tracker specialist headquartered in Italy, and is the world’s fourth largest according to IHS Markit. It signed a supply deal with Atlas Renewable Energy to deliver its tracker solutions to two large Brazilian solar projects. The $35 million agreement will see Convert ship trackers for 220 MW of PVs to Brazil. [pv magazine]

Sunrise in Rio de Janeiro
¶ Delhi’s metro rail network has been named as the only completely ‘green’ metro system in the world for adhering to green building standards. This feat was achieved after the DMRC obtained the platinum rating for adherence to green building norms for its 10 residential colonies from the Indian Green Building Council. [Business Standard]
¶ Chinese company Jereh Group has announced it has won a contract for two further sections of a geothermal power plant at Olkaria in Nigeria for state-owned power company KenGen. Under the contract, a consortium led by a subsidiary of Jereh Group will build up the facility’s total installed capacity to 61 MW. [Renewable Energy Magazine]

Steam rising at the Olkaria Geothermal Plant (Photo: Jereh Group)
¶ In a press release, the government of Kazakhstan’s Akmola Region has announced that the Kazakh investment company KBEnterprises is planning construction of a 100 MW solar power plant near Kabanbay, Tselinograd District, in the north of the country. The $165 million project will be built on a 300 hectare site. [pv magazine]
US:
¶ American Electric Power selected Quanta Services to provide engineering, procurement and construction services for the power transmission line for the 2-GW Wind Catcher project in Oklahoma. The link will consist of approximately 350 miles of a single circuit 765-kV power line. Quanta expects construction to start in late 2018. [reNews]

GE wind turbines (GE image)
¶ The EPA must enforce Obama era pollution limits for the oil and gas industry. Nine of the eleven judges of the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit issued this latest ruling after another ruling by the court in July that the EPA unlawfully tried to delay implementing the Obama-era methane pollution rule. [CNN]
¶ New York has been graced with strong sun and whipping winds that electricity companies increasingly harness for renewable energy. It has seen a 6,548% increase in the amount of energy it gets from the sun and a 473% increase in wind power production since 2007, according to a report. And it is not alone in seeing renewable energy grow. [TheInertia.com]

Solar array (Photo: Andreas Gücklhorn on Unsplash)
¶ Deepwater Wind will bid a combined 144 MW offshore wind and 40 MW energy storage project into the Massachusetts clean energy call. The US developer said the Revolution project will be put forward in reply to the segment of the state’s request for proposals that includes the promotion of energy diversity. The project could be scaled up, if needed. [reNews]
¶ LEEDCo and Fred Olsen Renewables’ 20.7-MW Icebreaker offshore wind project in Lake Erie has taken a big step forward. The Ohio Power Siting Board has found that the freshwater wind farm’s application is “in compliance and ready to be processed.” Icebreaker is expected to feature six MHI Vestas 3.45-MW turbines. [reNews]

Work in Lake Erie (LEEDCo image)
¶ The Navajo Tribal Utility Authority has started operating the 27.3-MW Kayenta Solar Project on 200 acres near Kayenta, Arizona. The closing of the Navajo Generating Station is leaving a hole in power generation in the region that ultimately will be filled with renewable energy, according to the solar farm’s project manager. [PennEnergy]
¶ Work has been suspended on two nuclear reactors being built by Westinghouse in South Carolina. Santee Cooper and South Carolina Electric & Gas Company said they had ordered a halt to construction of their jointly-owned project, the VC Summer plant, due to spiraling costs. The decision casts doubt on other nuclear projects. [Financial Times]
geoharvey is free and without ads.
 geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
geoharvey is not tax-deductible.
Posted in nuclear power, renewable power, solar, wind | Leave a Comment »
Tags: nuclear, nuclear power, renewable power, solar power, wind power
















































































































































































































